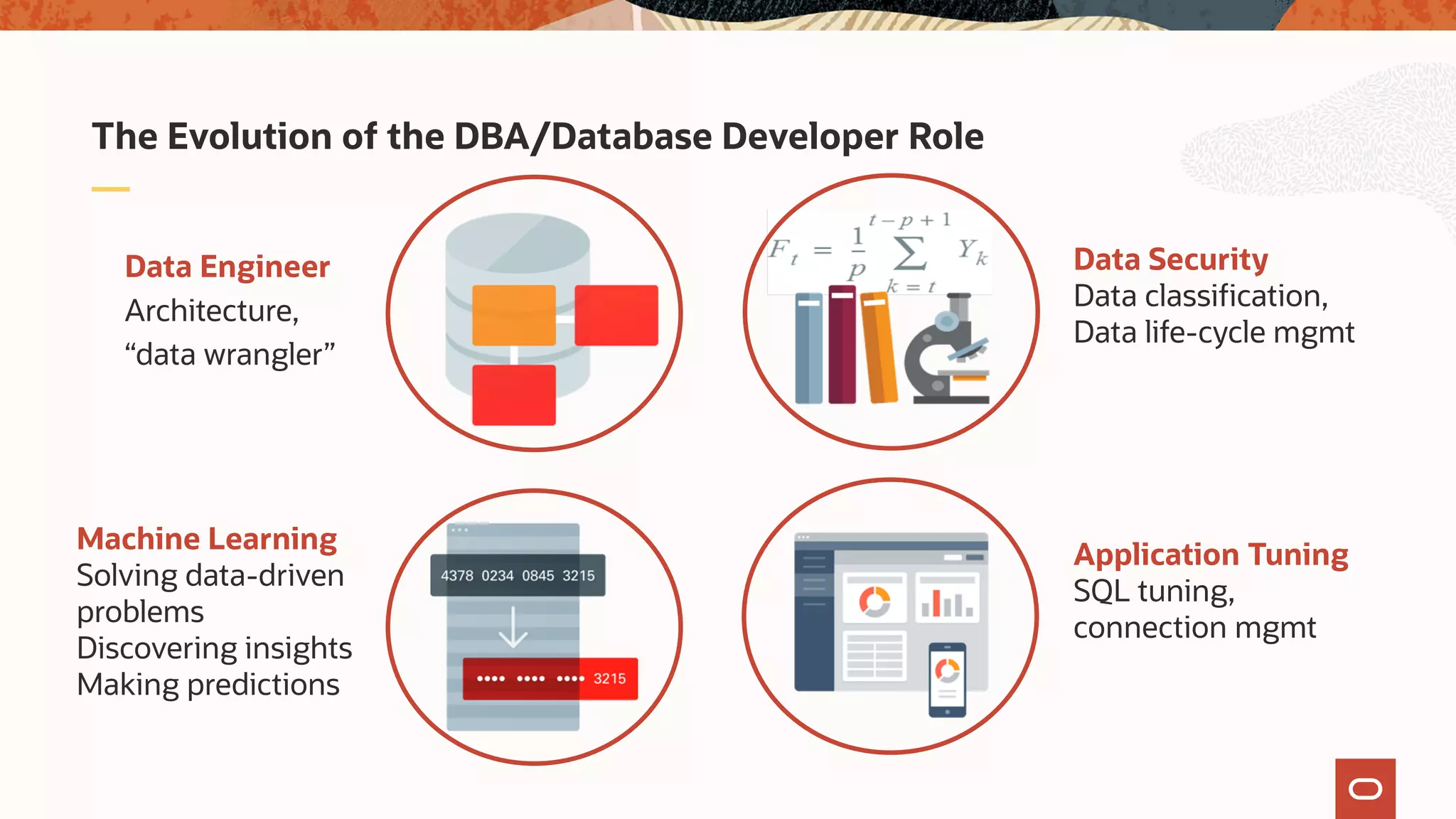
