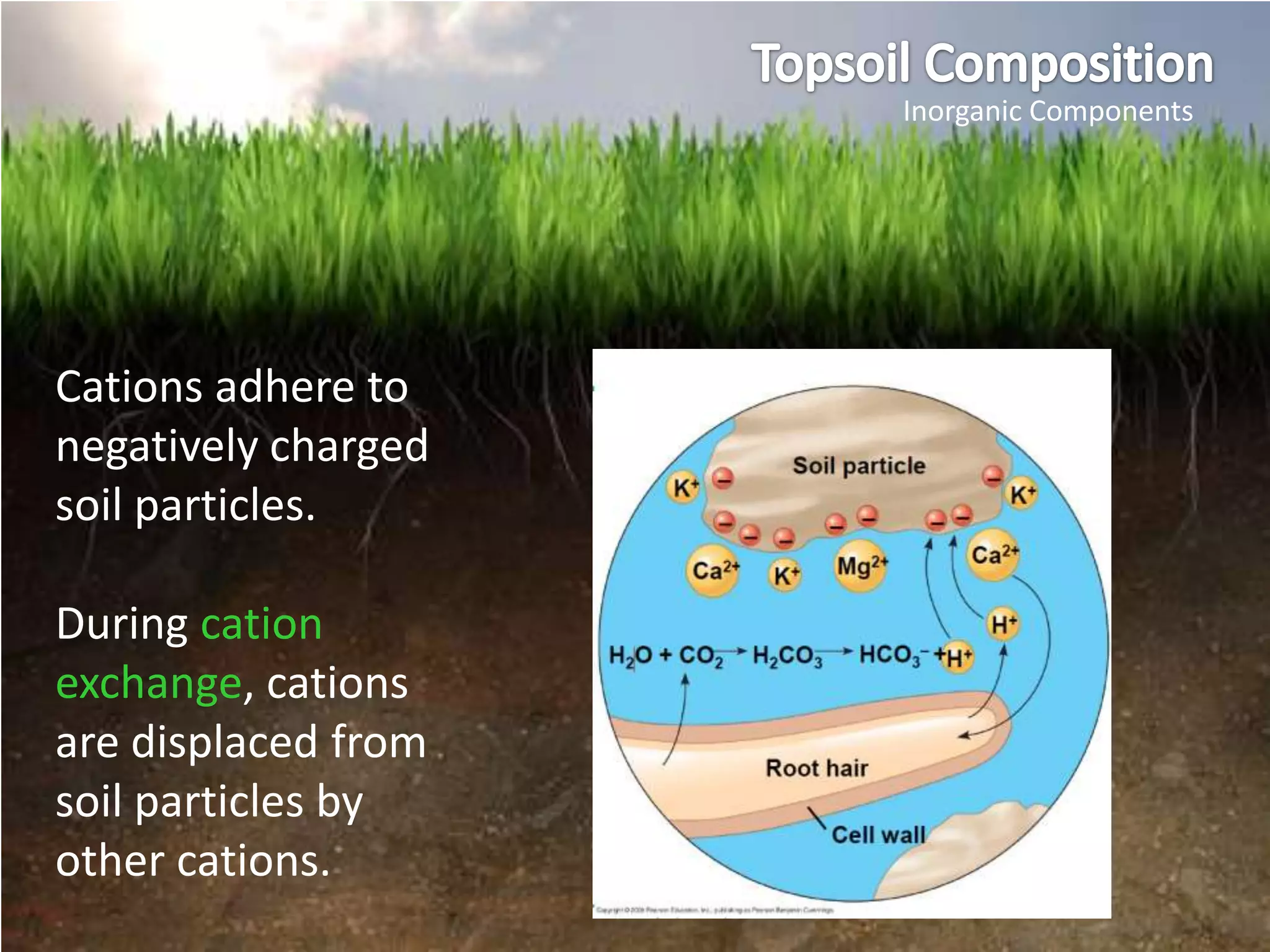
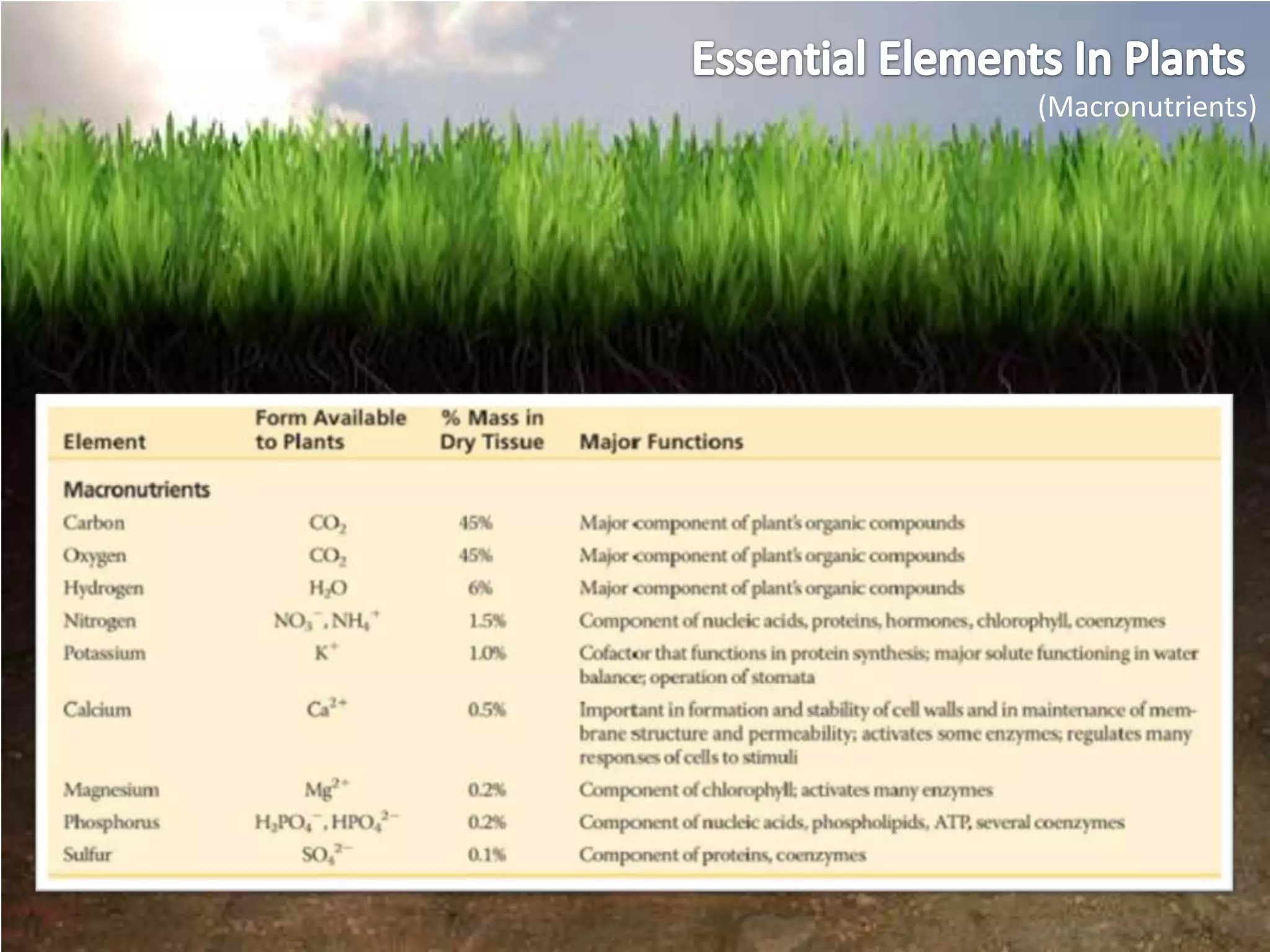
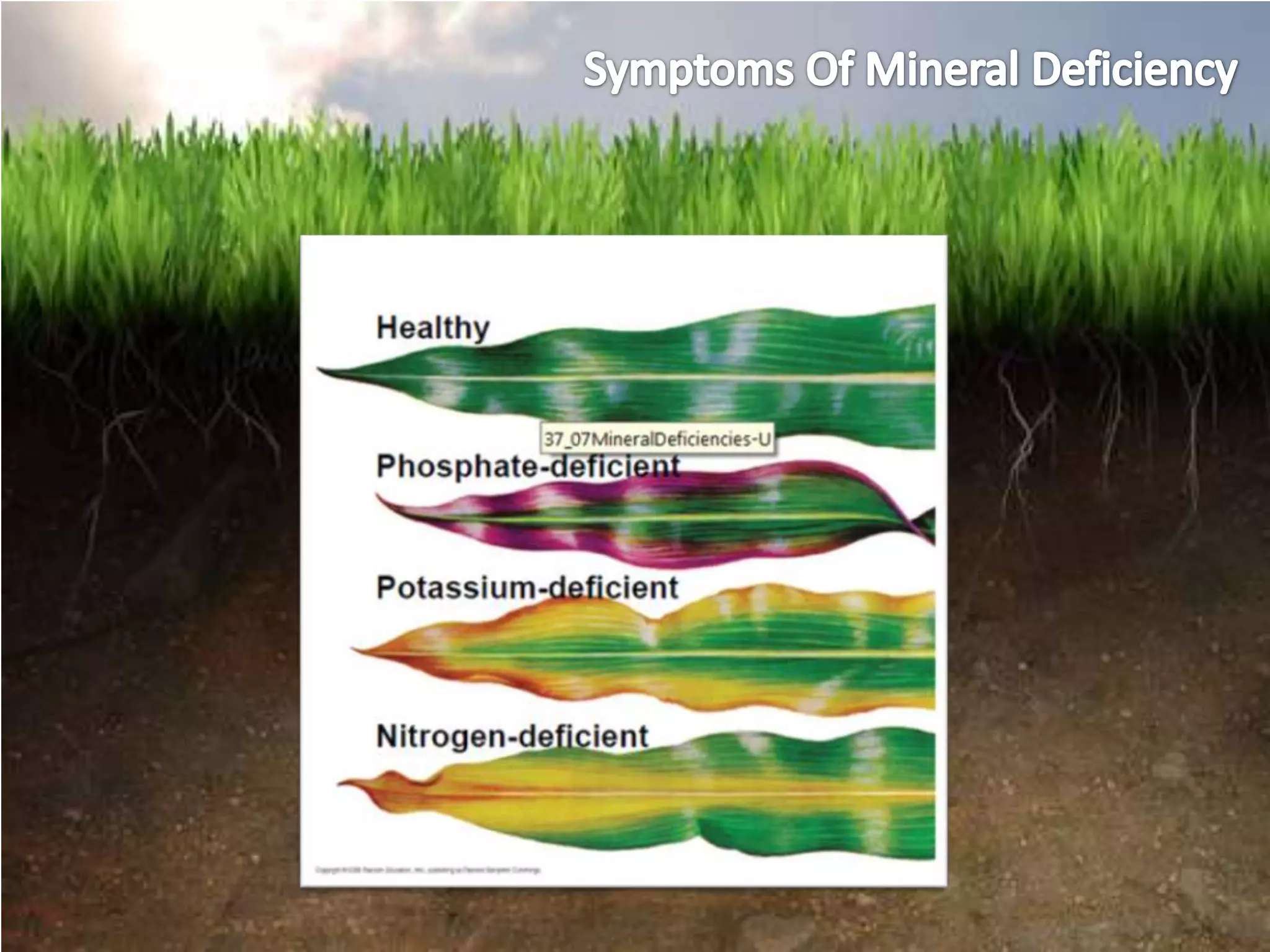
