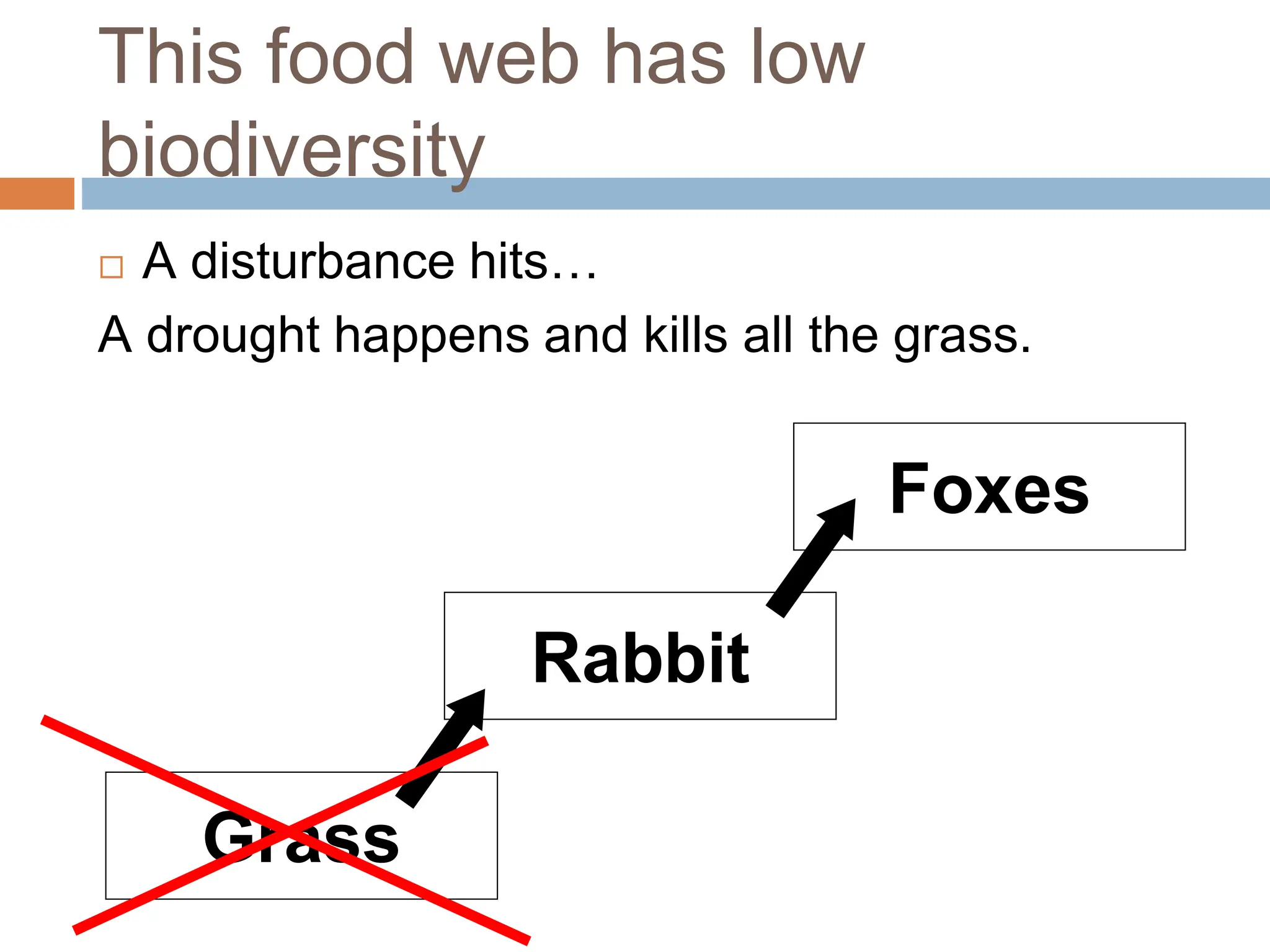
This document contains an agenda and content for a lesson on biodiversity and ecosystem stability. The agenda includes reviewing a catalyst, test averages, homework, defining biodiversity, discussing ecosystem stability, participating in stations/activities, and answering an exit question. Key points from the content include: high biodiversity leads to more stable ecosystems while low biodiversity results in unstable ecosystems; stable ecosystems experience little change when disturbed while unstable ecosystems experience large changes.