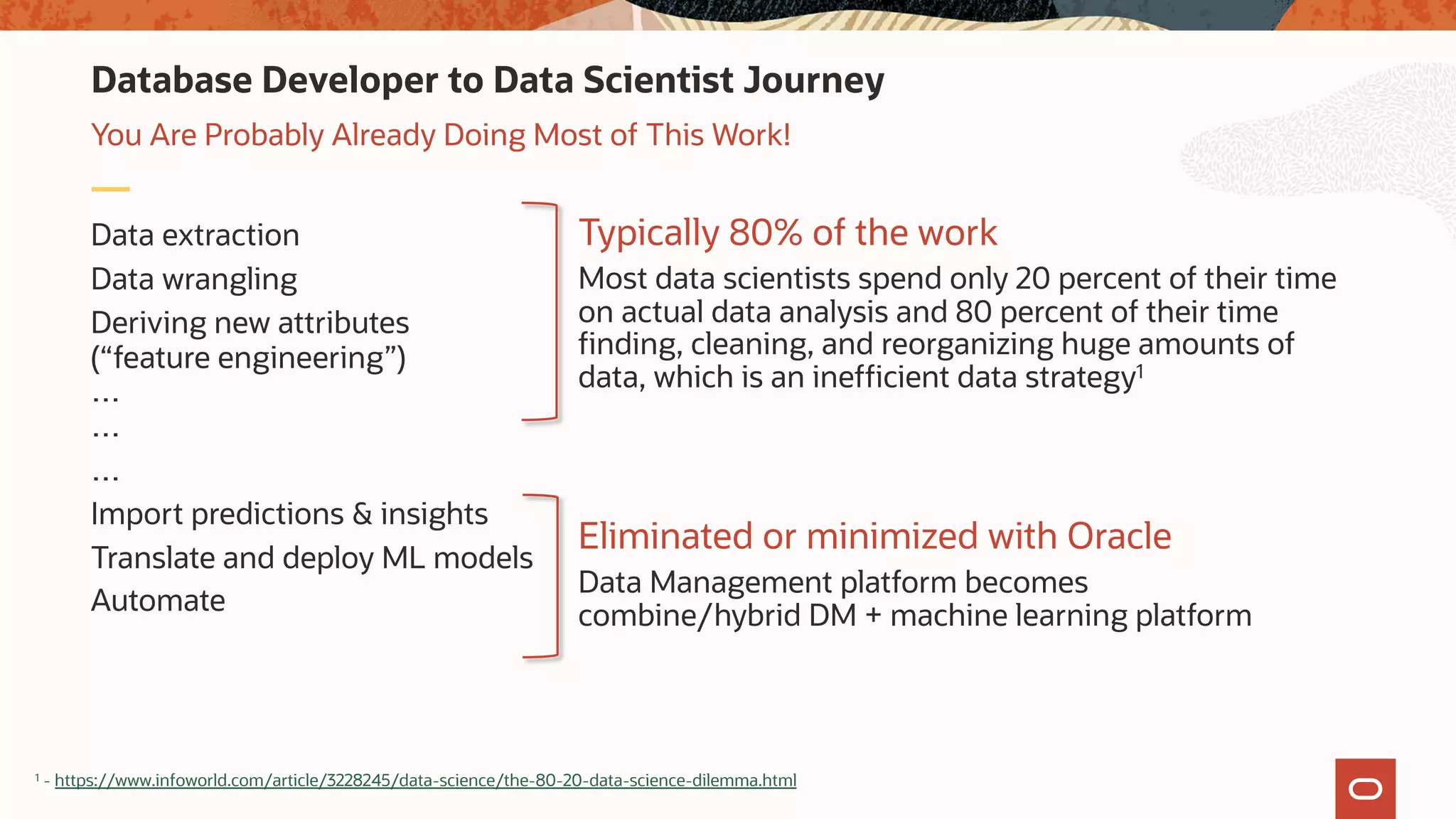
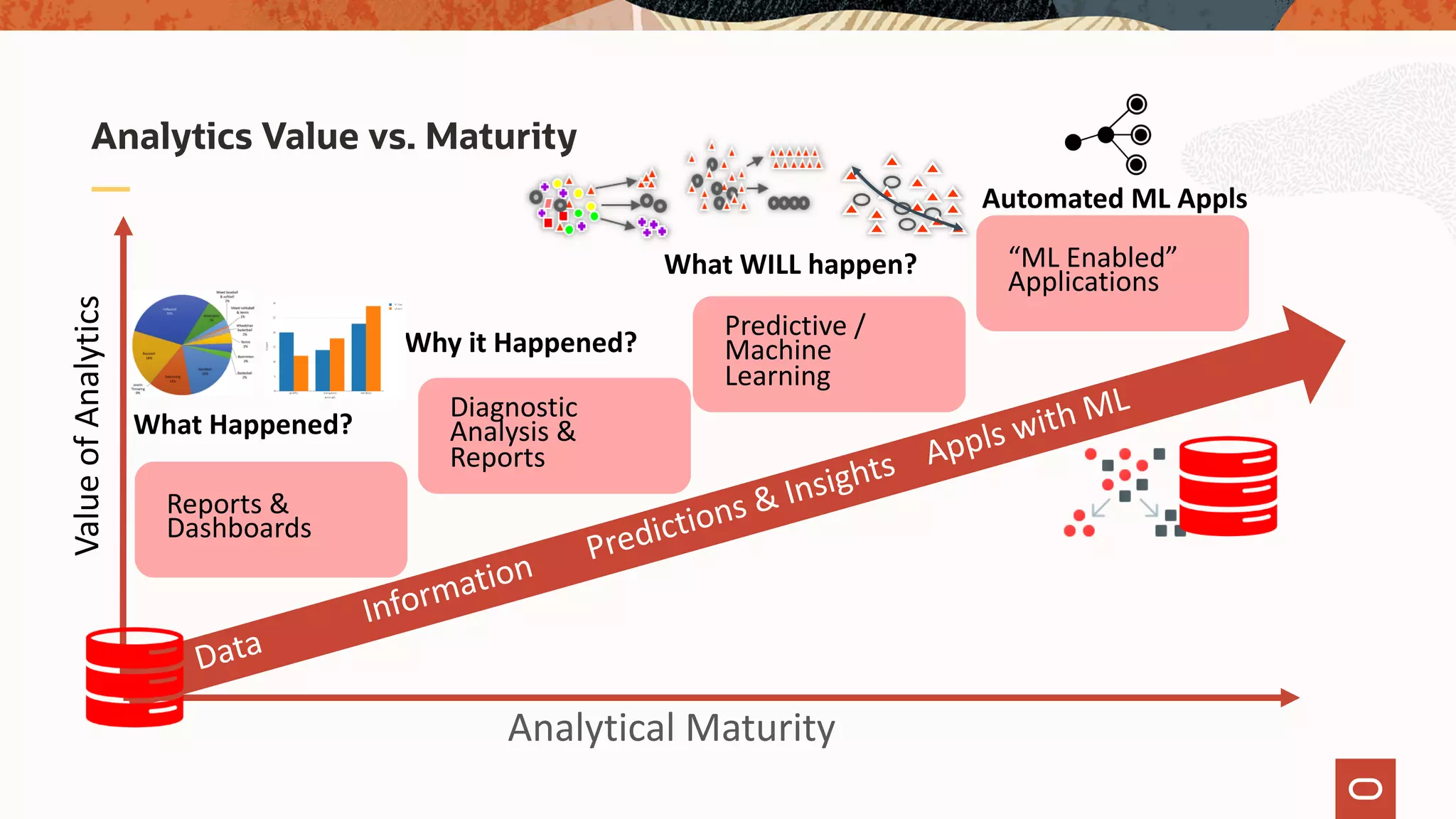
