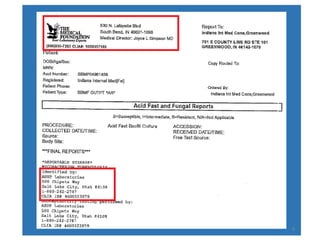
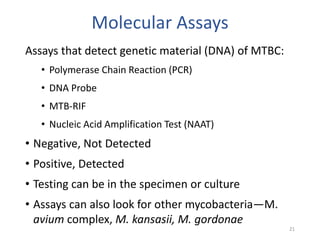
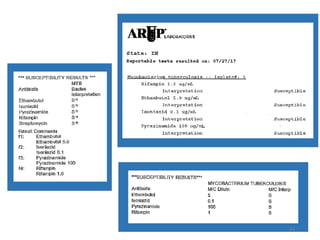
This document discusses how to decipher tuberculosis (TB) laboratory reports. It begins by explaining that labs performing diagnostic testing are regulated by CLIA to ensure quality standards. A typical lab report includes sections for laboratory information, patient information, specimen details, tests performed, and results interpretation. Test results may include AFB smear microscopy, molecular assays for detection of TB and drug resistance, culture outcomes, and antibiotic susceptibility results. Understanding the format and abbreviations used in lab reports is key to interpreting TB test results.