Embed presentation
Downloaded 504 times




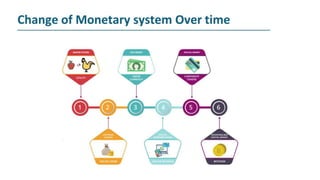



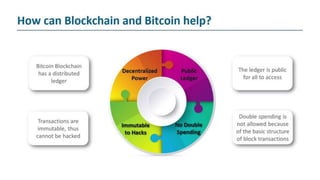

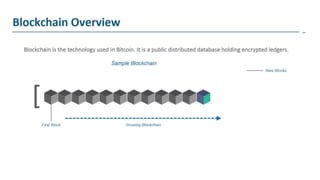
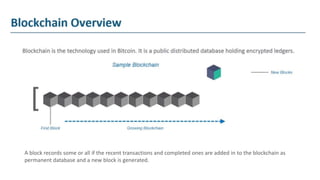
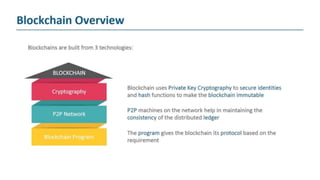
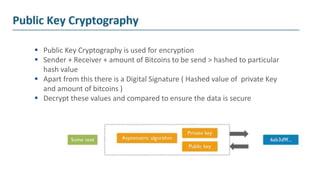
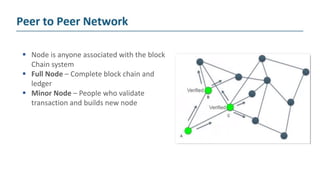
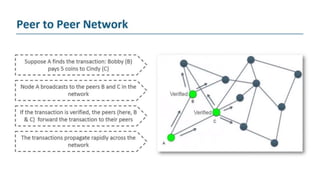


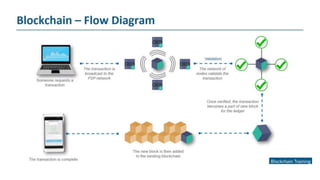

The document explains blockchain as a decentralized database invented by Satoshi Nakamoto, primarily used for Bitcoin, which addresses issues like double spending and transaction delays in the current monetary system. It describes how transactions are recorded in blocks, secured through public key cryptography, and validated by nodes in the network. Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, employs complex cryptographic methods with a maximum supply of 21 million coins, expected to be fully mined by 2040.



