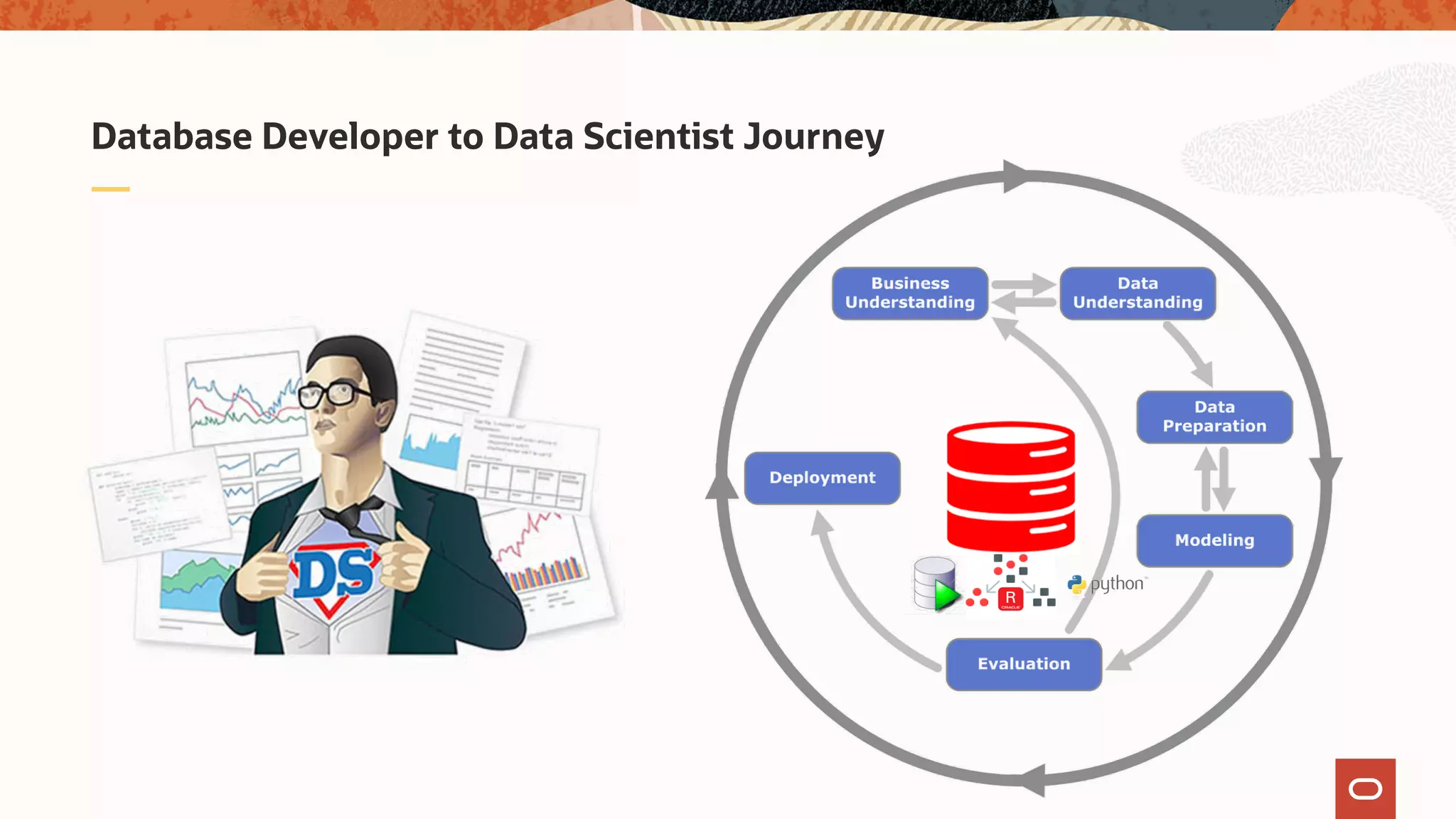
