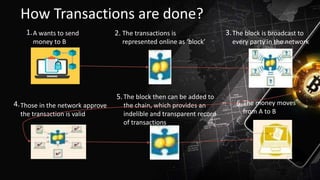
Blockchain technology allows for decentralized transactions across a peer-to-peer network without a central authority. It uses a distributed ledger to record all transactions in blocks that are linked through cryptography. This provides transparency and immutability. Potential applications of blockchain include financial transactions, supply chain management, digital voting, and smart contracts. Some key advantages are transparency, reduced costs, faster settlements, and decentralization.