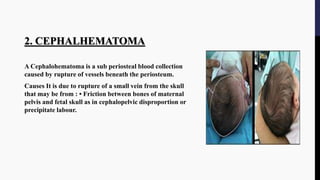
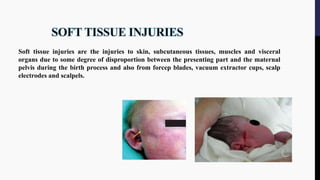
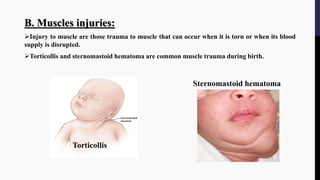
The document provides an overview of birth injuries, defining them as impairments of an infant's body function or structure due to adverse influences at birth, which may lead to severe outcomes such as neonatal death or morbidity. Key factors contributing to these injuries include maternal characteristics, labor conditions, and fetal presentations, with common injuries ranging from skull fractures to nerve injuries. Management strategies vary according to the type and severity of the injury, often requiring monitoring and interventions like surgical treatment or supportive care.