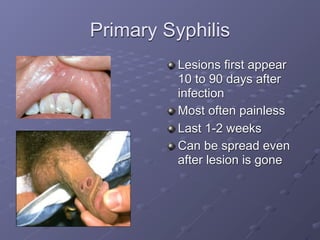
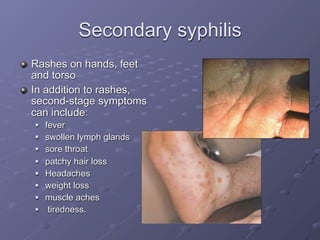
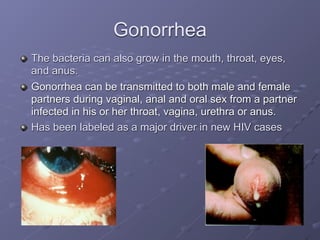
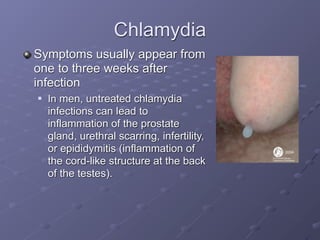
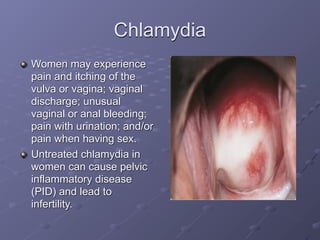
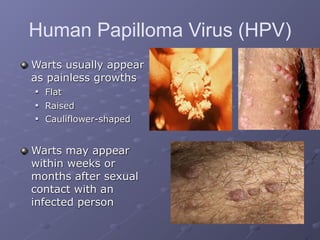
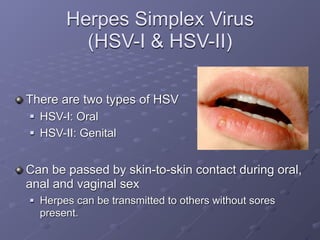
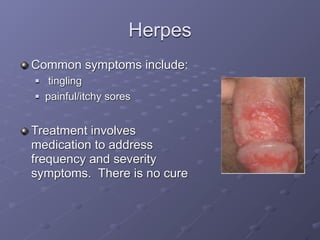
This document provides information on sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including their causes, symptoms, and prevention. It discusses the main categories of bacterial and viral STIs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, hepatitis A/B/C, herpes, HIV, human papillomavirus, and syphilis. Key points covered include how STIs can be transmitted and increase HIV risk, the importance of getting tested regularly, and strategies for prevention through condom and barrier use, partner communication, and limiting sexual partners. Resources for testing and treatment in San Francisco are also listed.