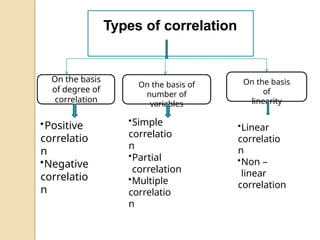
Correlation analysis measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two quantitative variables. It produces a correlation coefficient (e.g., Pearson's r) that ranges from -1 to +1, indicating the degree to which the variables change together. A positive correlation implies variables increase or decrease in tandem, while a negative correlation suggests they move inversely.