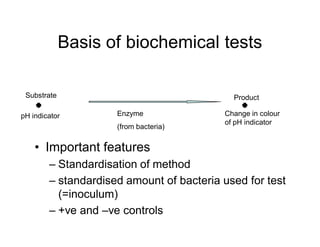
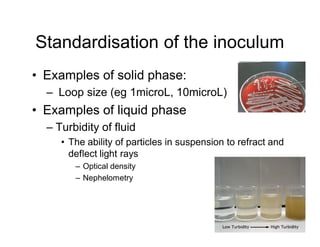
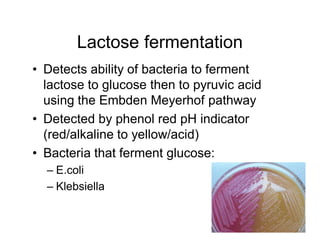
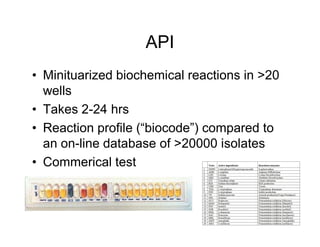
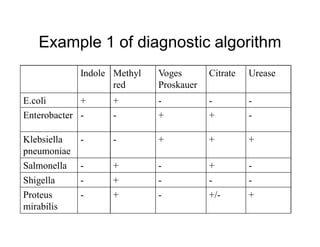
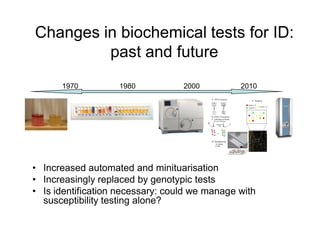
This document discusses biochemical identification of bacteria. It begins by distinguishing phenotypic tests, which detect physical bacterial properties influenced by gene expression, from genotypic tests, which detect the genetic code directly. Biochemical tests are considered phenotypic. The document outlines pros and cons of biochemical tests, how they work by detecting enzyme reactions, examples of common tests, and how diagnostic algorithms incorporate multiple tests for identification. It notes biochemical tests are being increasingly replaced by automated and genetic methods.