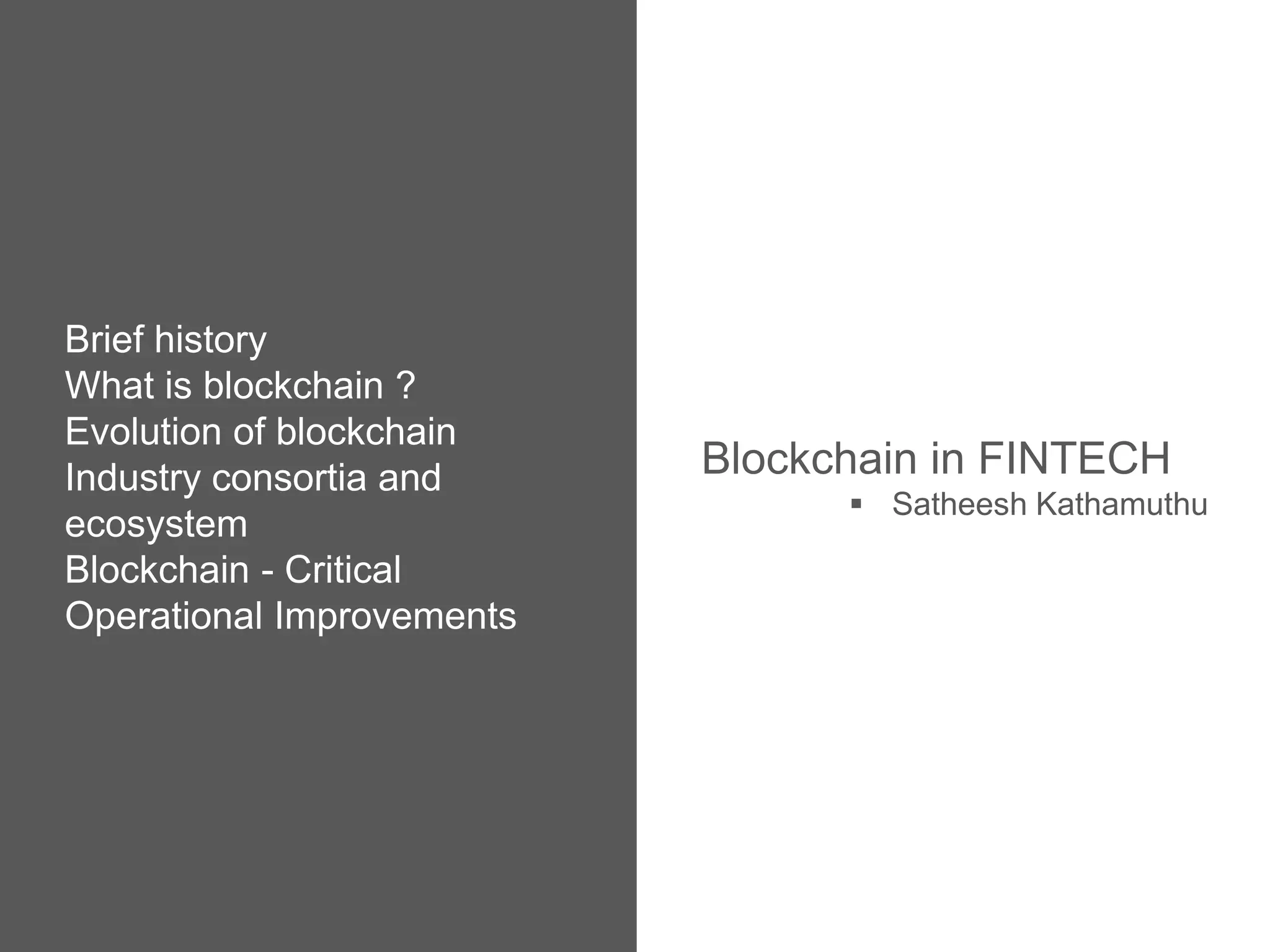
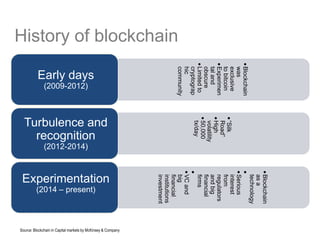
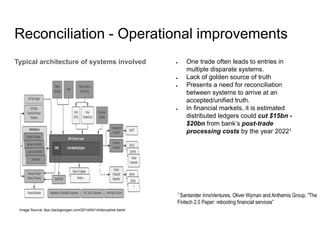
Blockchain has evolved from being used exclusively for bitcoin (Blockchain 1.0) to also enabling contracts (Blockchain 2.0) to now supporting applications beyond finance (Blockchain 3.0). Major industry consortia like Hyperledger, R3CEV, and others are working on blockchain applications. Blockchains can provide critical operational improvements like reducing reconciliation costs between disparate financial systems from $15-20B by 2022. Blockchain is now being applied in areas like cross-border payments, private securities exchanges, and replacing stock settlement systems to improve post-trade processing.