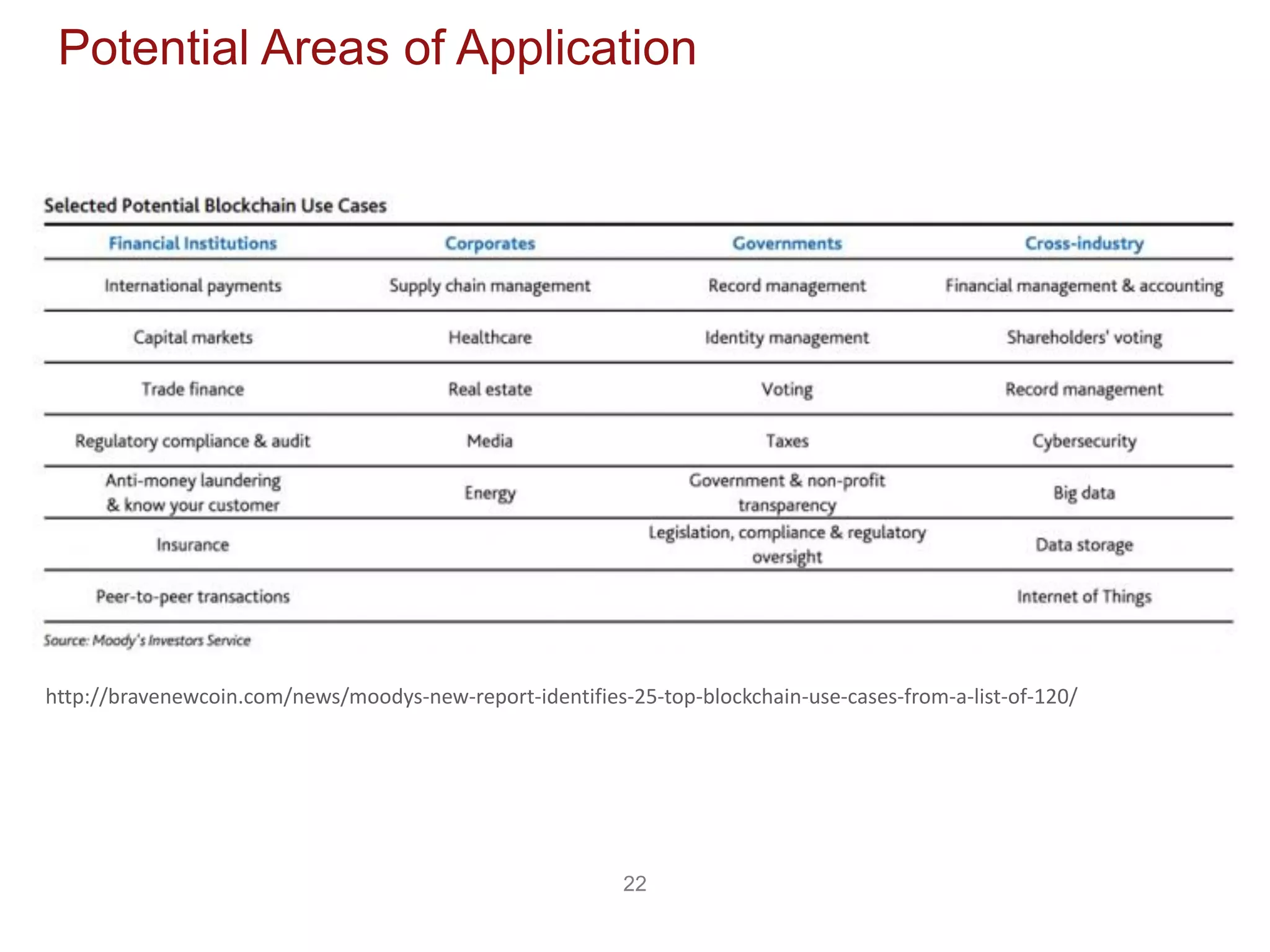
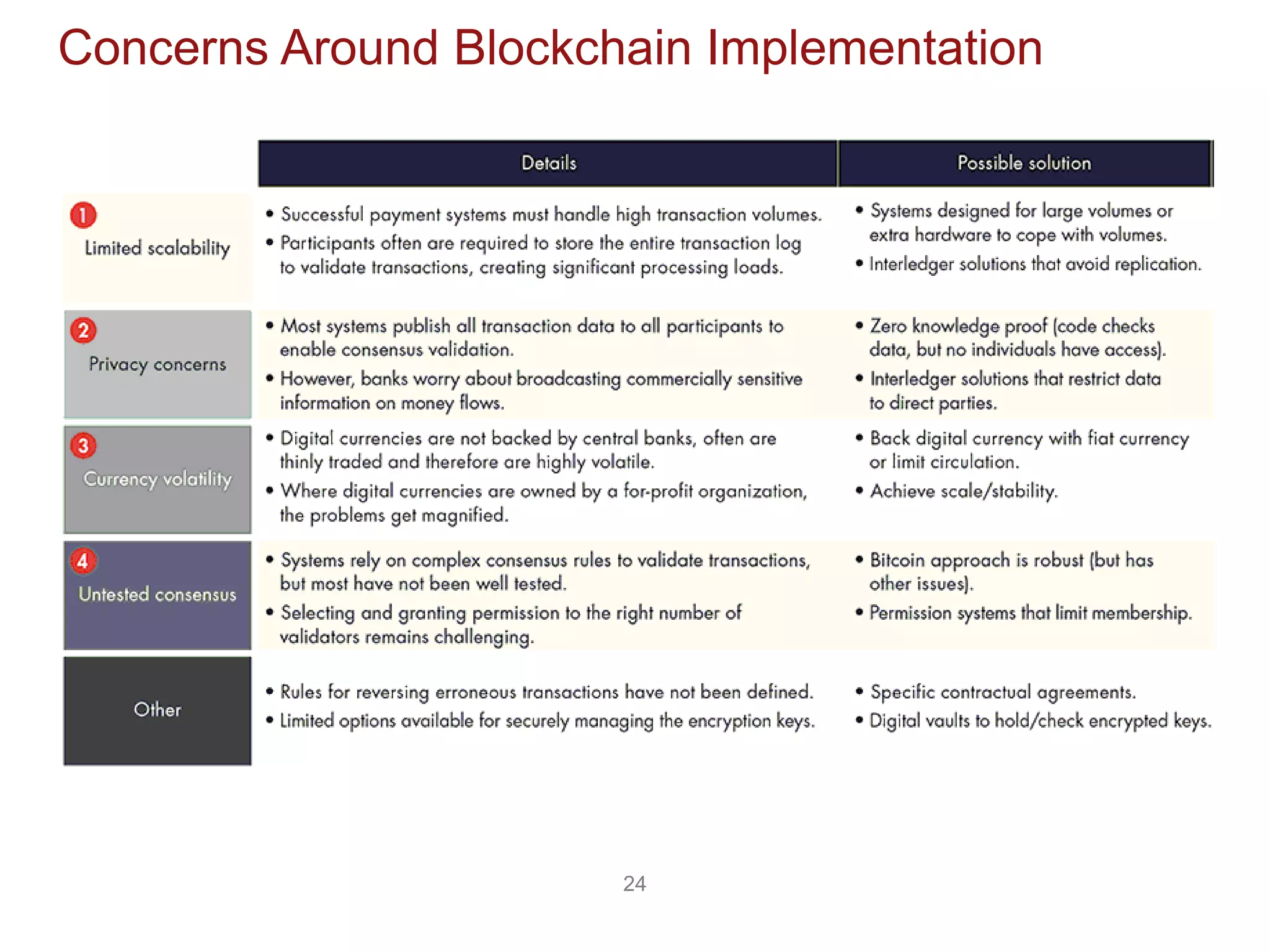
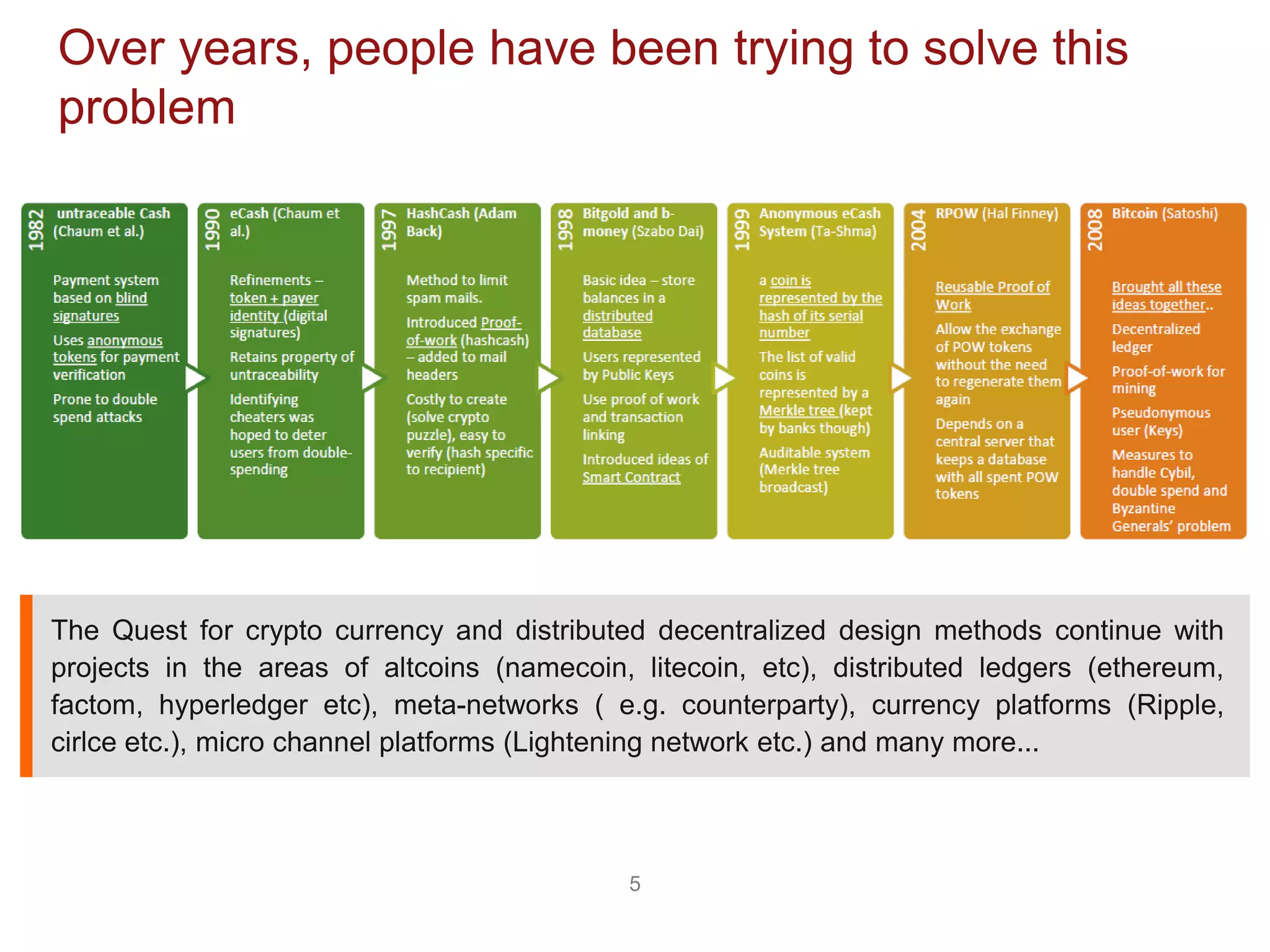
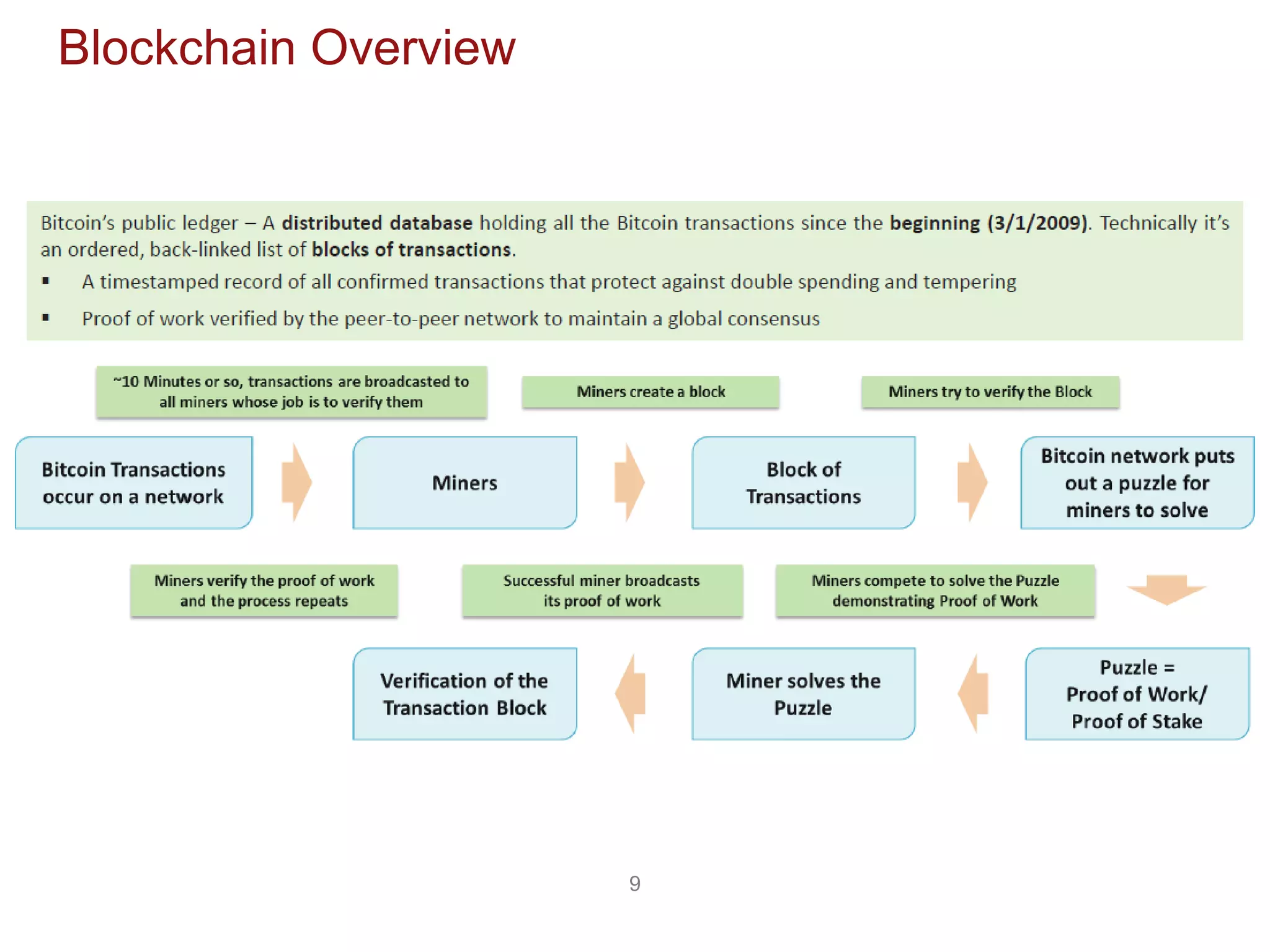
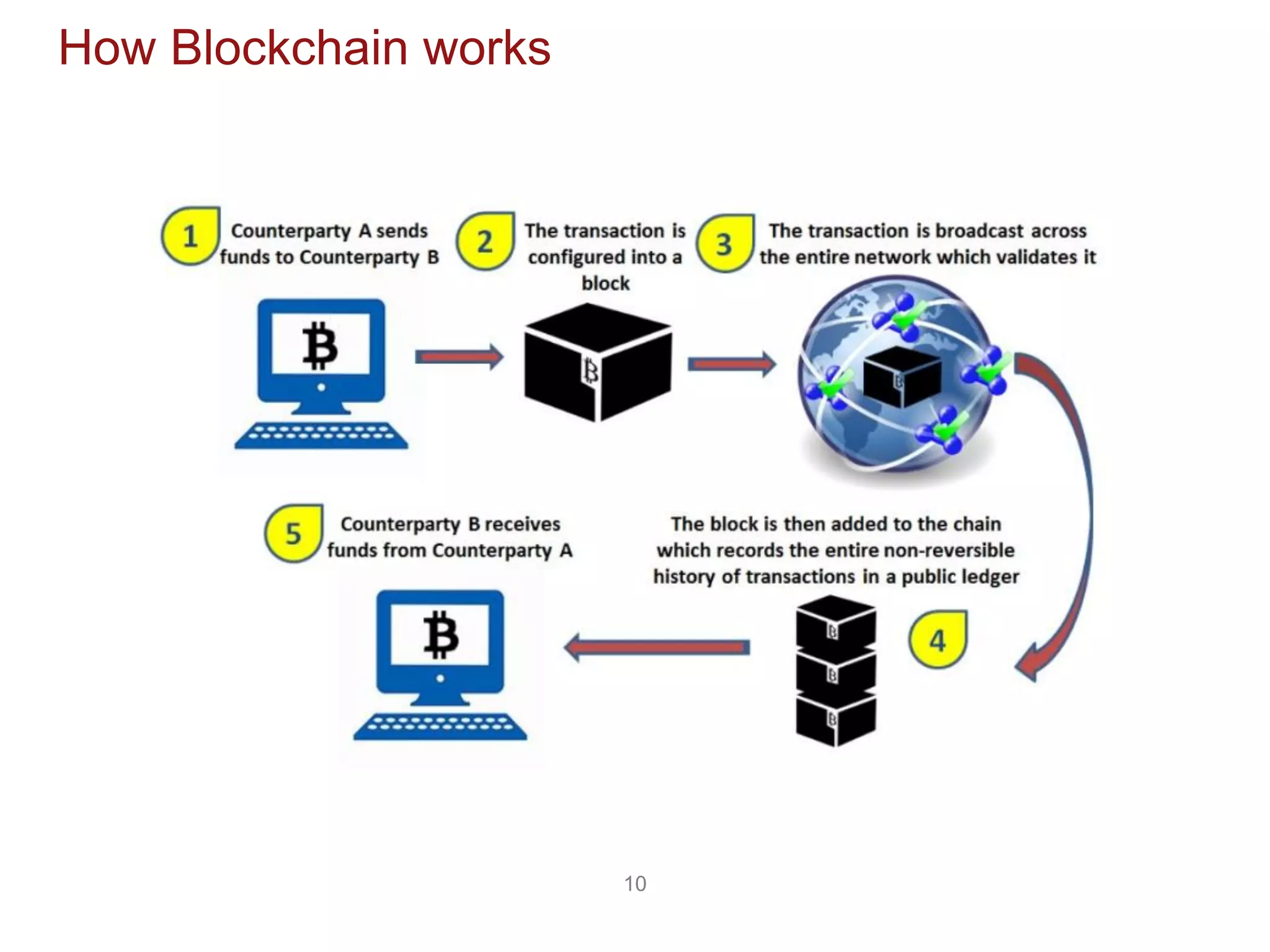
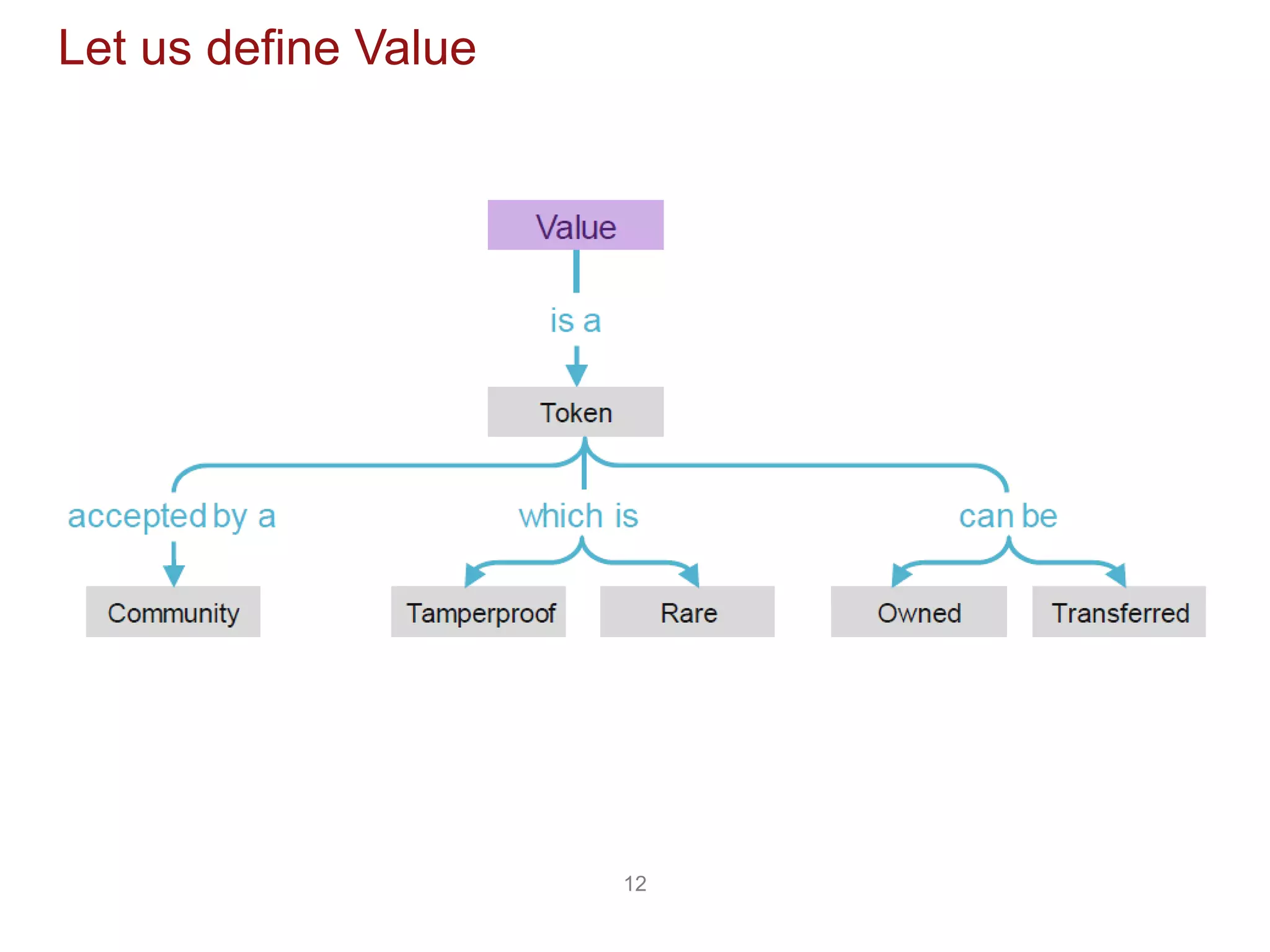
The document discusses the transformative potential of blockchain technology, highlighting its ability to decentralize power, enhance security, and improve financial transactions. It