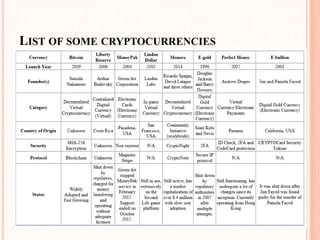
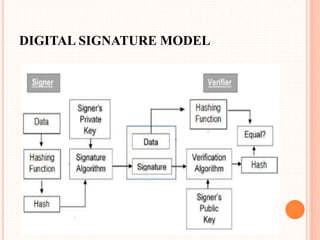
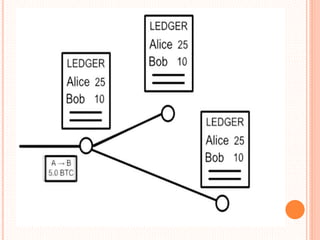
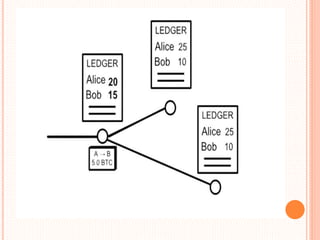
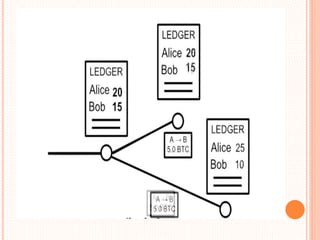
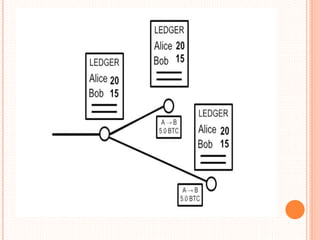
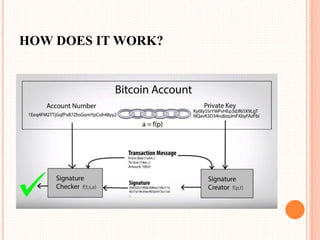
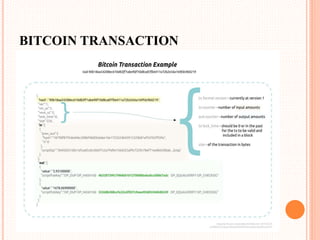
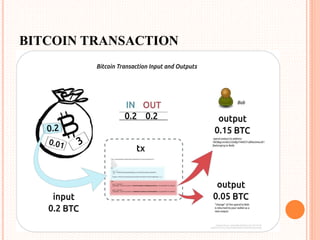
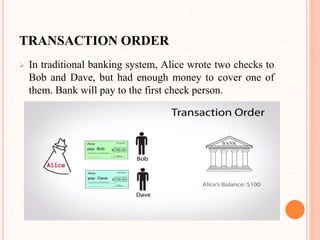
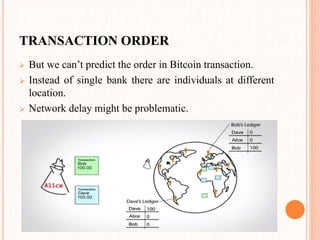
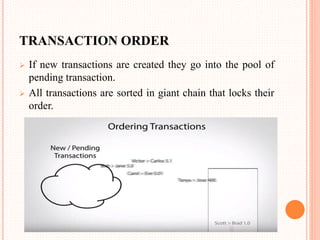
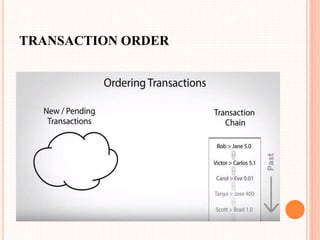
This document provides an overview of cryptocurrency and Bitcoin. It defines cryptocurrency as a digital currency that uses cryptography for security. Bitcoin, created in 2009, was the first decentralized cryptocurrency. The document then discusses how Bitcoin works at a basic level, including how transactions are verified and recorded in a public ledger called the blockchain. It also covers Bitcoin mining, wallets, and some advantages and disadvantages of cryptocurrency.