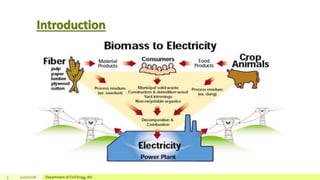
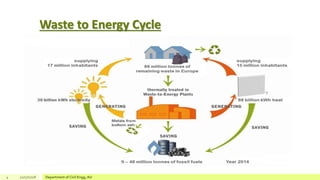
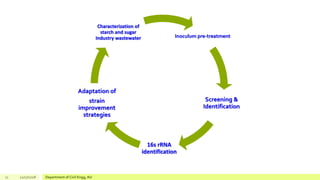
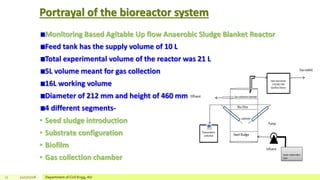
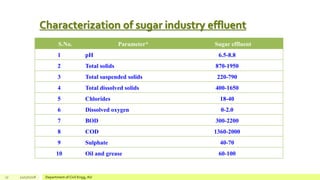
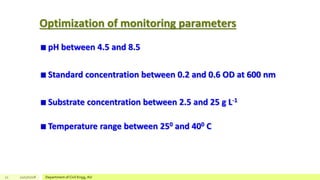
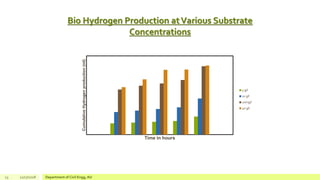
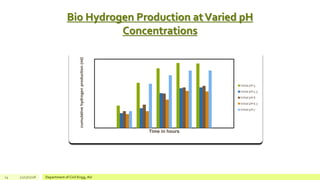
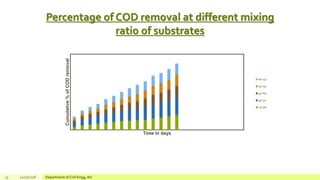
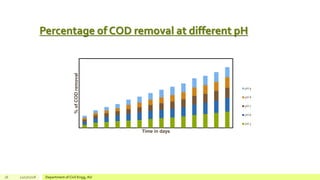
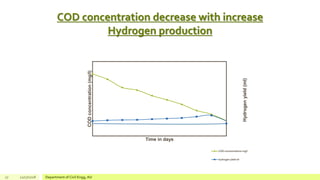
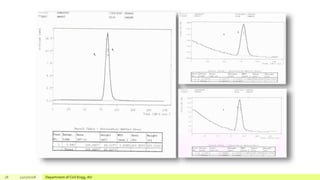
The document describes a study on enhancing biohydrogen production from carbohydrate-rich industrial wastewater under anaerobic conditions. A pilot-scale Monitoring Based Agitable Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (MAUASB) reactor was constructed and operated for 5 months using sugar industry wastewater as the substrate. The maximum COD removal efficiency was 81% at pH 5.0, and hydrogen production peaked at 272.4 ml on the 8th day at pH 5.1 before decreasing due to methanogenesis. The study demonstrated the feasibility of using the MAUASB reactor to treat sugar wastewater and produce biohydrogen as a renewable energy source.