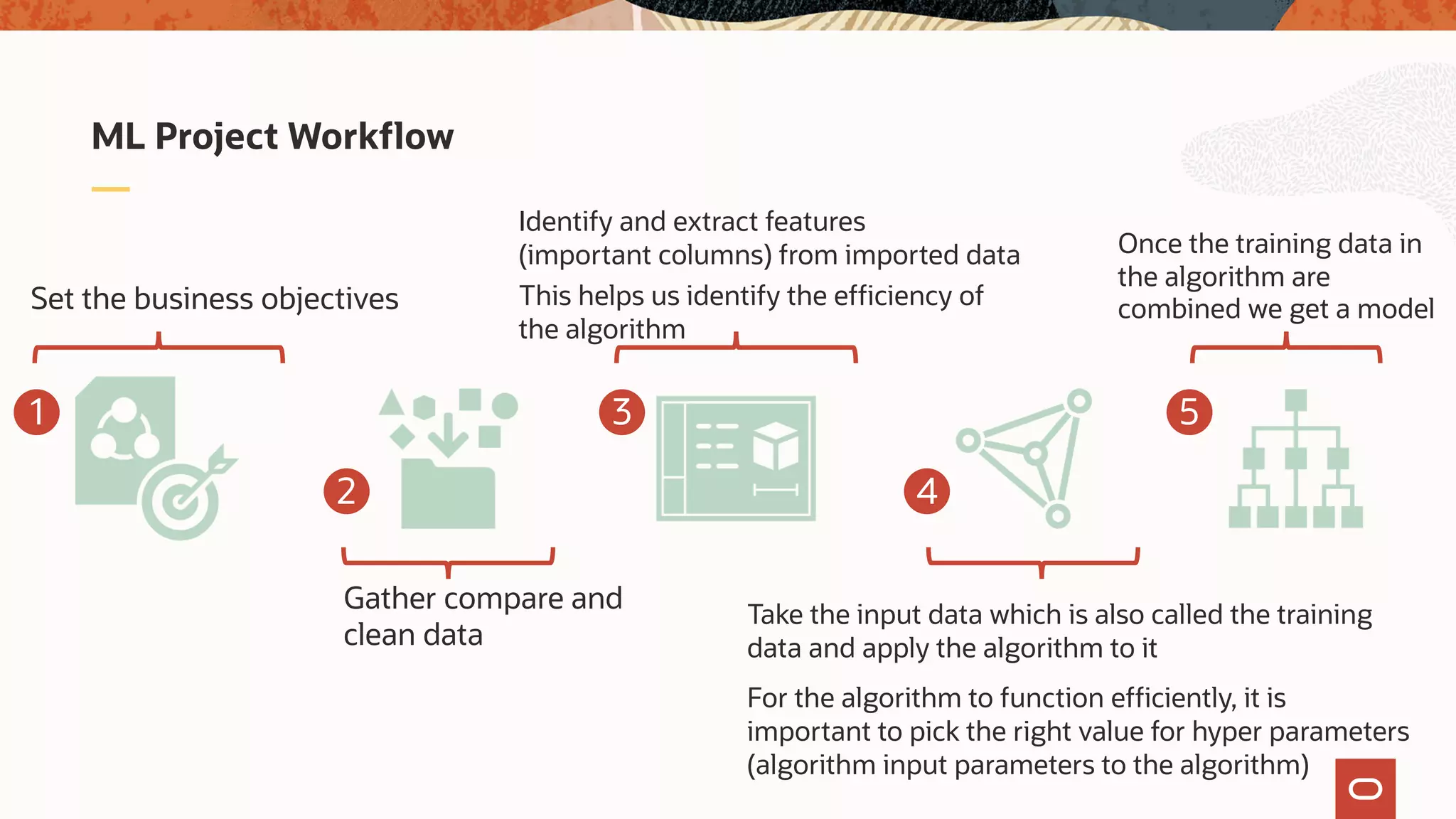
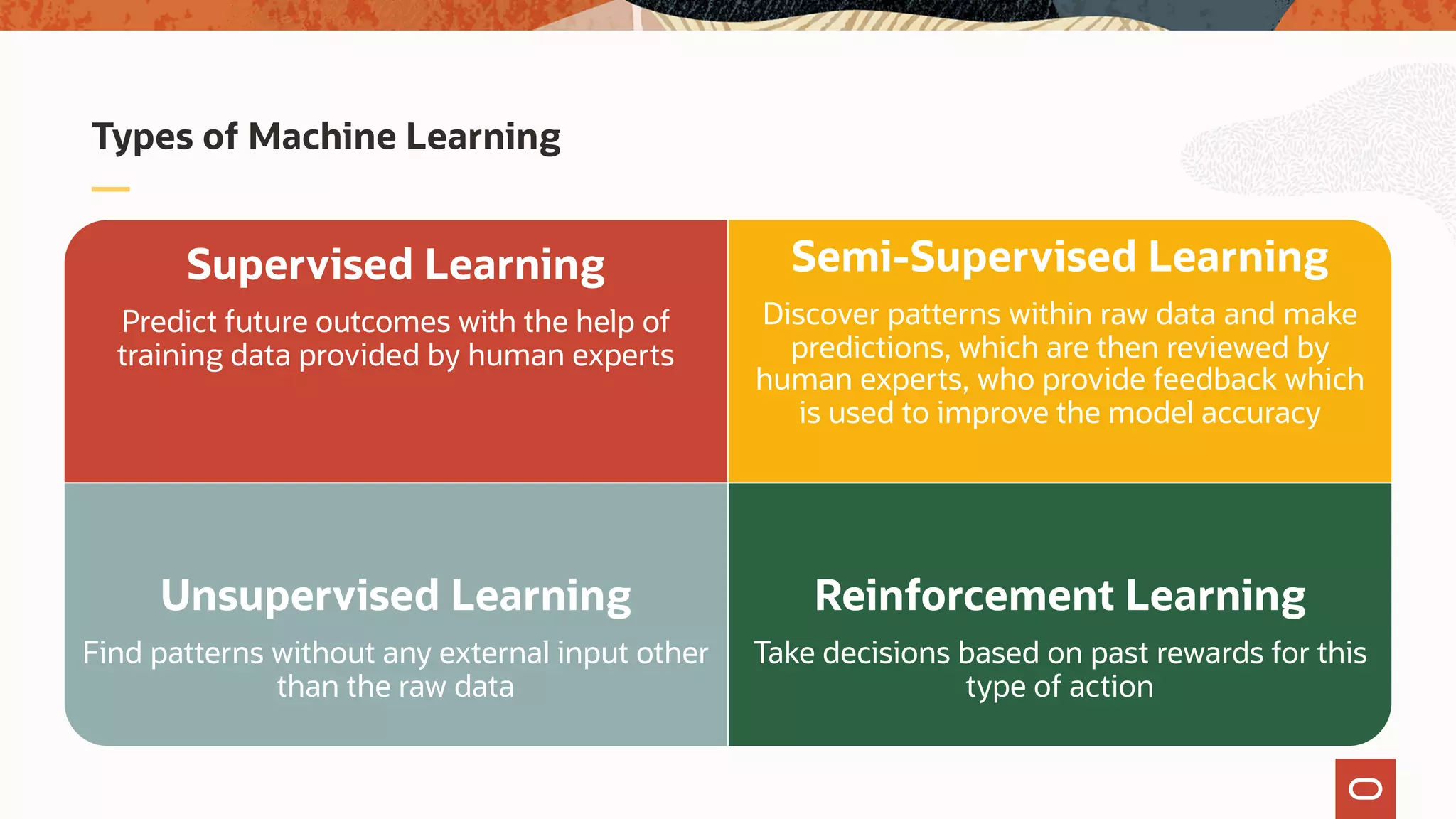
