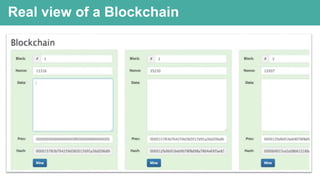
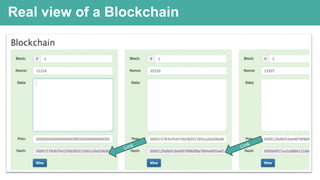
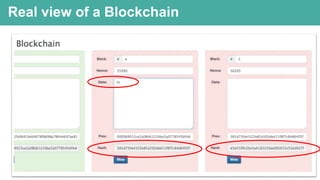
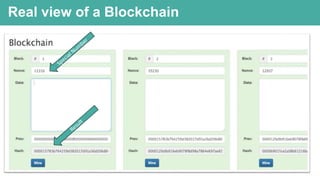
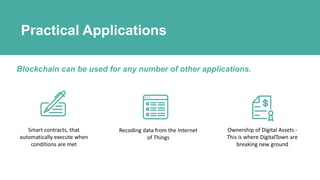
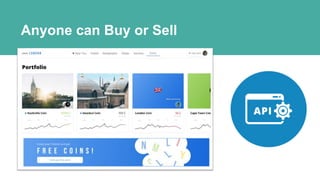
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows for peer-to-peer transactions without a central authority. DigitalTown is using blockchain to allow global citizens to purchase coins representing ownership stakes in smart cities. These coins can be traded on the blockchain in a secure and decentralized manner. The presentation introduces blockchain and explains how DigitalTown's solution works, including how citizens can obtain free initial coins and later trade coins using the blockchain.