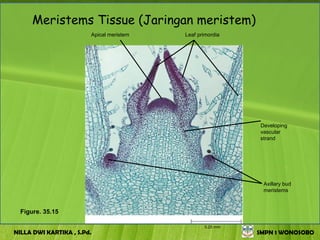
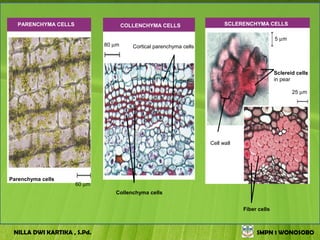
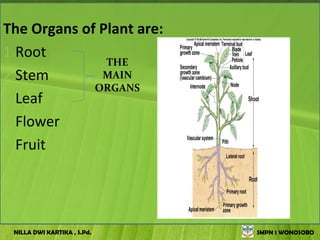
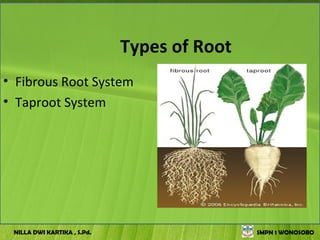
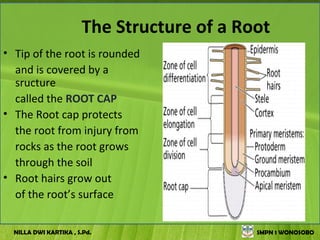
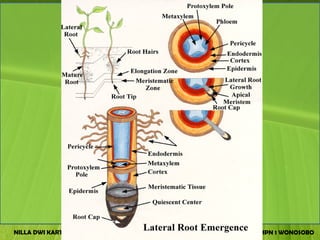
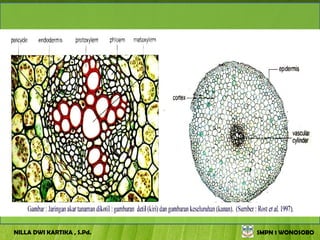
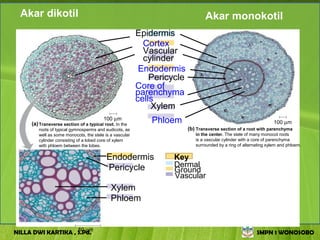
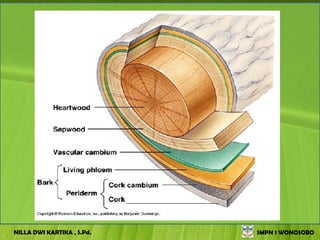
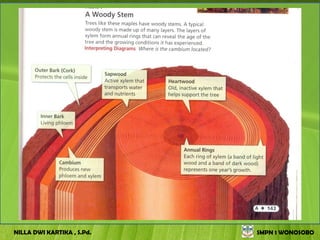
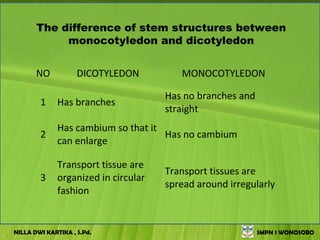
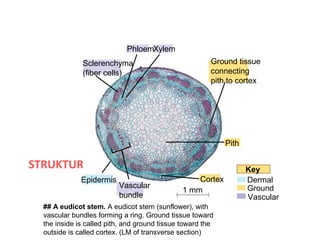
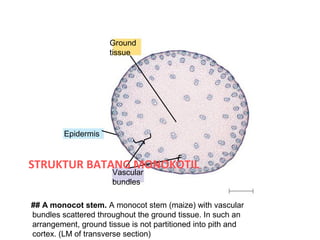
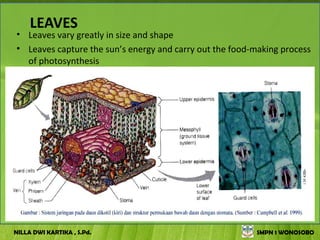
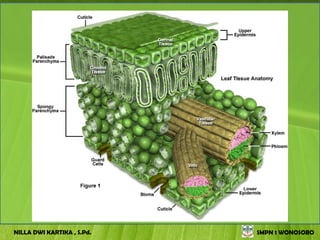
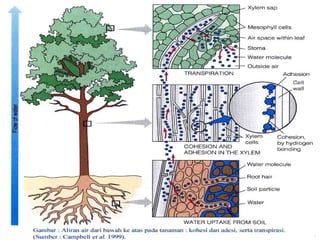
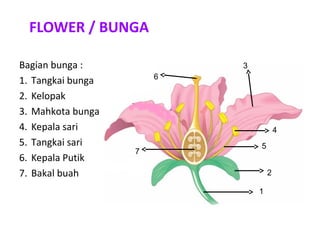
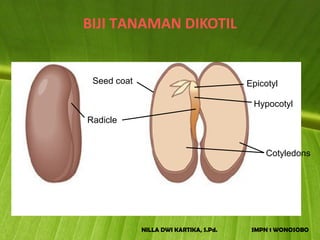
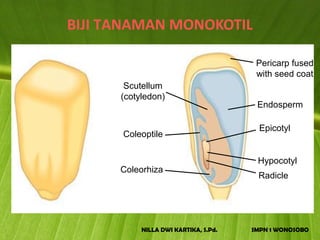
The document discusses the structure and functions of plant bodies. It describes the main tissues that make up plant organs, including meristem, epidermis, cortex, and vascular tissues. It then explains the main plant organs - roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. Roots function to absorb water and minerals, anchor the plant, and store food. Stems carry substances between roots and leaves, provide support and store food. The document provides detailed diagrams and descriptions of root and stem structures.