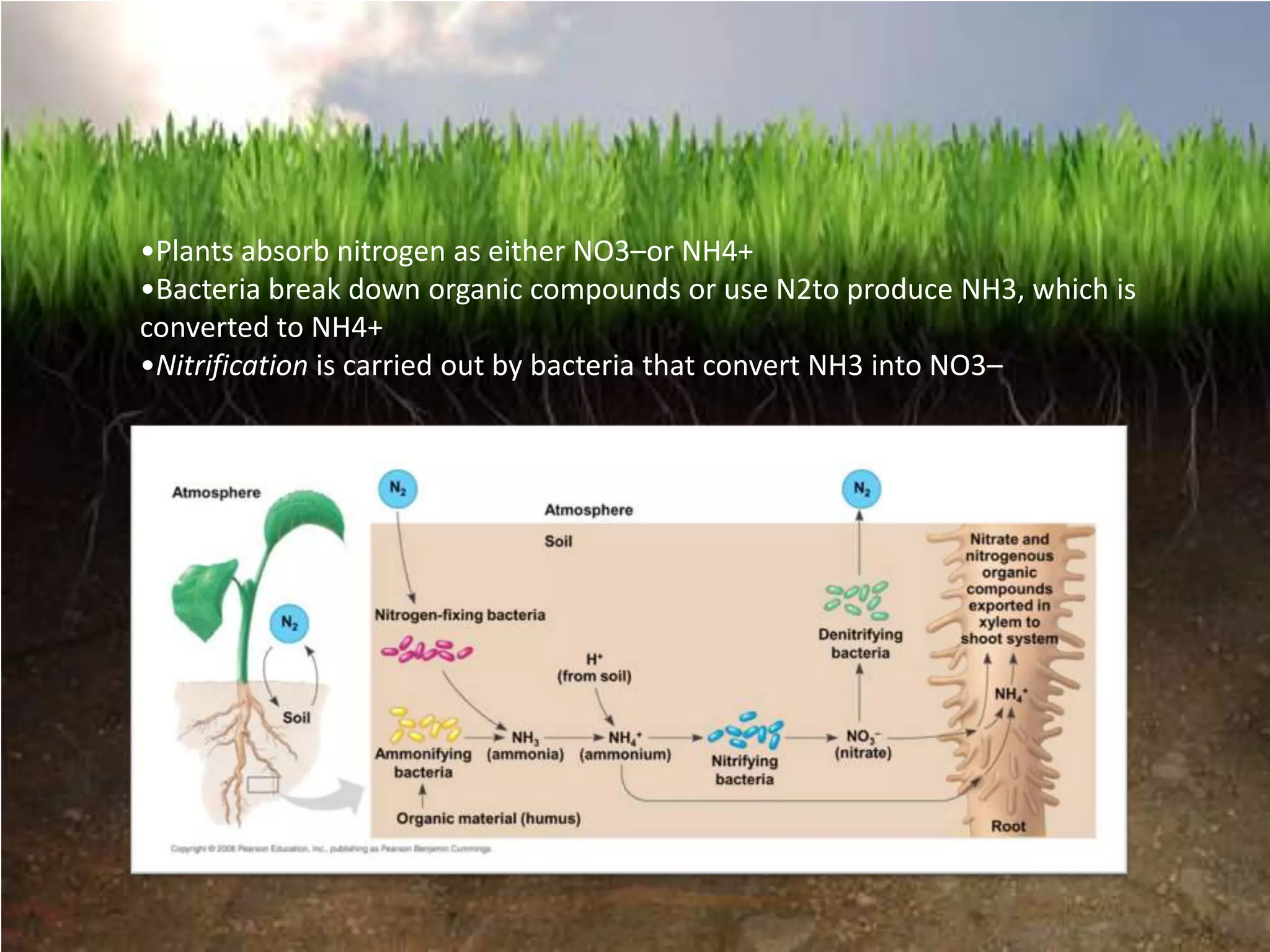
The document summarizes key concepts about soils and plant nutrition:
- Soil is made up of particles classified by size and arranged in horizons, with loam being the most fertile topsoil. The soil contains inorganic components like minerals and organic components like humus.
