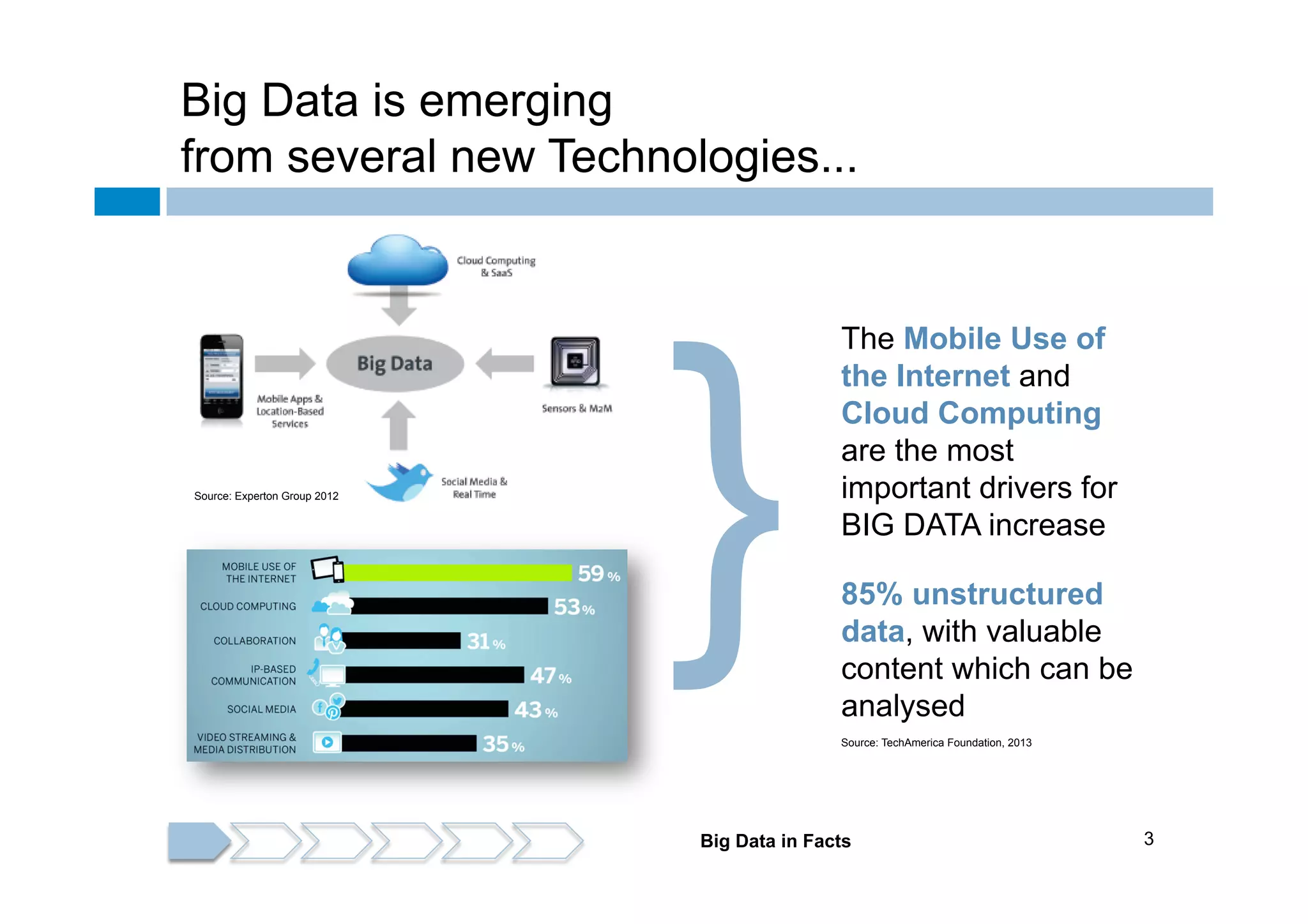
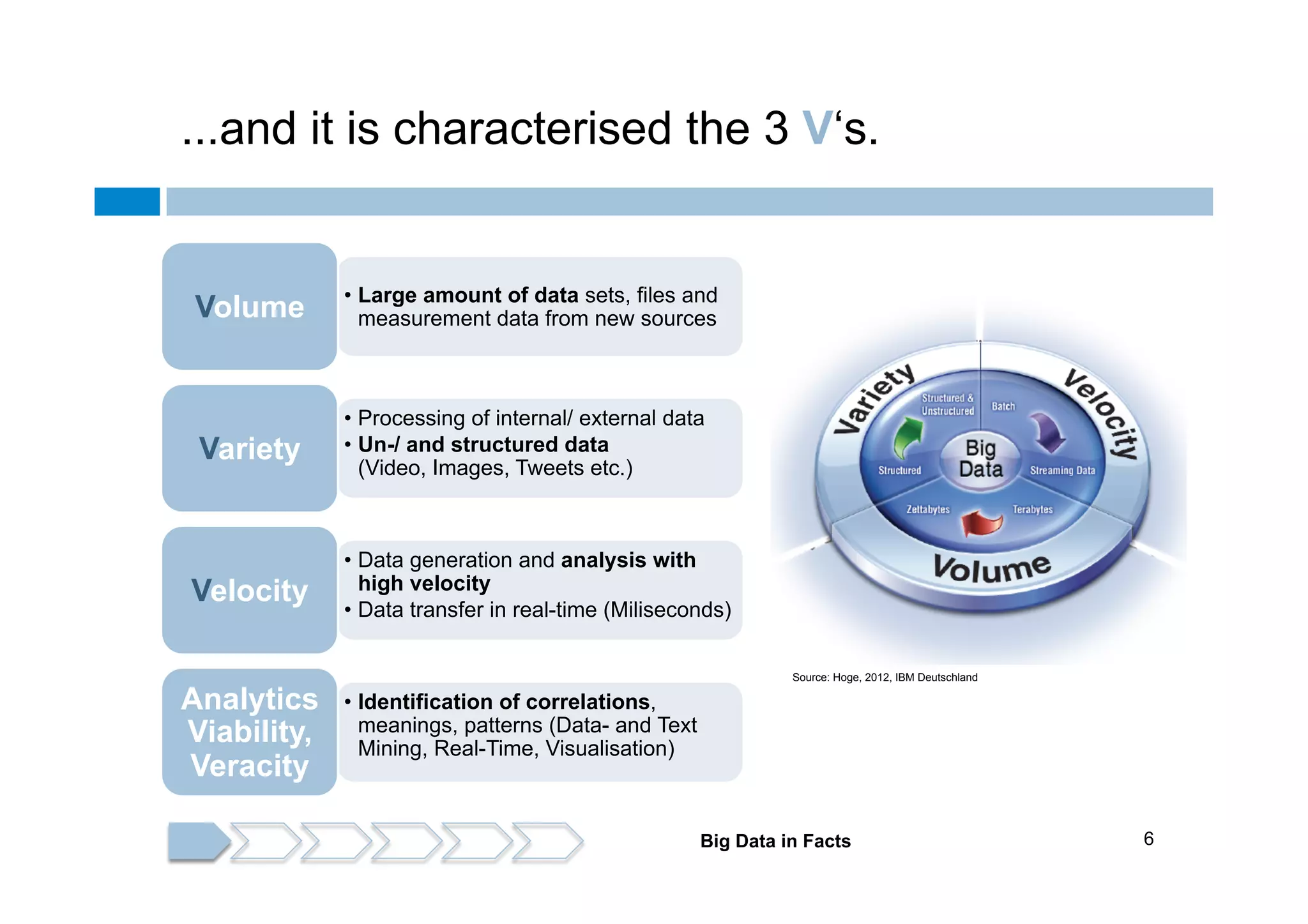
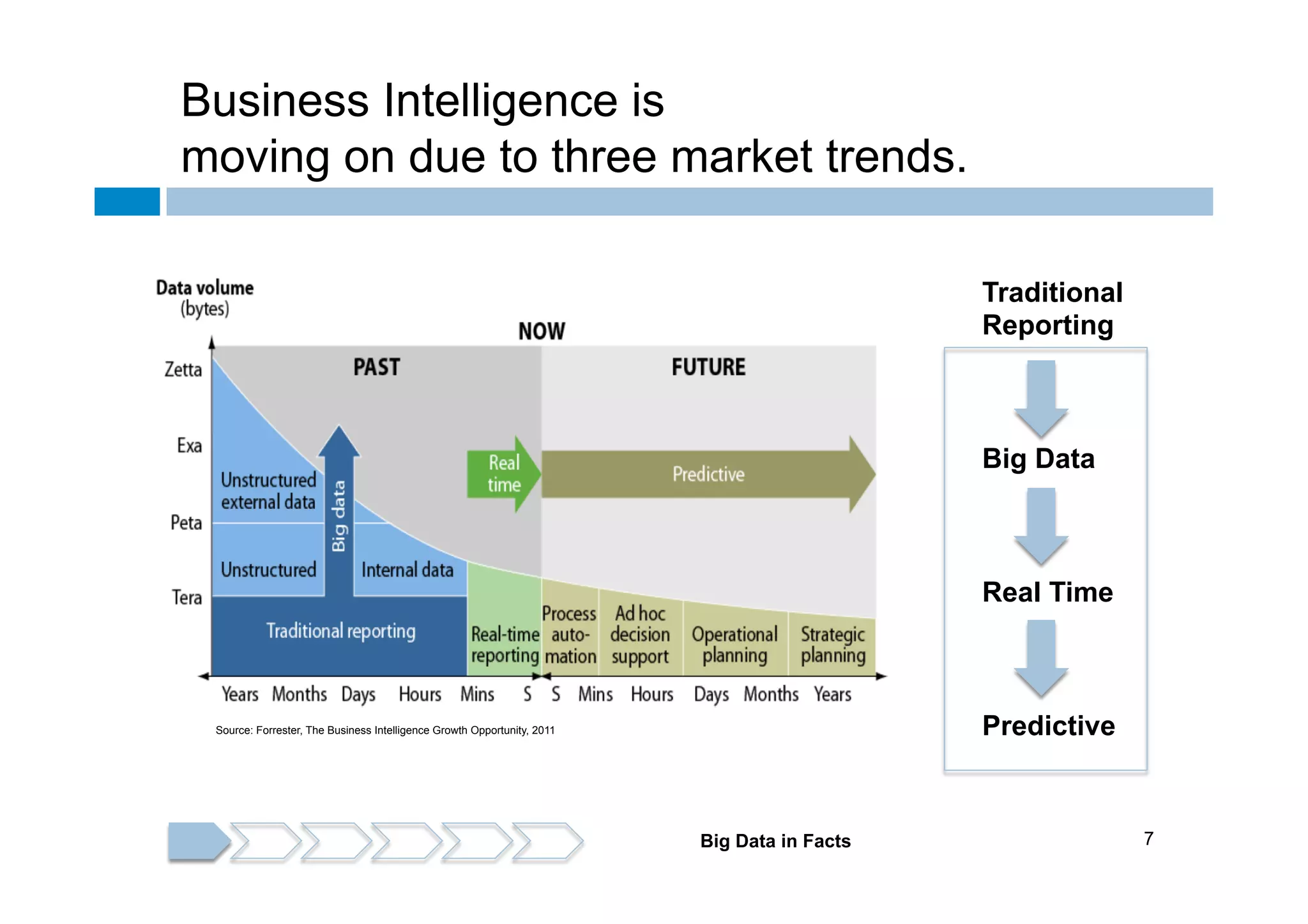
