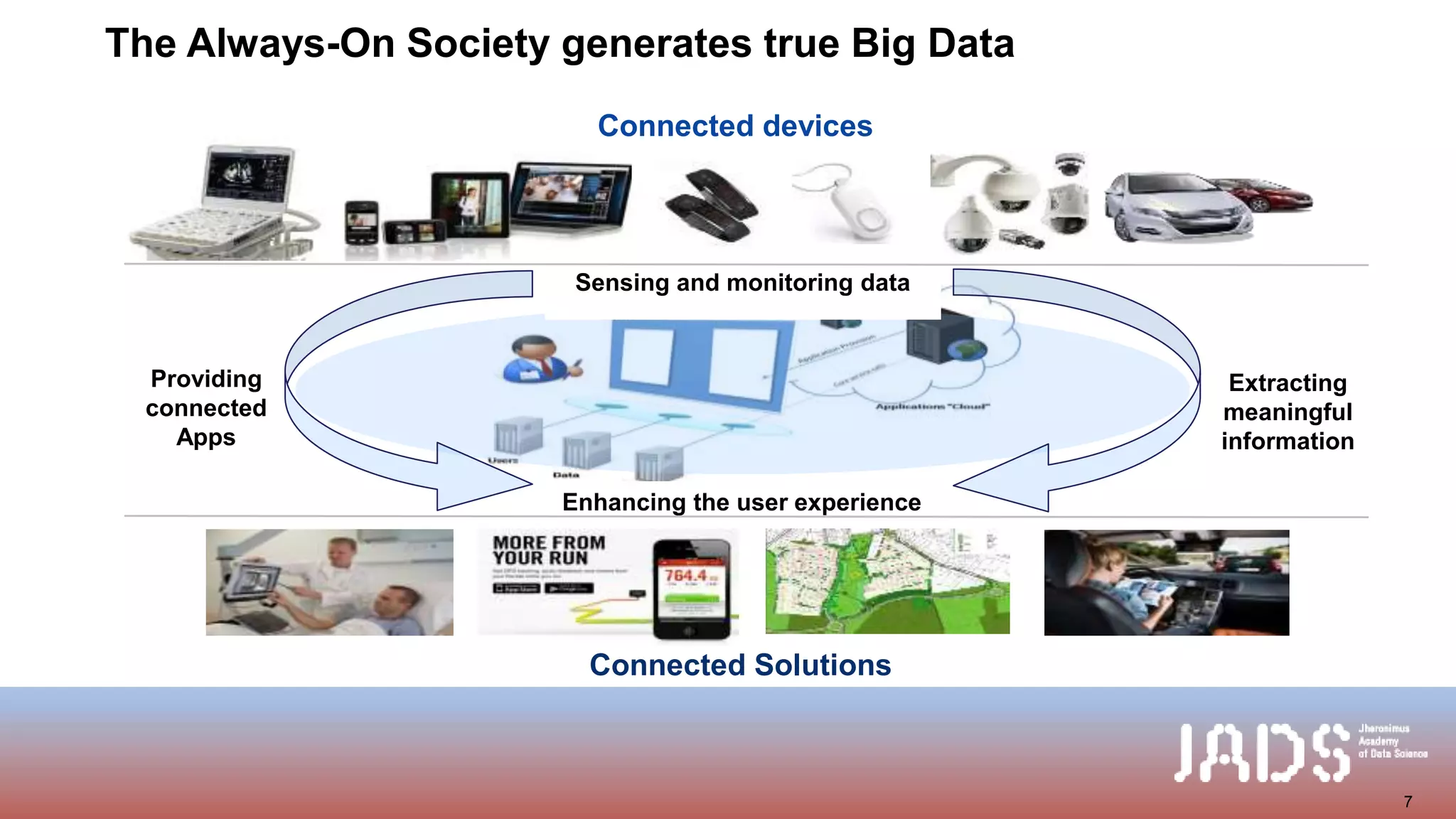
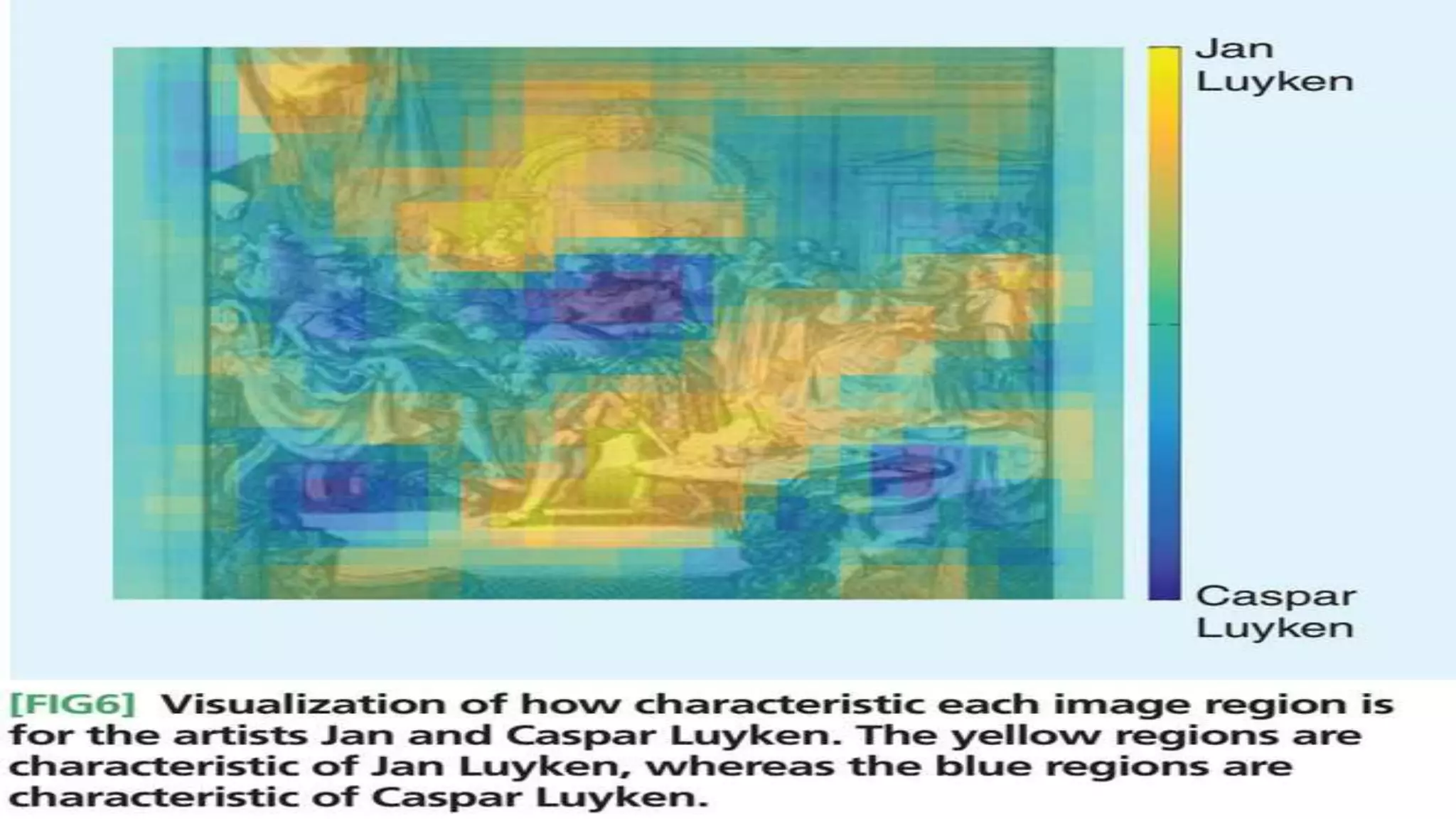
The document discusses creating value from data and overcoming hype around data science. It summarizes that data science has the potential to create value through customer insights, improved processes, and new products, but realizing this value is challenging. Three key challenges are 1) extracting meaningful information from data, 2) bringing business and IT together in joint data science programs and organizations, and 3) developing data skills and an organizational culture that supports data-driven decision making. Overcoming these challenges is necessary to build mature data science capabilities and unlock the full value of data.

