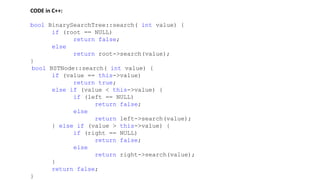
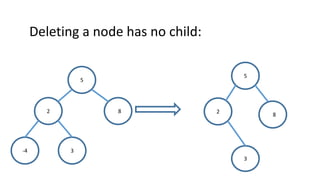
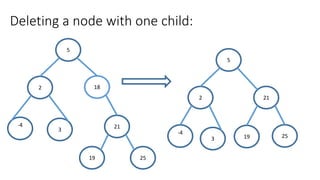
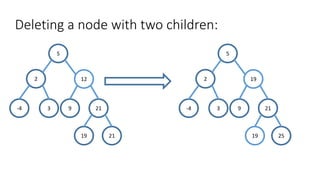
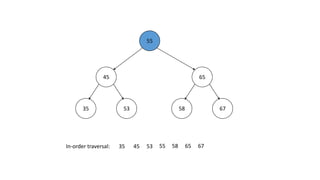
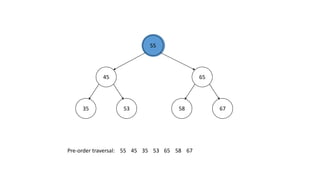
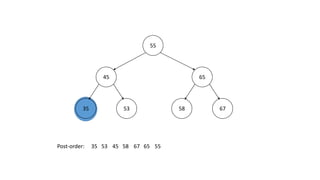
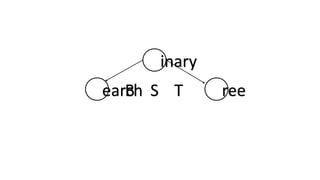
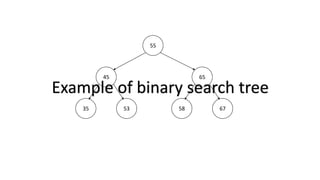
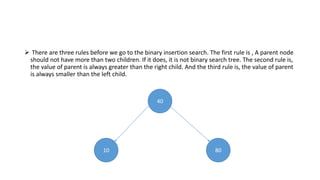
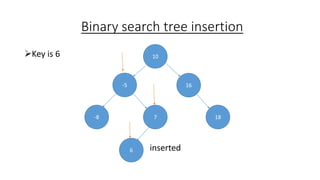
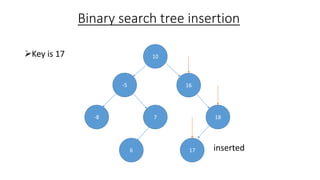
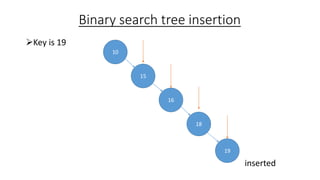
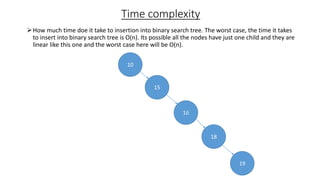
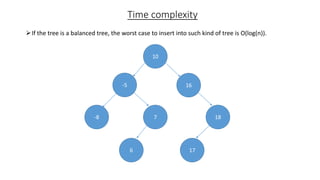
The document outlines the definition and operations of binary search trees (BST), including insertion, search, deletion, and traversal methods. It describes the rules for maintaining a BST and provides time complexity for various operations, indicating that searching and inserting in a balanced tree has an average complexity of O(log n). Additionally, it offers real-life applications and references for further reading.









![Algorithm:
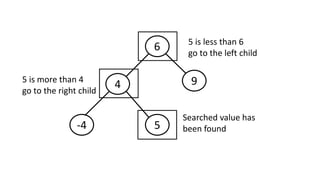
Here k is the key that is searched for and x is the start
node.
BST-Search(x, k)
1. y ← x
2. while y ≠ nil do
3. if key[y] = k then return y
4. else if key[y] < k then y ← right[y]
5. else y ← left[y]
6. return (“NOT FOUND”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binary-search-tree-171001030657/85/Binary-Search-Tree-19-320.jpg)