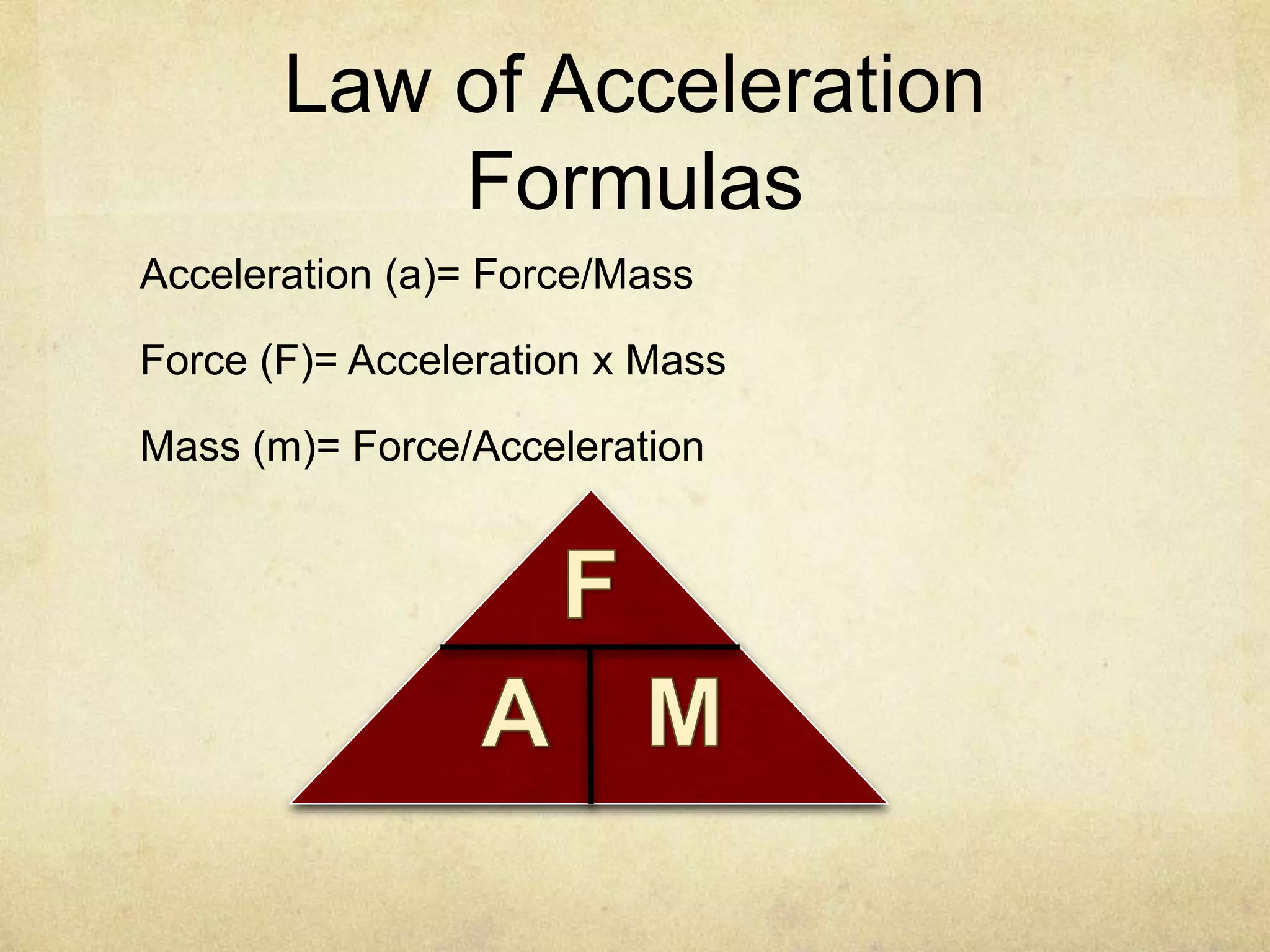
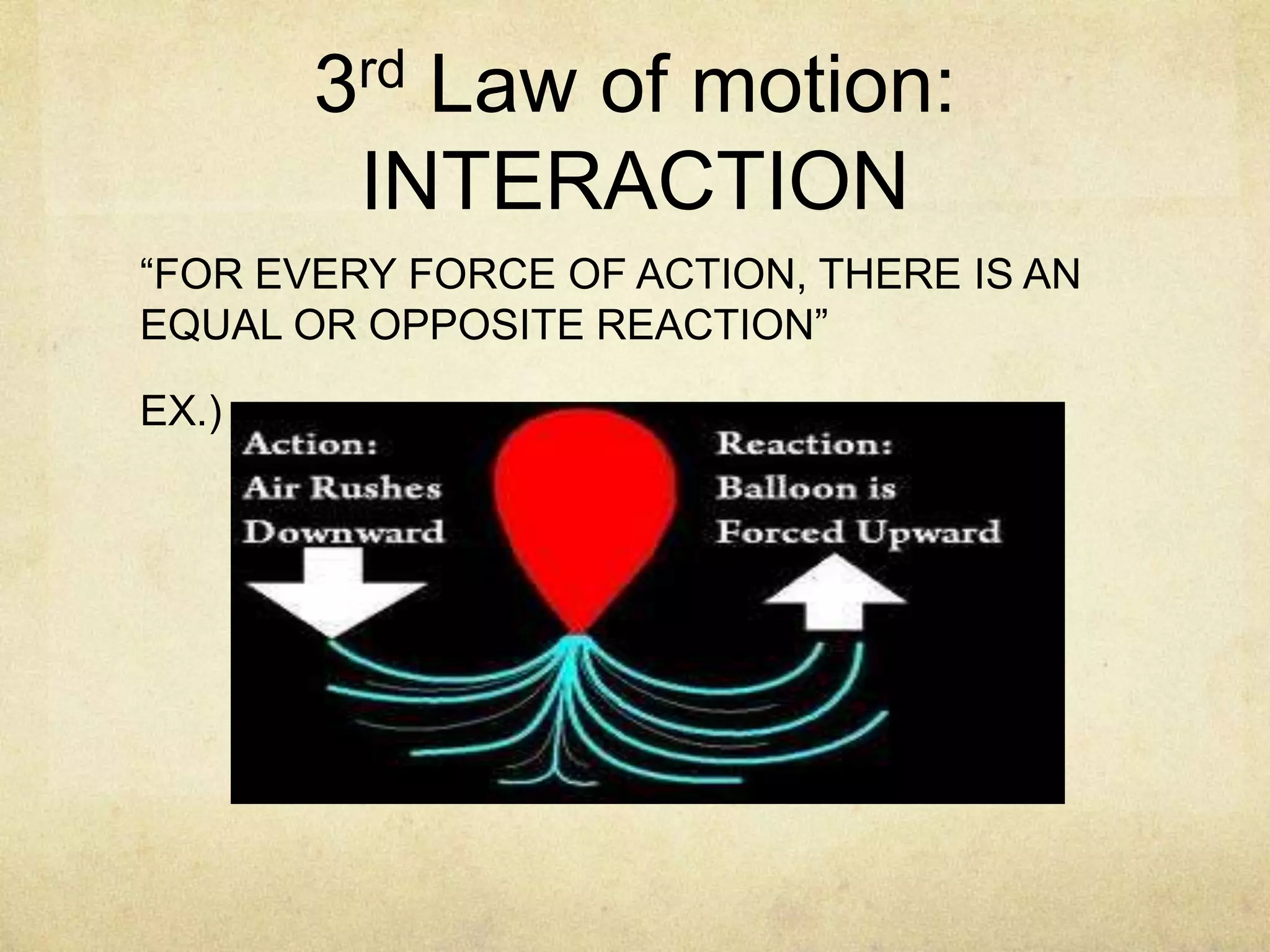
This document provides an overview of the laws of motion. It begins with questions about inertia, motion, and the scientists who studied motion. It then states that dynamics is the branch of science that studies the three laws of motion. It identifies Isaac Newton as the scientist who created the three laws of motion by building upon Galileo Galilei's work. The three laws are then defined: 1) inertia, 2) acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass, and 3) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are given for each law.