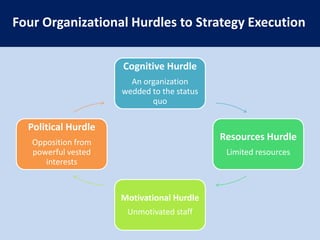
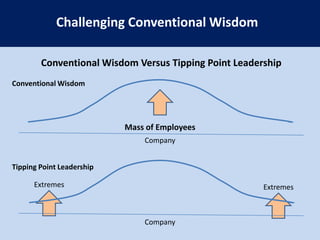
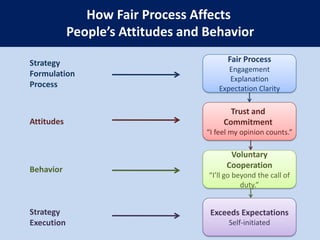
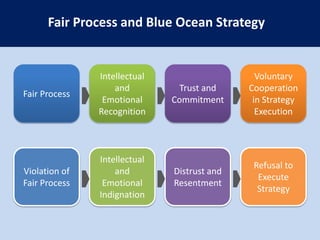
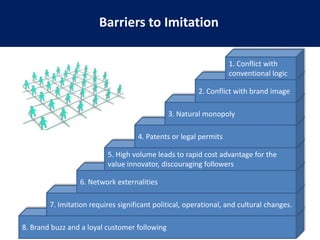
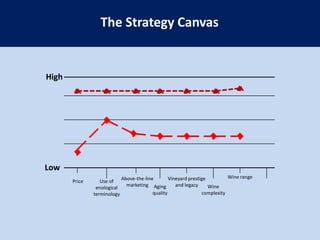
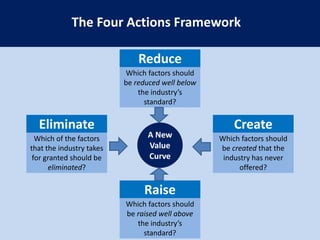
This document summarizes the key concepts from the book "Blue Ocean Strategy" by W. Chan Kim and Renee Mauborgne. The authors propose that companies can create "blue oceans" of uncontested market space by pursuing value innovation that raises buyer value and reduces costs. They outline tools like the strategy canvas and four actions framework to help companies visualize new strategic approaches. The document also discusses how to overcome organizational hurdles to executing blue ocean strategies and the importance of fair process in gaining support for new strategies.








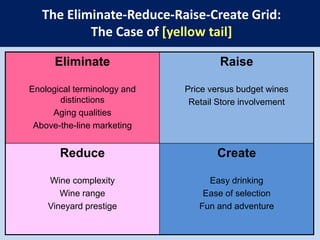
![The Eliminate-Reduce-Raise-Create Grid:The Case of [yellow tail]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blueoceanstrategy-110808212053-phpapp02/85/Blue-ocean-strategy-12-320.jpg)