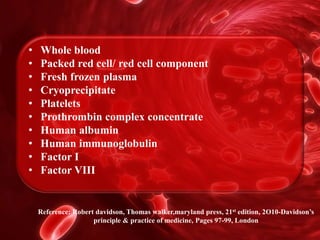
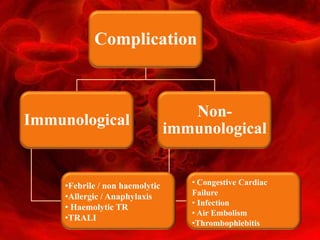
Blood transfusion involves receiving blood or blood products intravenously to replace lost components. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions and can involve whole blood, packed red cells, plasma, platelets, or other factors. Eligible donors are generally healthy individuals between 18-60 years old meeting criteria for weight, hemoglobin levels, pulse, and blood pressure. Donors are screened for diseases and blood is cross-matched for type and tested to help prevent complications like infections, reactions, or organ failure from massive transfusions.