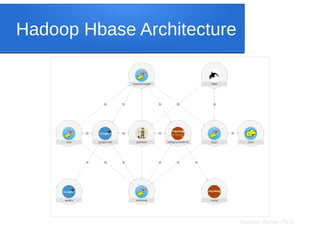
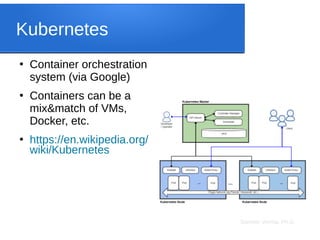
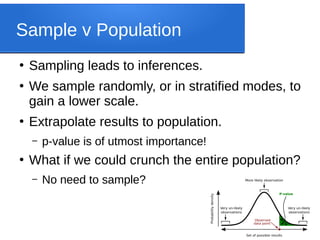
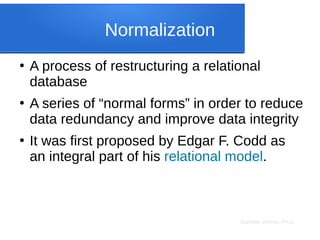
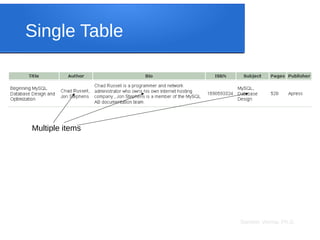
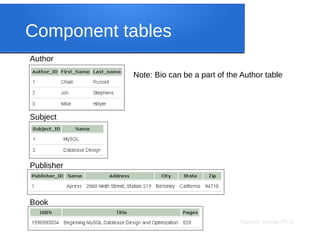
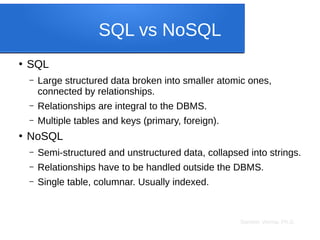
The document discusses big data analytics, focusing on key concepts such as volume, variety, velocity, and veracity of data. It covers data normalization, NoSQL versus SQL databases, and the importance of cloud computing and orchestration tools like Hadoop and Kubernetes in managing big data. Additionally, it highlights trends and methodologies in data handling and processing for effective analysis and reporting.








![Sameer Verma, Ph.D.
JavaScript Object Notation
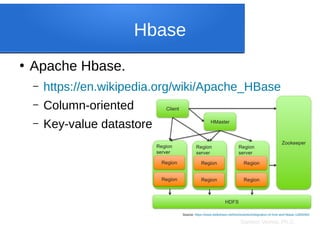
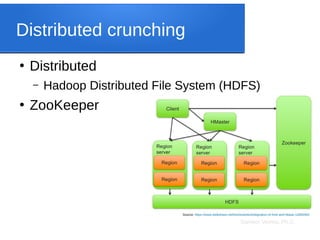
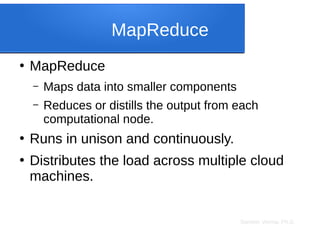
●
JSON or JavaScript Object Notation
{
"Table1": [
{
"id": 0,
"title": "Beginning MySQL Database Design and
Optimization"
},
{
"id": 1,
"firstname": "Jon"
},
{
"id": 2,
"lastname": "Stephens"
}
]
}
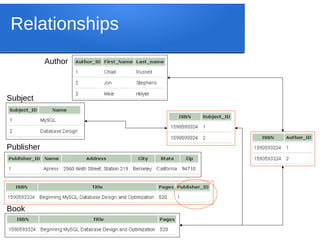
Title First Name Last Name
Beginning
MySQL
Database
Design and
Optimizatio
n
Jon Stephens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/big-data-analytics-tech-220402053835/85/Big-Data-Analytics-Concepts-Technologies-and-Operations-15-320.jpg)


![Sameer Verma, Ph.D.
Column DB
●
A columnar database is a table with one
column (and one more for indexing).
●
Collapse (serialize) multiple “fields” into one
string.
{"Table1": [{"id": 0,"title": "Beginning MySQL Database Design and Optimization"},{"id": 1,"firstname": "Jon"},{"id": 2,"lastname": "Stephens"}]}
Title First Name Last Name
Beginning
MySQL
Database
Design and
Optimization
Jon Stephens becomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/big-data-analytics-tech-220402053835/85/Big-Data-Analytics-Concepts-Technologies-and-Operations-21-320.jpg)