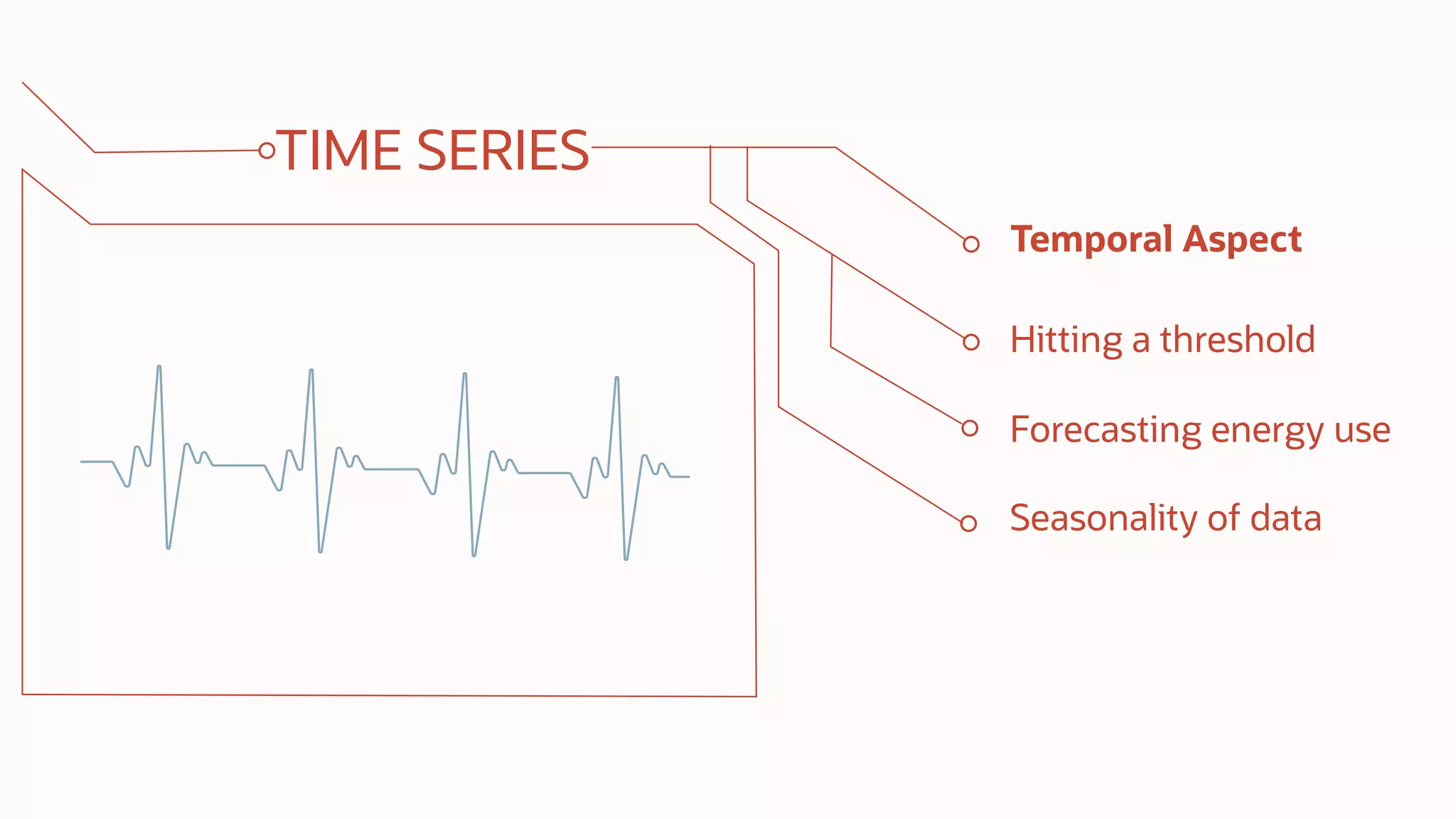