![CONTENT
• The disruptive force called data science
• Cool examples (Minimal)
• JADS – Bringing business and IT together
• The Graduate School Mariënburg – Data, Entrepreneurship & Innovation
• Unlocking the Value of Data Science – The Data Driven Organization
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-3-2048.jpg)
![The Usual Story
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-4-2048.jpg)

![The Datafication era started in the early 1800’s
Mathew Fontaine Maury, Virginia 1806-1873Florence Nightingale , London 1820-1910 [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-6-2048.jpg)




![The vision is clear: data is the new oil water
[12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-12-2048.jpg)
![[13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-13-2048.jpg)









![Education: nine data science programs offered at three locations
Graduate School Den Bosch
Joint Bachelor Data Science
2000
Students
[25]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-25-2048.jpg)
![Our Capability Framework
Data Science
Research Meth
Computer Science
Data
Technologies
Data
Visualization Mathematics Statistics
Legal
(Privacy, IP) Ethical
Smart Industries
Finance
Analytics
Smart
Cities
HR & Org
Analytics
Other
TiU & TU/e
Domains
(e.g Legal
Analytics)
Start-up &
Scale-ups
Digital
Transformation
Creativity &
Innovation
Entrepreneurial
Marketing
Entrepreneurial
Finance
EthicalHTI
Artificial
Intelligence
= basic technical skills = basic science skills = entrepreneurial skills = domain specific skills= cognitive skills
Marketing &
Branding
Health
Analytics
[26]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-26-2048.jpg)
![Data Innovation & Data Entrepreneurship
Transforming data into value through analysis and visualization
Research: we will have one generic research theme …
[27]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-27-2048.jpg)
![… and six dedicated research themes
Branding and marketing
Analyzing customer behavior and
mapping needs on business
propositions.
Productivity and maintenance
Monitoring performance remotely
and enabling long-distance control
and maintenance.
Personal care and wellbeing
Monitoring non-intrusively
biomarkers and body functions and
feeding back information.
Finance and insurance
Developing data driven options for
innovative financial and insurance
related business improvements.
City management and control
Enabling adaptive public space
support by urban service
management and commissioning.
Agro, food, and life science
Providing decision support by
correlating information from different life-
science related sources. [28]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-28-2048.jpg)
![Relevance: Intense collaboration with industry in education and research
Ambition & Quality: world class staff & students to make an impact
Multi-disciplinary: Mixing business and IT to drive innovation
Novelty: educational programs are newly designed using DS design criteria
Size: 2000 students in various programs with 3 research centers
Five unique elements of our proposition
[29]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-29-2048.jpg)


