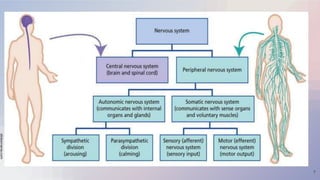
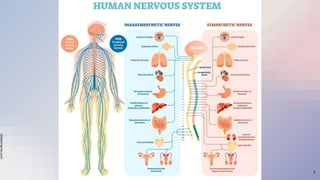
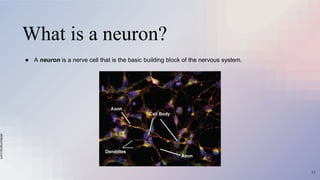
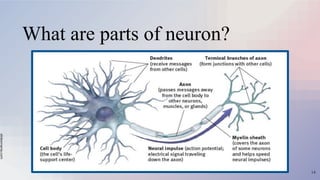
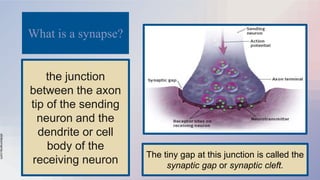
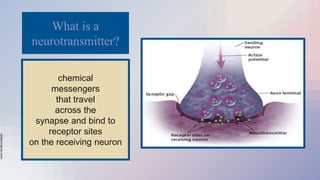
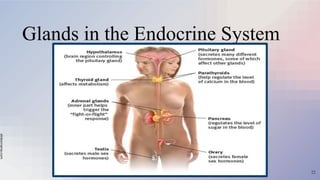
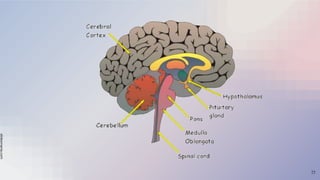
The document provides an overview of the nervous and endocrine systems, explaining how they control responses to threats and manage body functions. It discusses the roles of neurons, synapses, and neurotransmitters in communication, as well as key brain structures like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Additionally, it highlights the functions of specific glands, including the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, in regulating bodily processes.