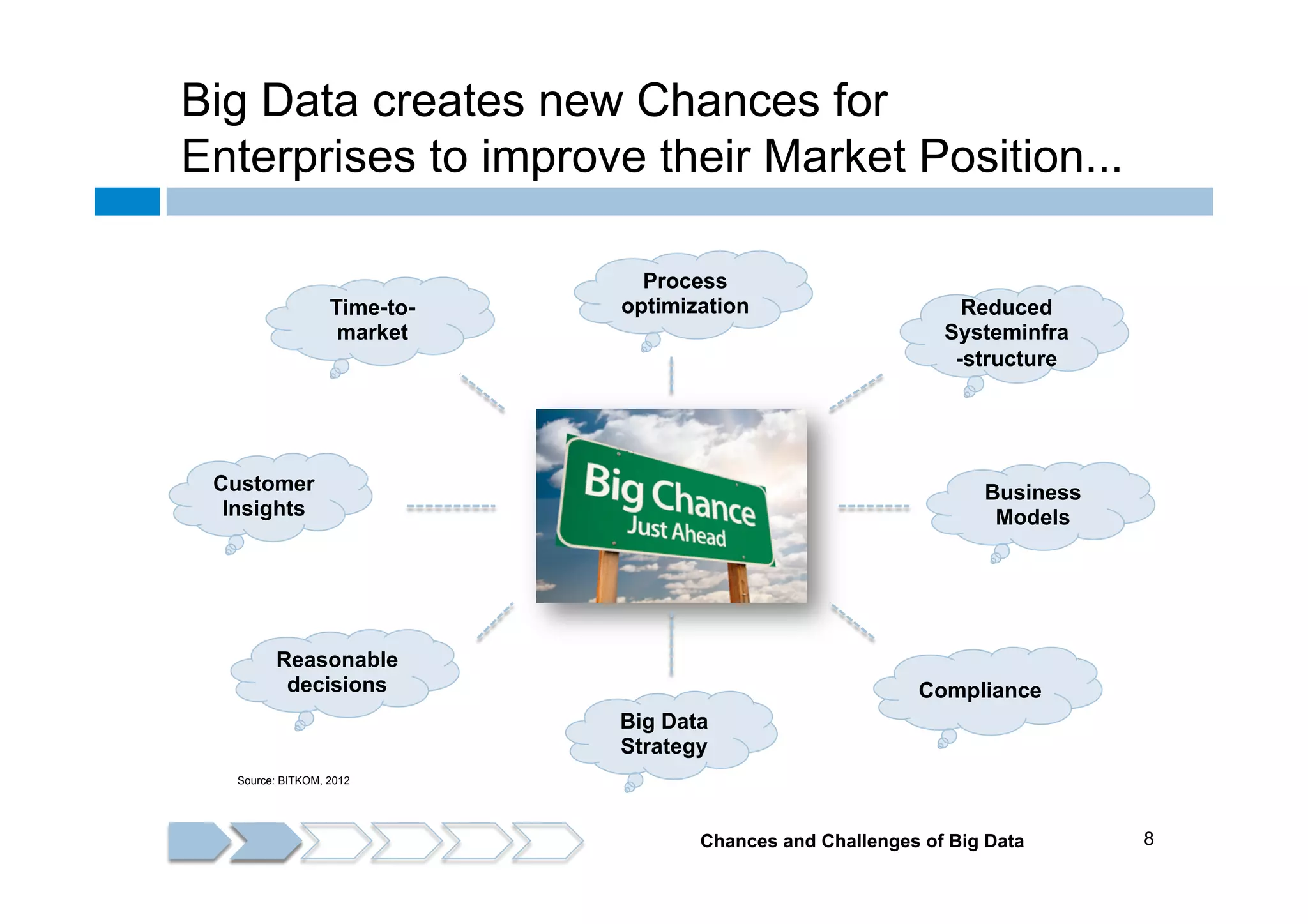
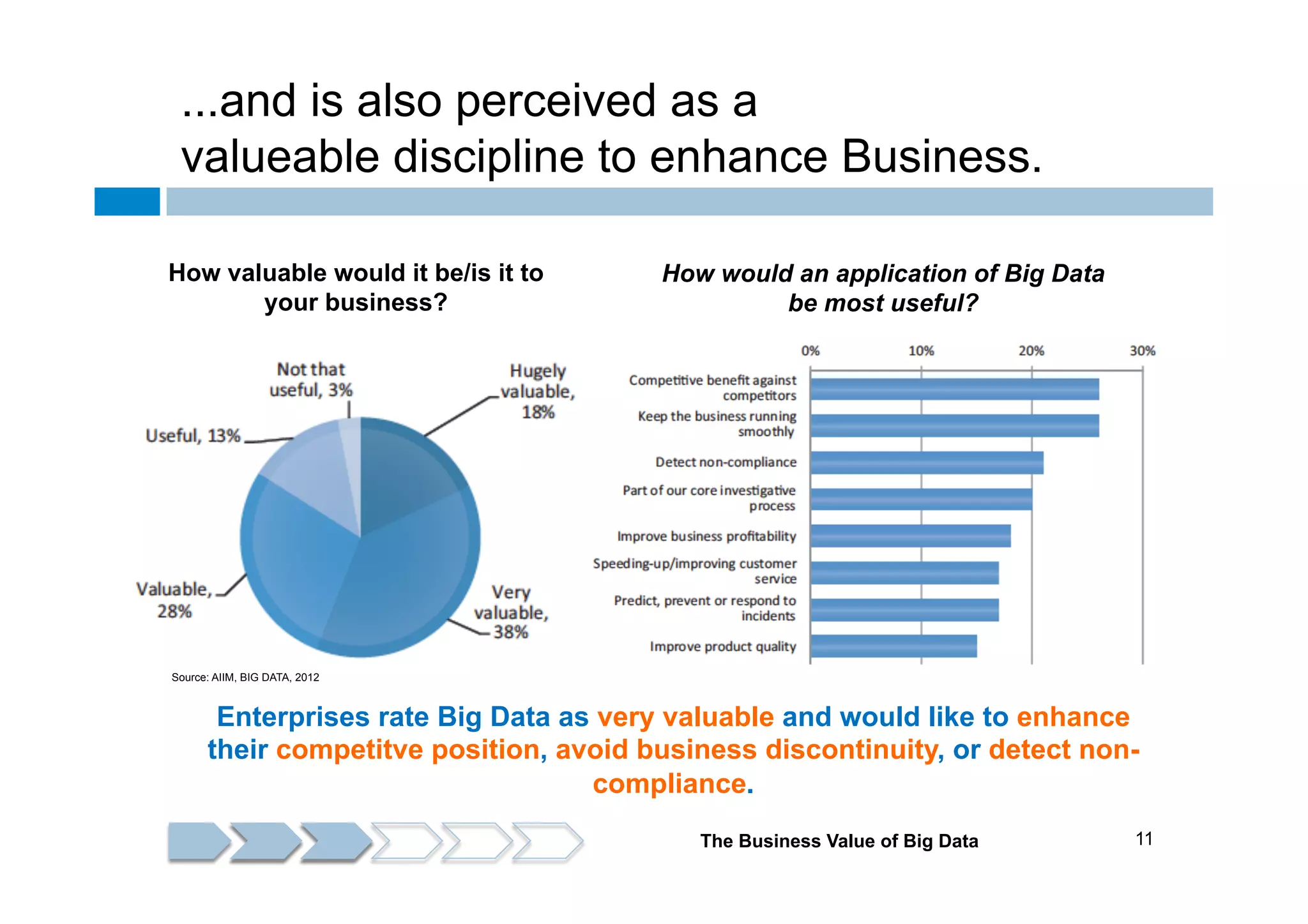