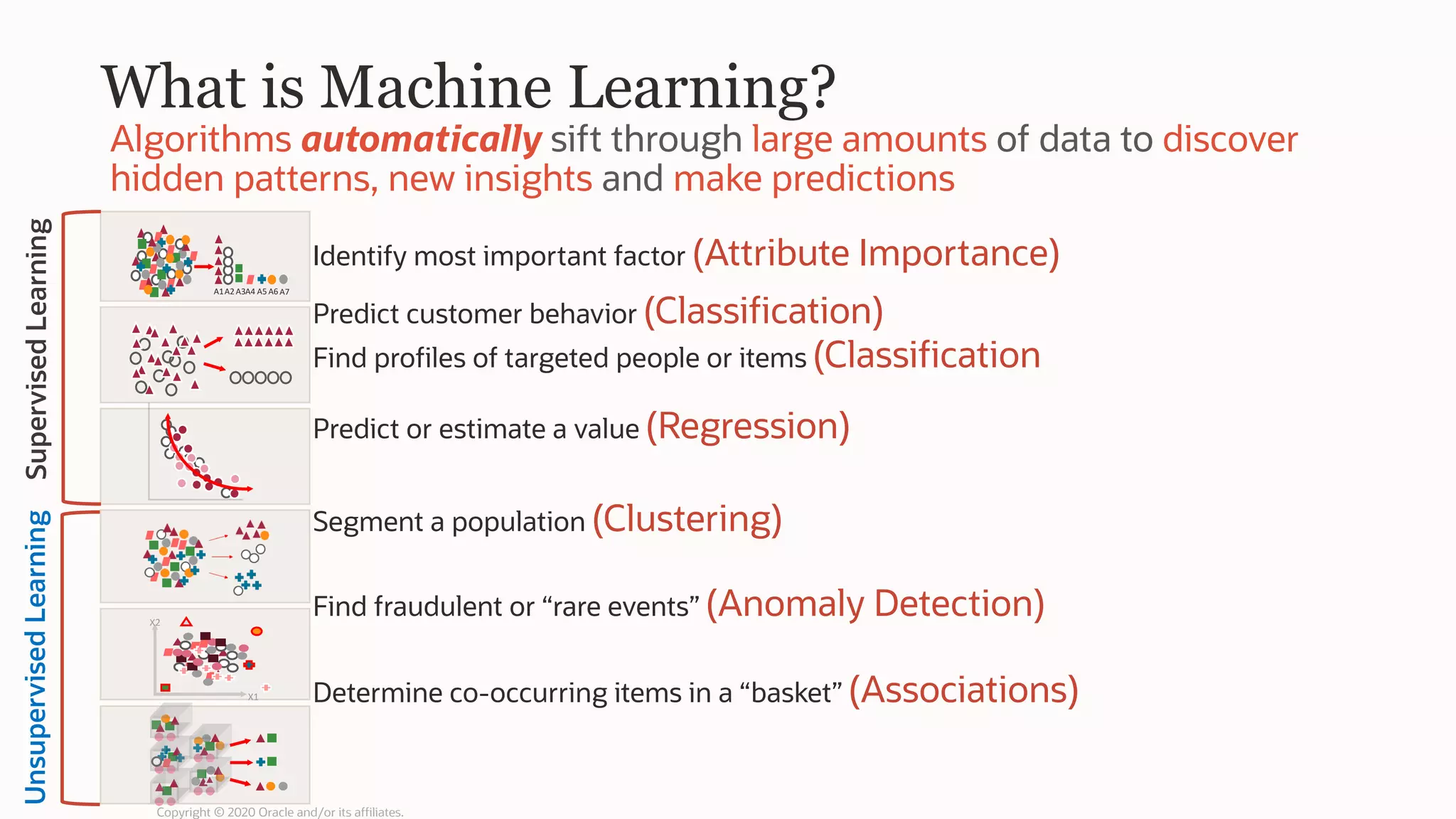
