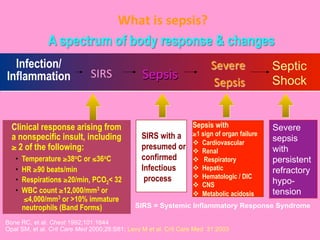
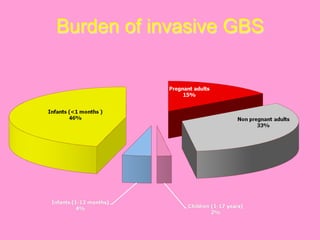
This document discusses obstetric sepsis. It begins by defining sepsis and its spectrum from SIRS to septic shock. Common causes of obstetric sepsis include septic abortion, PROM, chorioamnionitis, and postpartum endometritis. Common organisms include E. coli, Klebsiella, streptococci, and staphylococci. Sepsis causes a systemic inflammatory response and release of inflammatory mediators that can lead to endothelial dysfunction, organ damage, and septic shock. Management involves controlling infection with antibiotics, removing the infection source, and providing supportive care like fluid resuscitation and vasopressors. Specific treatments depend on the type and severity of infection.