1) Ecology is the study of interactions between organisms and their environment. The biosphere is made up of all ecosystems on Earth spanning land, water, and air that support life.
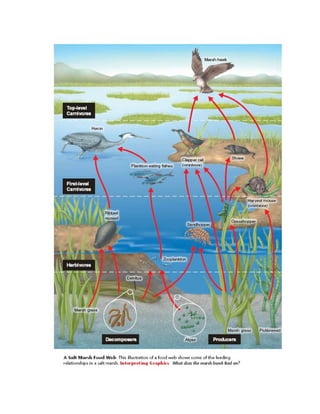
2) Ecologists study different levels of organization from species to the entire biosphere. Energy flows through ecosystems from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs like plants, then to heterotrophs such as animals.
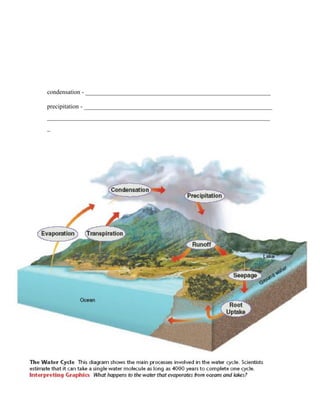
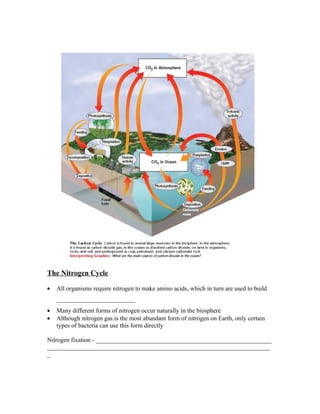
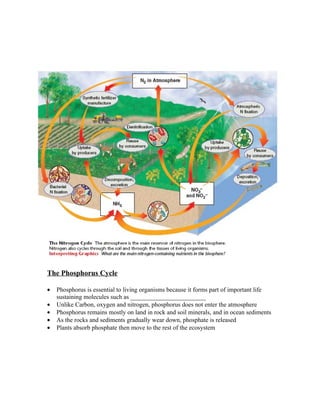
3) Matter cycles through ecosystems as well in processes like the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles which are essential to sustain life. Water cycles through evaporation, transpiration, condensation, and precipitation while nutrients cycle through ecosystems via biological and geochemical processes.