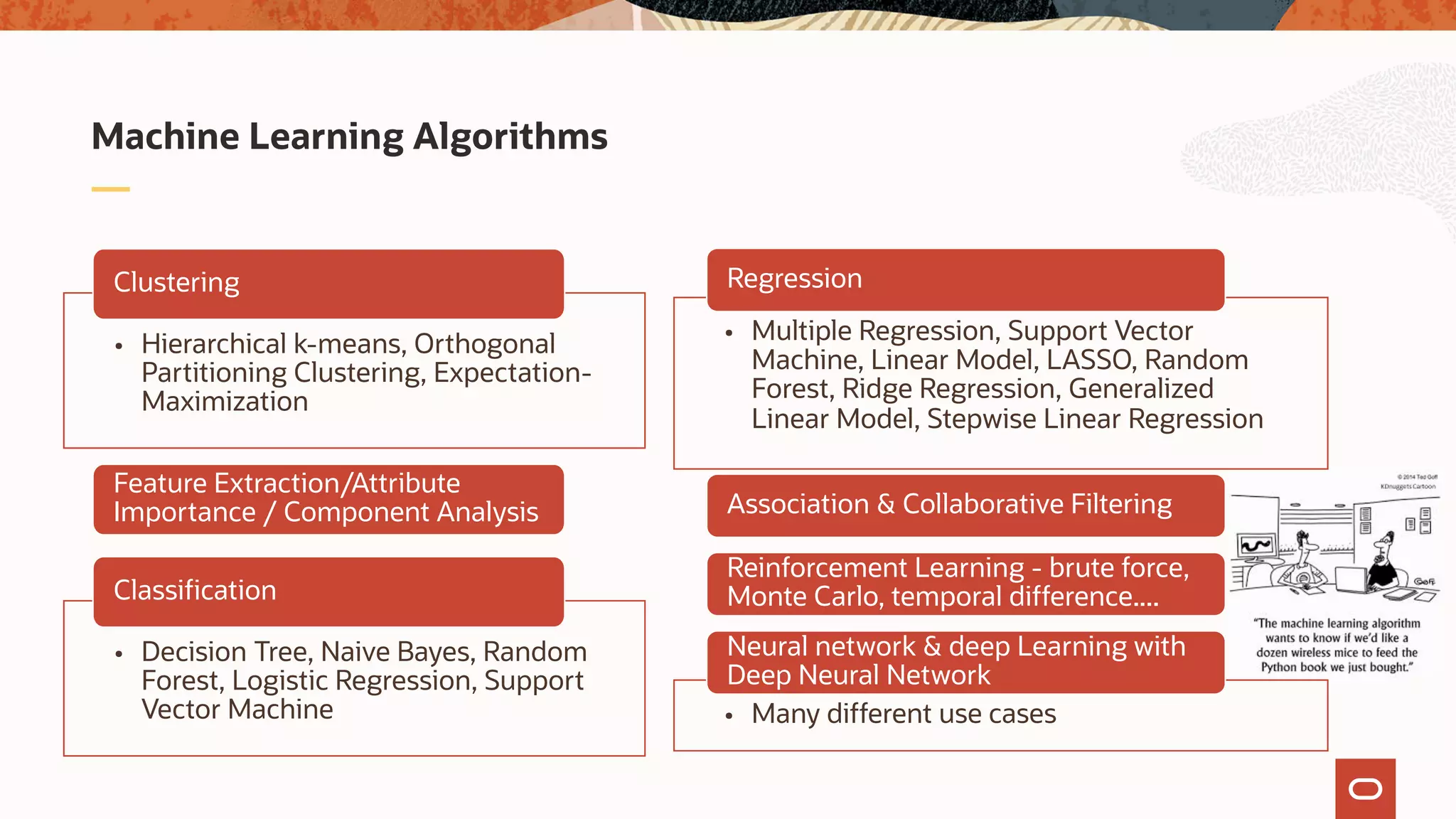
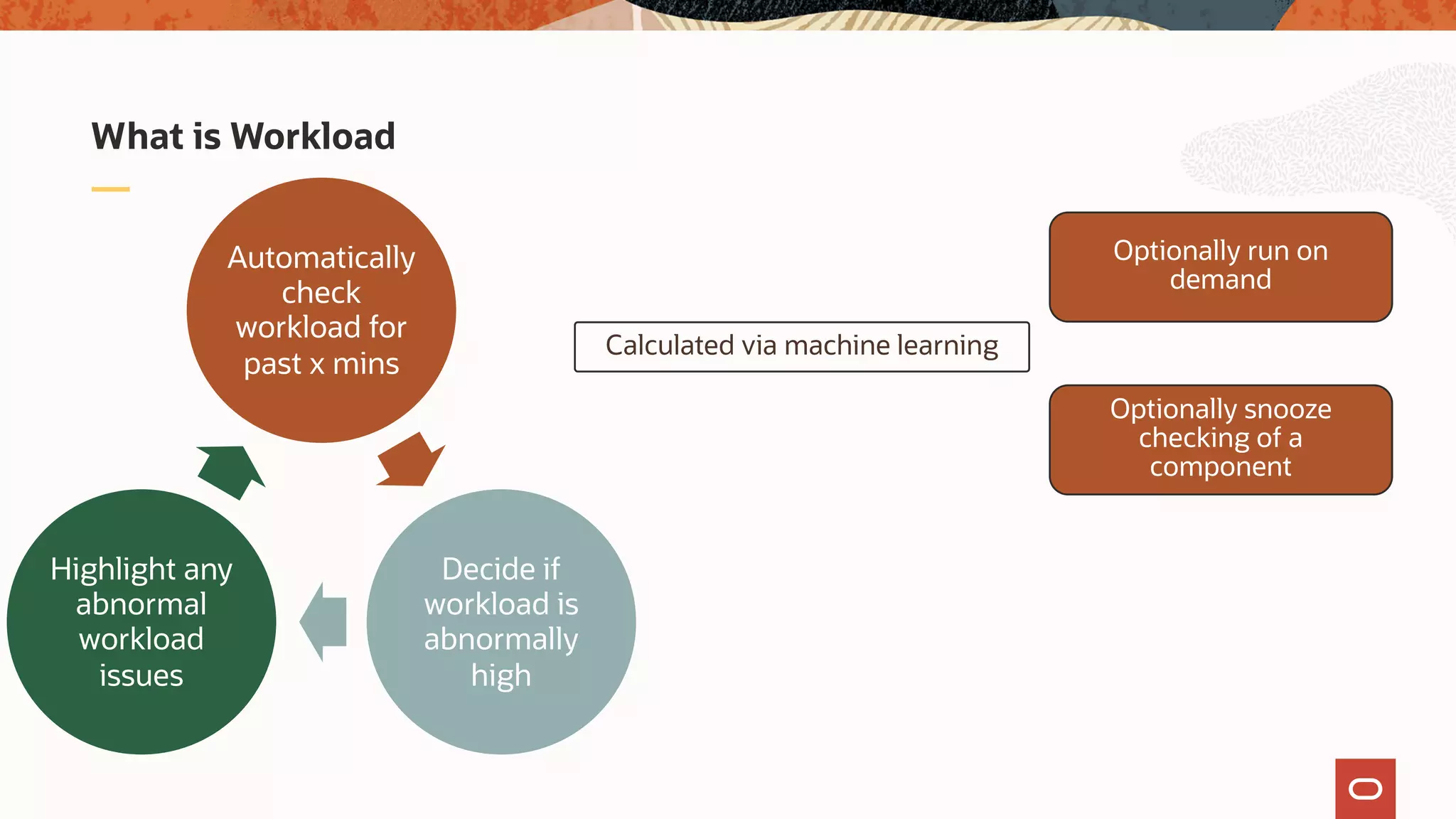