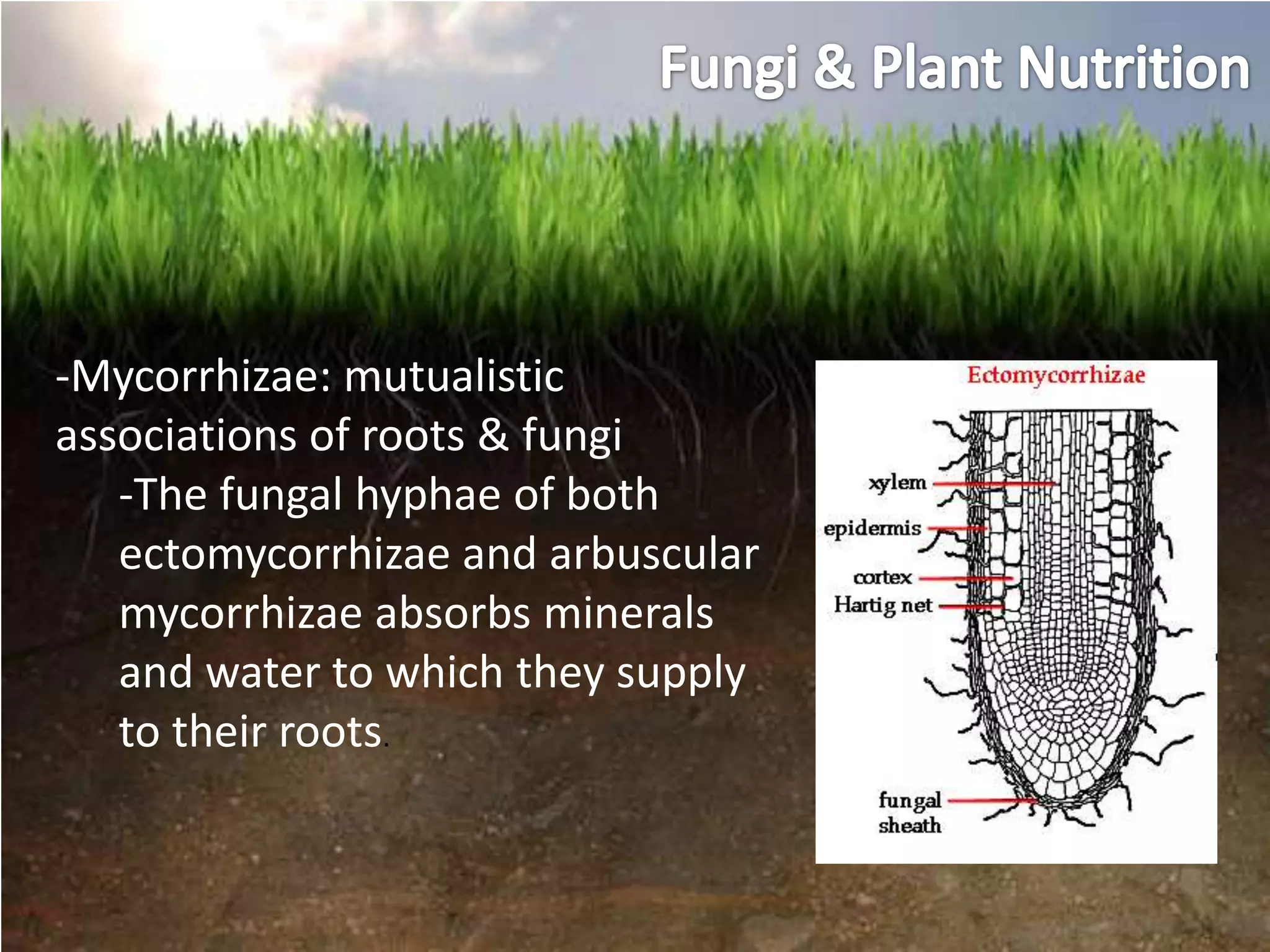
- Plants obtain essential inorganic nutrients from the soil, and have evolved relationships with soil microbes to aid nutrient uptake through processes like nitrogen fixation and mycorrhizal associations.
- Sustainable agriculture aims to farm in an environmentally-friendly way through practices such as irrigation, fertilization, erosion control and composting.