![Creating (societal/commercial) value with data
[32]
Data
Science
JADS
Data driven organizations
and entrepreneurial
disruption
Data IP, Algorithmic
Transparency, Data
Portability
Human Computer
Decision Making
Society
Business
Data
Technology
How to
create
value?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-32-2048.jpg)

![[34]
Entrepreneurship = the art & science of
spotting and grabbing opportunities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-34-2048.jpg)

![Unlocking Value out of Data
• The triple pathway to unlocking Data Value
• Volume, Variety, Velocity, Veracity and Value
• The Process of Data Science
• The Business Models of Data Science
• The Organization & Teams of Data Science
• The Difficulties of building a Data Science Capability
[36]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-36-2048.jpg)
![The Triple Pathway to Data Value
Customer
Insights
Process
Information
Product
Innovation
[37]
• There are various ways to extract
value from Data:
• Improved customer relations
• Effective and efficient processes
• New products and services
• The current focus is mainly on
improving customer understanding
A
BC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-37-2048.jpg)
![[38]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-38-2048.jpg)
![The Potential Value of Big Data is determined by it’s uniqueness
Value
Volume
Variety Veracity
Velocity
[39]
+/-
+
-
+/-
VRIS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-39-2048.jpg)
![The High-Level Process of Data Science
Data
Engineering
Data Mining
& Analytics
Data
Decision
Making &
Visualization
Data Entre-
preneurship
[40]
Law &
Ethics
• Data value can be created in every
phase of the data value process
• Data value can be destroyed in
every phase of the data value
process
• Without potential value, there is no
way value can be created](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-40-2048.jpg)
![[41]
INDUSTRY CHANGE AHEAD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-41-2048.jpg)
![The Changing Data value Process
[42]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-42-2048.jpg)
![The Fit between Business Model & Product-Market Strategy
[43]
• How to connect with factor and product
markets?
• Which parties to bring together to exploit a
business opportunity, and how to link them to
the focal firm to enable transactions (i.e.,
what exchange mechanisms to adopt?)
• What information or goods to exchange
among the parties, and what resources and
capabilities to deploy to enable the
exchanges?
• How to control the transactions between the
parties, and what incentives to adopt for the
parties?
• What positioning to adopt against rivals
• What kind of generic strategy to adopt (i.e., cost
leadership and/or differentiation)?
• When to enter the market?
• What data products/data services to sell?*
• What prices to set?
• What customers to serve?*
• Which geographic markets to address?*
Business Model Product Market Strategy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-43-2048.jpg)
![Examples of data science business models
[44]
Premium Freemium Open Source
Razor and
Blades
End users are offered a
service or product in
exchange for payment.
Basic services or
products are offered free
of charge. Profit is made
by having end users pay
for extended features.
Data are offered for
free through cross
subsidization.
Data sets are stored for free
and accessible to everyone
via (APIs) (‘‘razors’’), while
users are charged as-a-
service (‘‘blades’’).
Demand
Platform
Supply
Platform
Subsidizes
White-Label
Dev
The company provides a
one-stop shop of data
sets. Revenue is made in
exchange for advanced
services and refined data
sets or flows.
Idem, but company get
charged for services
delivered
Data is used as a tool to
attract attention from
customers. The company
expects that the public
will then favor its brand.
A company wants to use
PSI as an attraction tool
but does not have the
competencies required to
do so
Source: Ferro and Osella (2013)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-44-2048.jpg)
![[45]
LOWER TRANSACTION COSTS….
….MORE BUSINESS MODEL LAYERS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-45-2048.jpg)
![[46]
The Mature Data Science Organization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-46-2048.jpg)
![[47]
Data Science is not Business Intelligence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-47-2048.jpg)
![Project Aristotle: Google’s question on how to build teams
Google Myths
[48]
“ Building the best team means combining the
best people”
‘It’s better to put introverts together’’
“Teams are more effective when everyone is friends
away from work”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-48-2048.jpg)
![[49]
Data Science Maturity is generally low
A Data Driven Organization Has:
•Data Technology
•Data Processes
•Data Governance
•Data Skills & Data Culture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-49-2048.jpg)
![[50]
Problems at the end and beginning of the value
chain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jadsarjanvandenborn-160923091818/75/Jads-arjan-van-den-born-50-2048.jpg)
