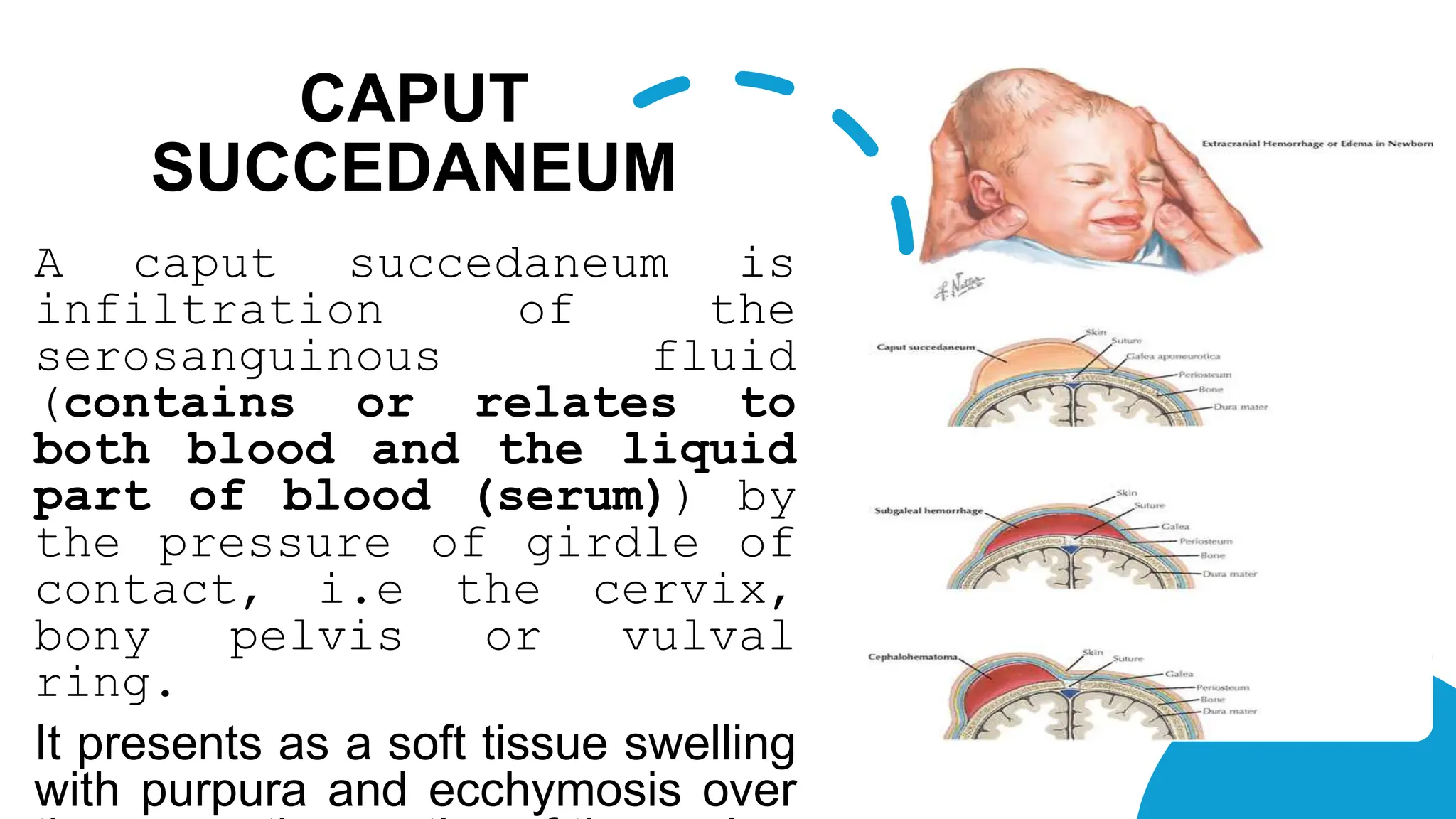
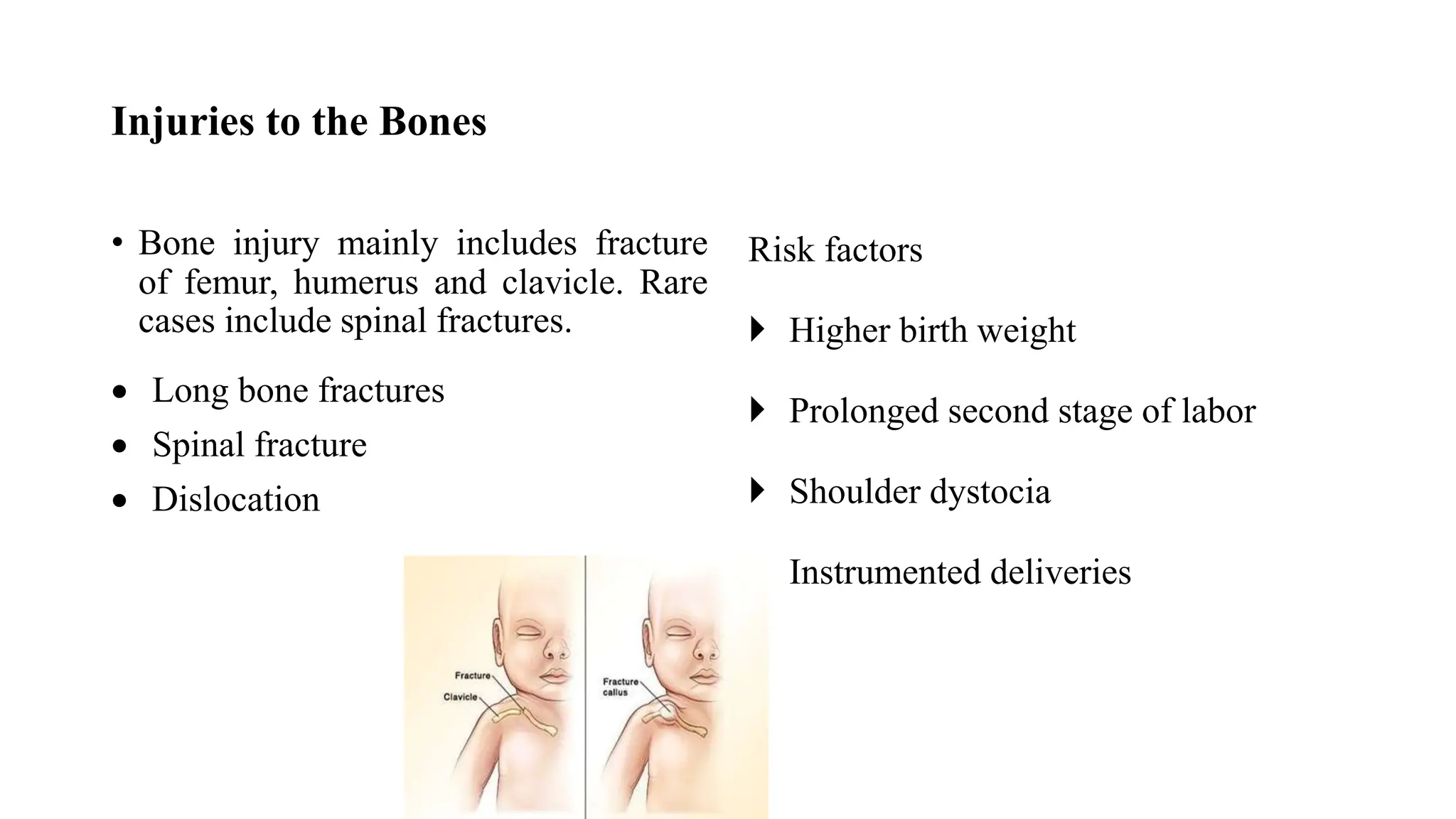
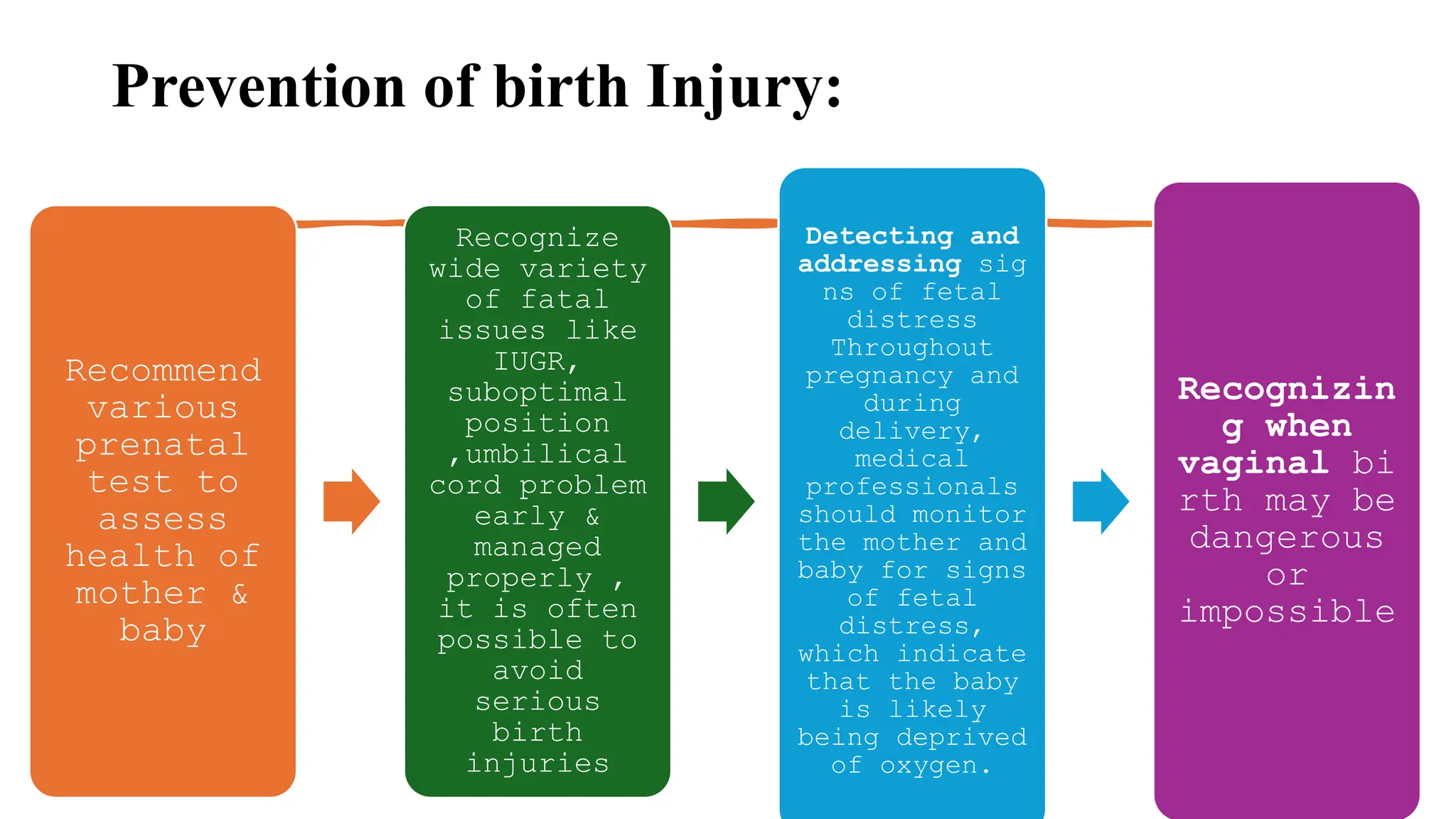
Birth injuries can affect either the mother or baby and are caused by complications during the birthing process. Risk factors include a mother's first birth, small stature, pelvic anomalies, prolonged labor, or fetal issues like abnormal positioning. Potential injuries include head trauma, fractures, nerve damage, or soft tissue injuries. Prevention focuses on careful monitoring during labor, identifying issues like fetal distress early, and managing high risk deliveries cautiously.