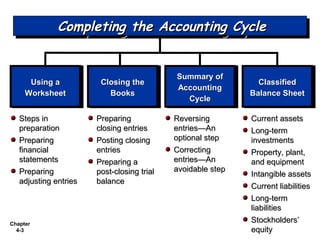
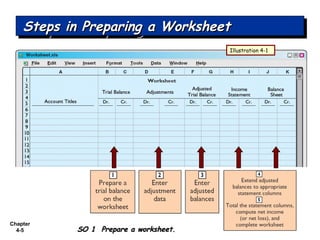
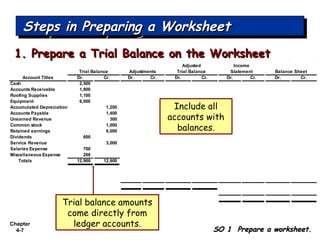
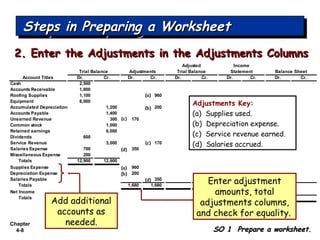
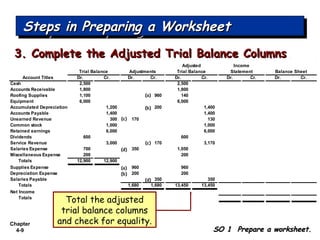
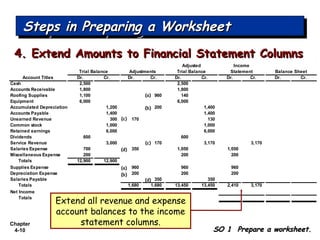
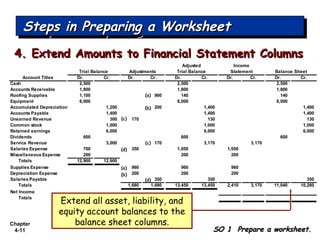
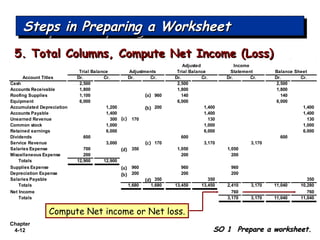
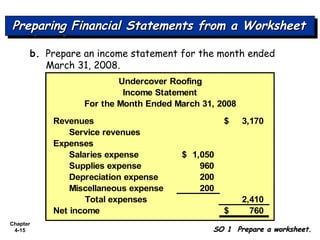
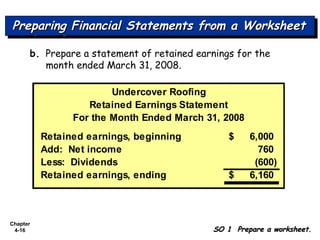
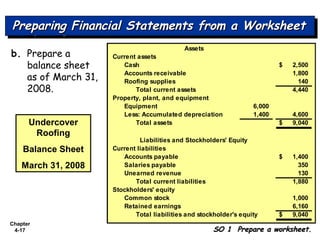
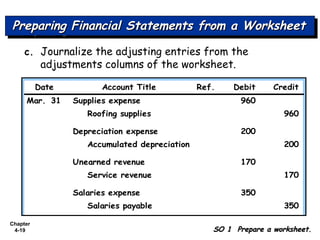
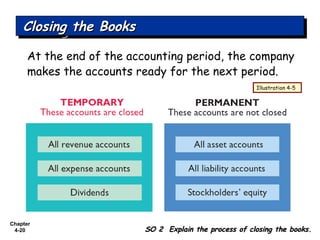
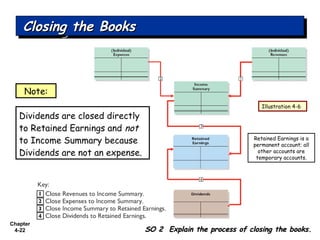
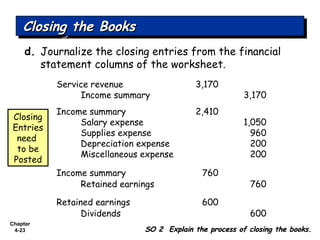
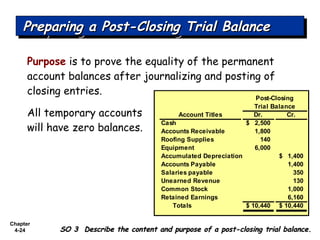
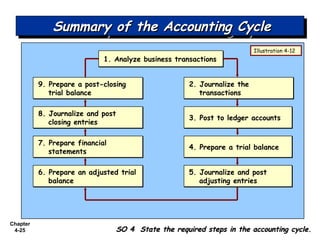
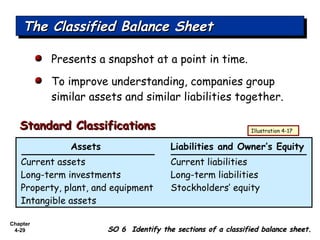
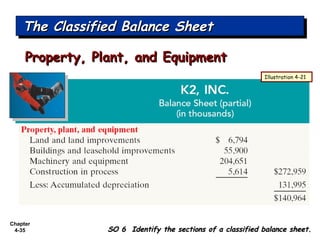
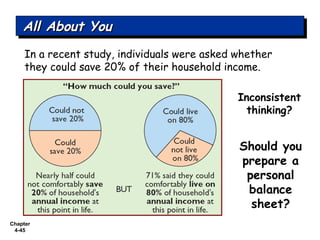
Chapter 4 focuses on completing the accounting cycle, which includes preparing worksheets, adjusting entries, closing the books, and generating financial statements. Key steps involve preparing trial balances, making adjustments, and summarizing outcomes such as the income statement and the balance sheet. The chapter emphasizes the purpose and process of closing entries and preparing a post-closing trial balance to ensure accurate account balances.