contrasts traditional banking systems and their shortcomings with blockchain's capabilities, emphasizing its ability to facilitate peer-to-peer value transfers and reduce transaction costs. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as smart contracts and various types of blockchain, alongside insights from industry experts regarding the implications and future applications of this technology.









![19
Why are we Talking about Blockchain ?
"If, so many incredibly smart people are working on this and
investing their time and energy, let alone the money that is
flowing into it, 'it's not something that we can all ignore.
However, the community of innovators need to understand
the complexity behind payments"
Ebru Pakcan, Head-Global Payments, citi
“The emerging Technology is fascinating and ING is not in
wait and watch mode but we are in see and do mode”
Mark Buitenhek
Global Head of Payments and Cash Management (PCM)
for ING
" I believe - and this is my personal view - that blockchain
technology will not only change the way we do payments but
it will change the whole trading and settlement topic....When
somebody with a strong brand and security level establishes
it as a reliable service, then the whole industry will follow.
That is my personal prediction."
Oliver Bussman, CIO UBS
“As we build more and more complex infrastructure the
whole maintenance and [impact for] changing regulations is
becoming extremely difficult for most of the banks. What is
being demonstrated here is the quite eye opening and
definitely something to look out for."
Gautam Jain, MD & Global Head-Client Access
• The Bank of England recognized the technology as 'significant innovation' that could have "far-reaching implications".
• New York State has released Bitcoin World's first license - BitLicense!
• Financial Conduct Authority (UK) is investigating ways in which the blockchain can be used in the formal financial
services industry
Source: WSJ, Banktech, American Banker, CoinDesk, BusinessInsider, Financial News, Twitter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchainparadigmshiftv11-170907101248/75/Block-chain-A-Paradigm-Shift-19-2048.jpg)