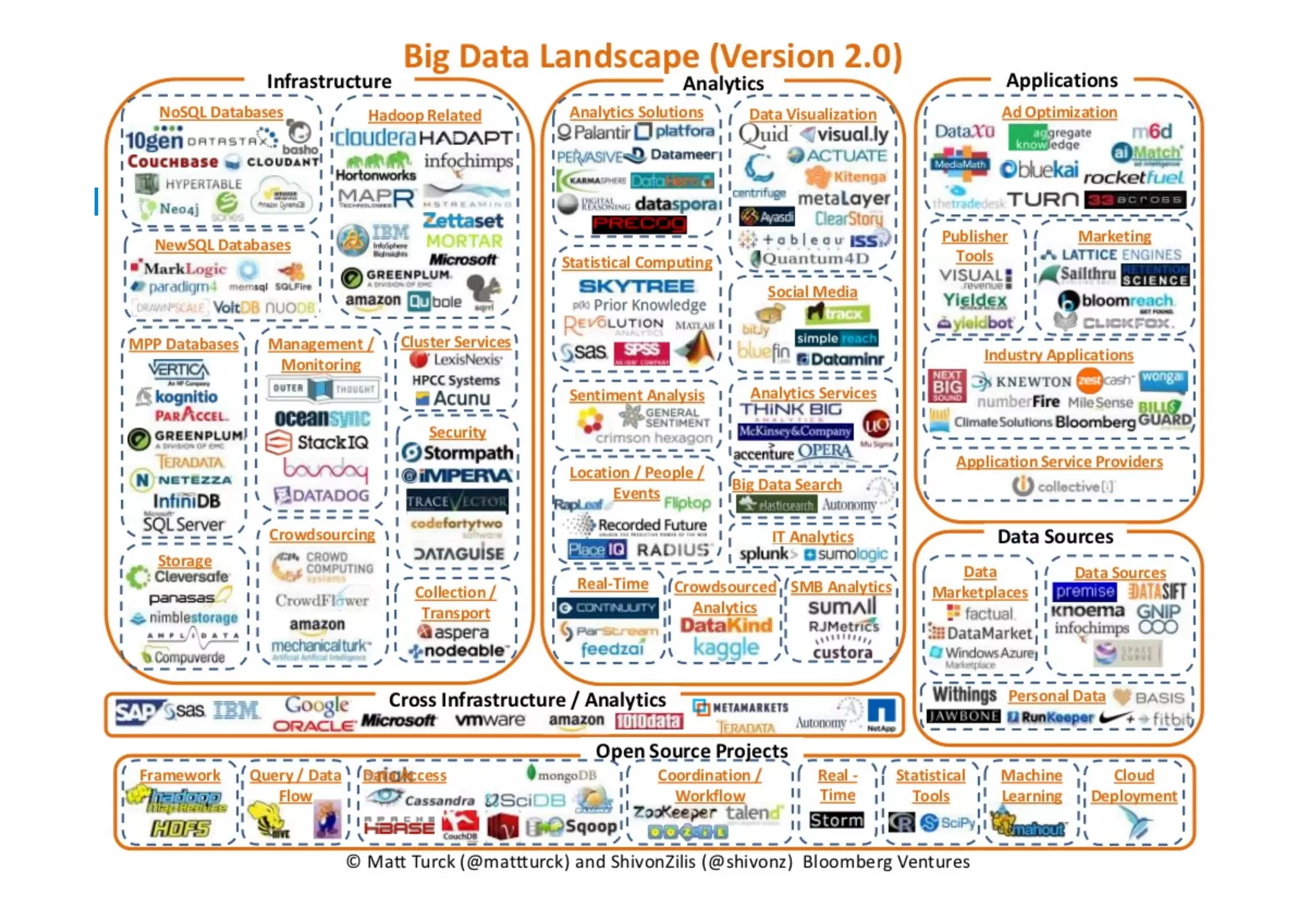
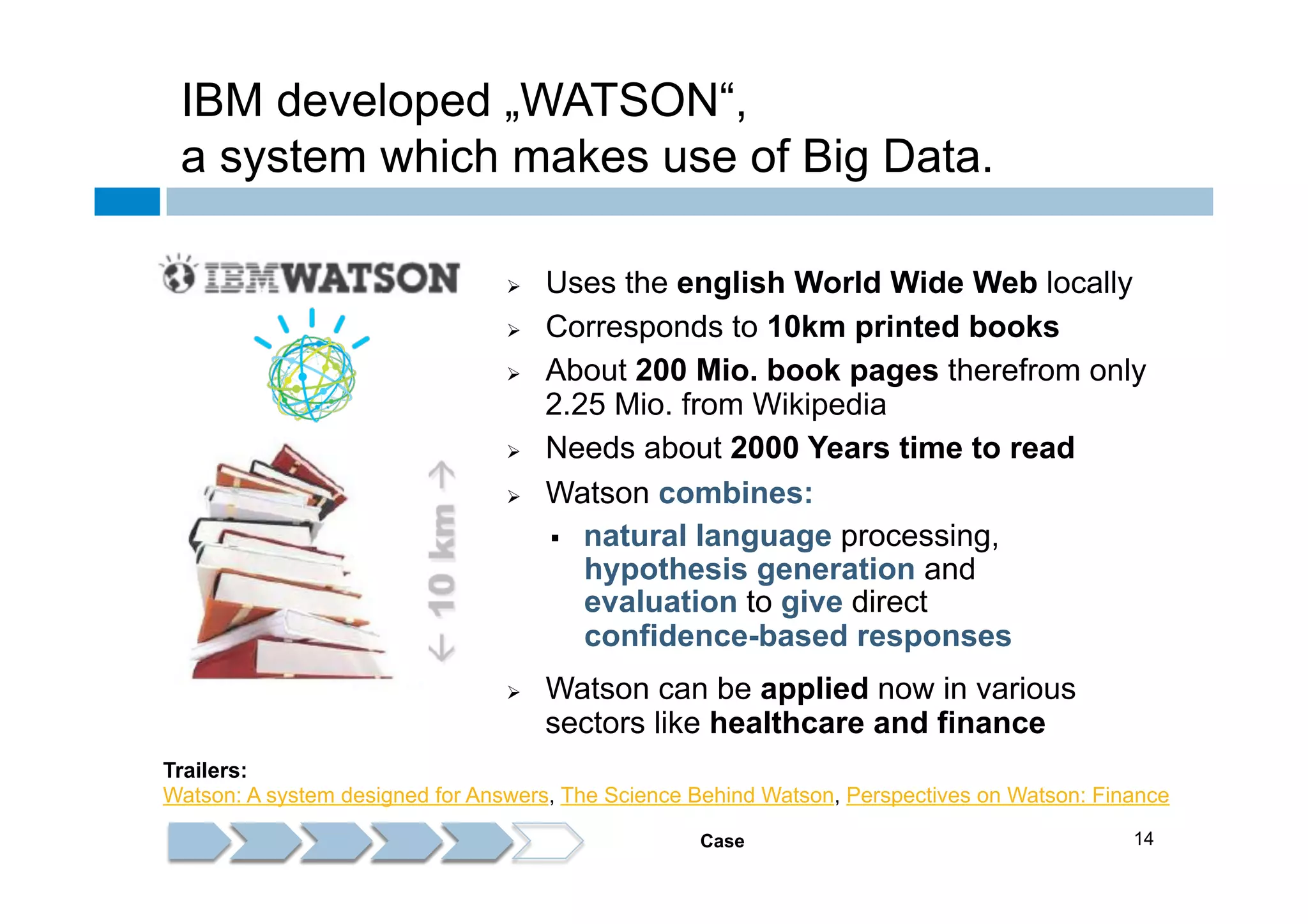
The document discusses the emergence and implications of big data, characterized by the three V's: volume, variety, and velocity. It highlights the potential benefits of big data for businesses across various sectors, including improved market positioning and operational efficiency, while also addressing challenges such as data loss and security. Furthermore, it emphasizes the significance of systems like IBM's Watson that utilize big data to enhance decision-making and generate valuable insights.