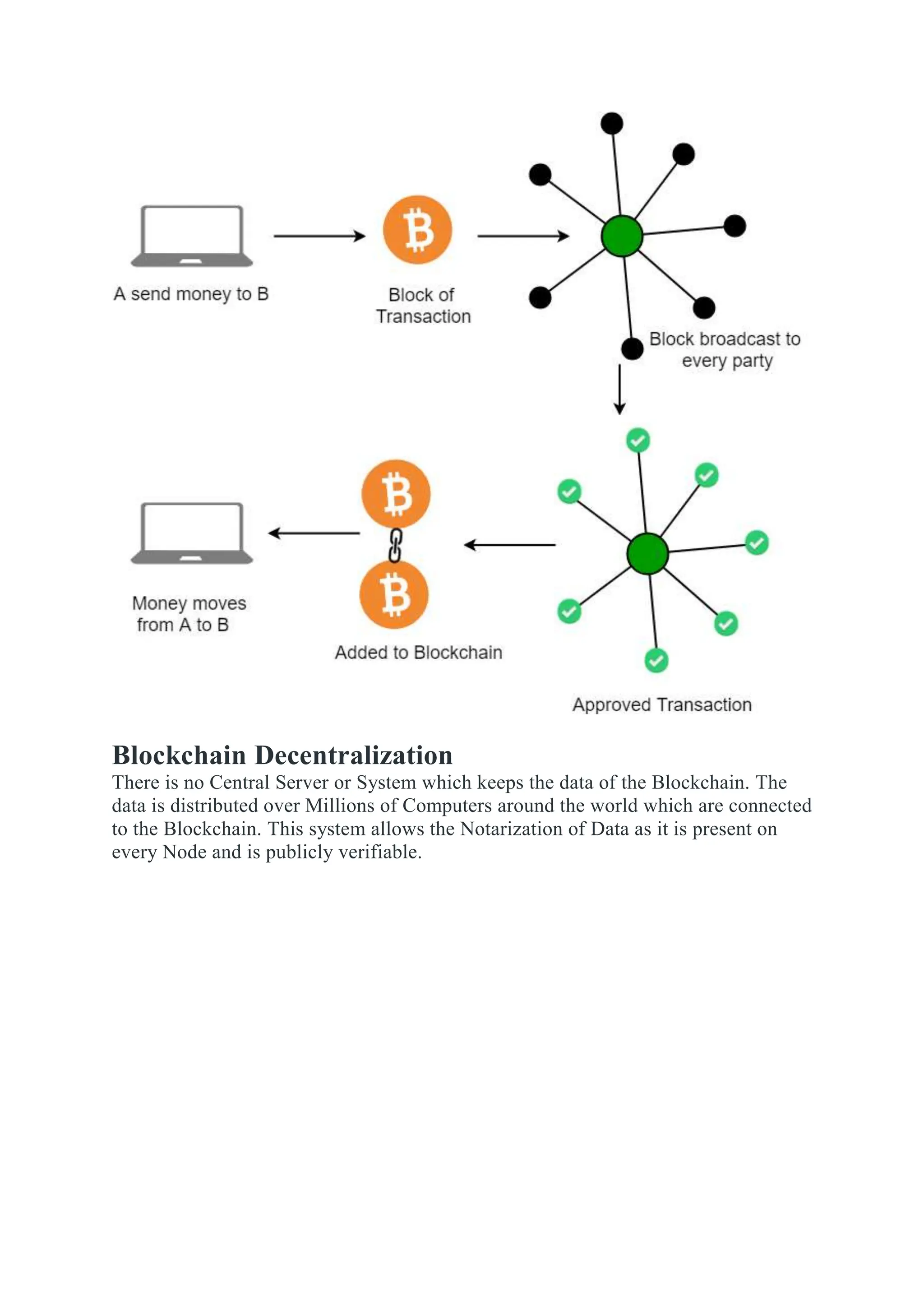
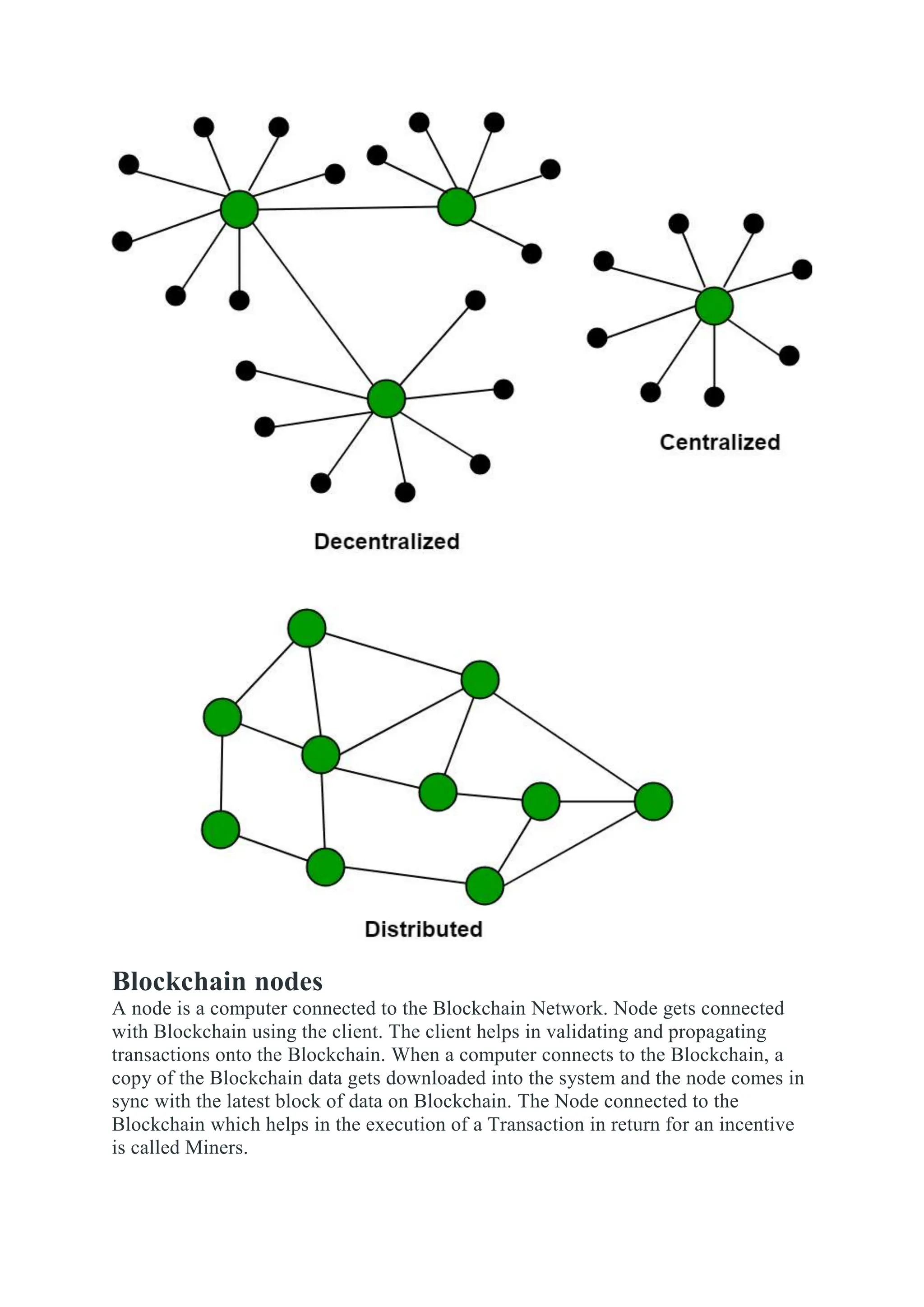
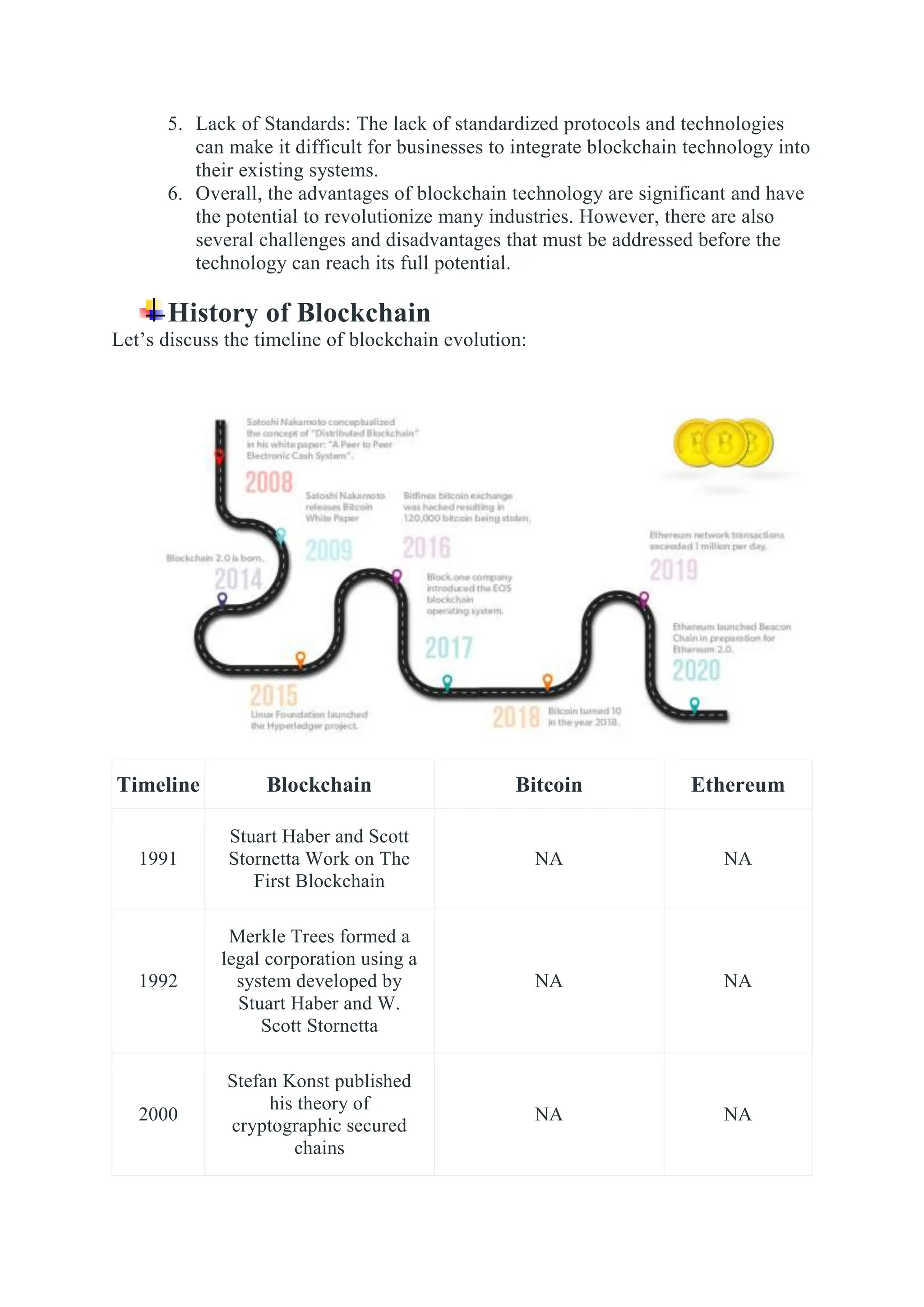
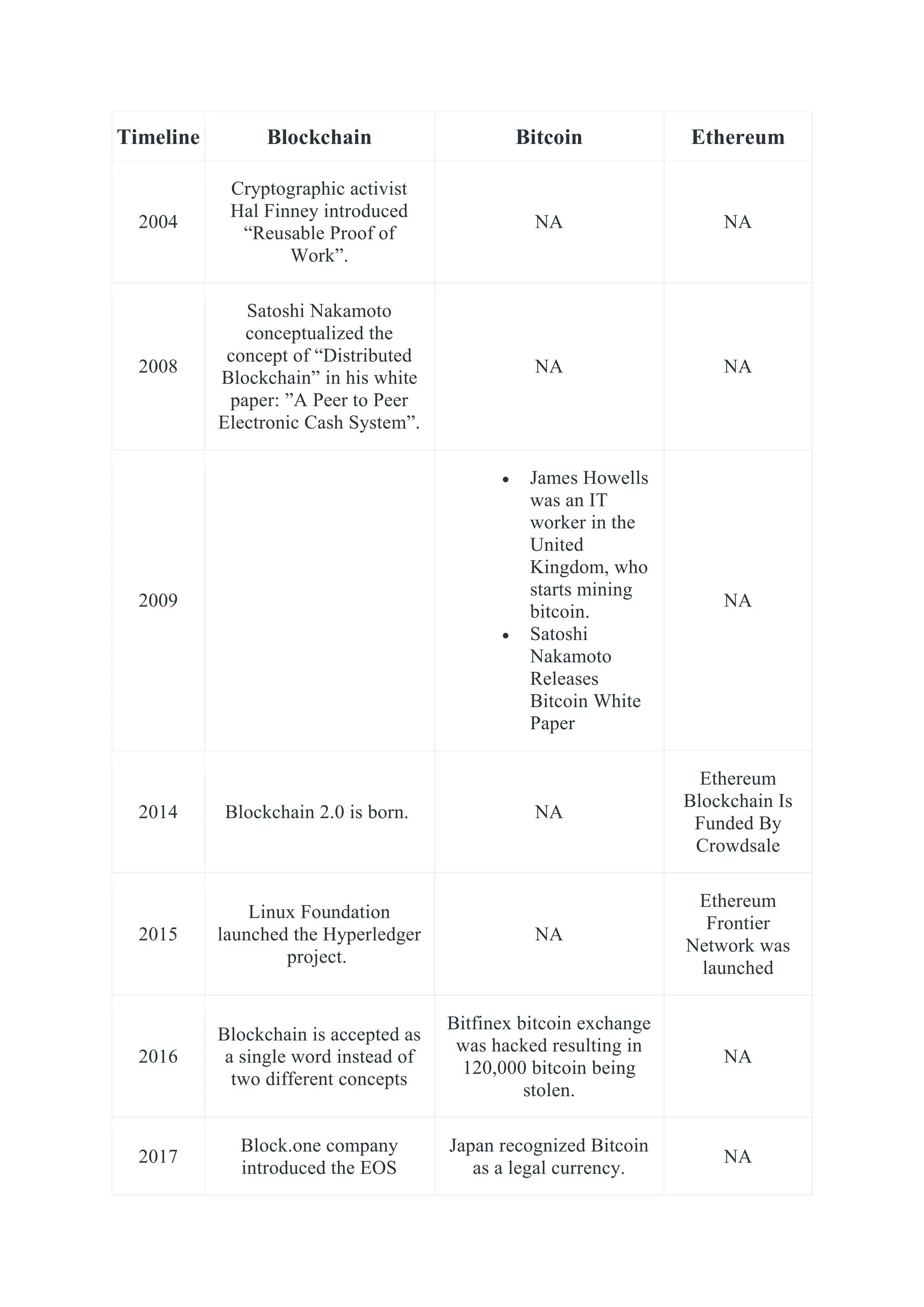
Blockchain is a distributed ledger of transactions or digital events that is shared among participants in a network. Each transaction is verified by consensus of participants and stored in a chronological and immutable chain of blocks. Blockchain technology was introduced with Bitcoin in 2008 as a way to record cryptocurrency transactions in a verifiable and permanent way without the need for a central authority. Common applications of blockchain include cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, supply chain management, digital identity, and decentralized systems.