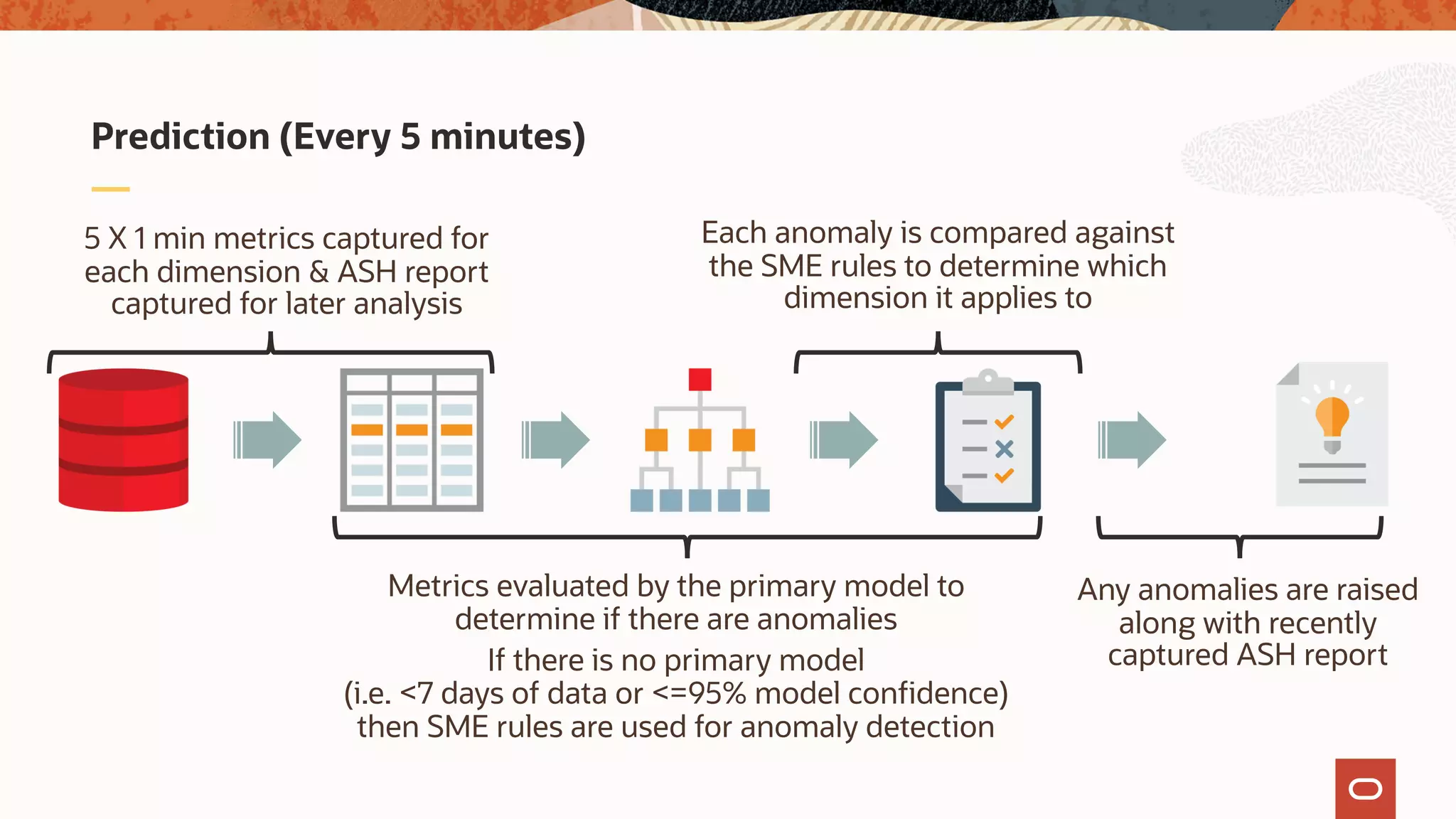
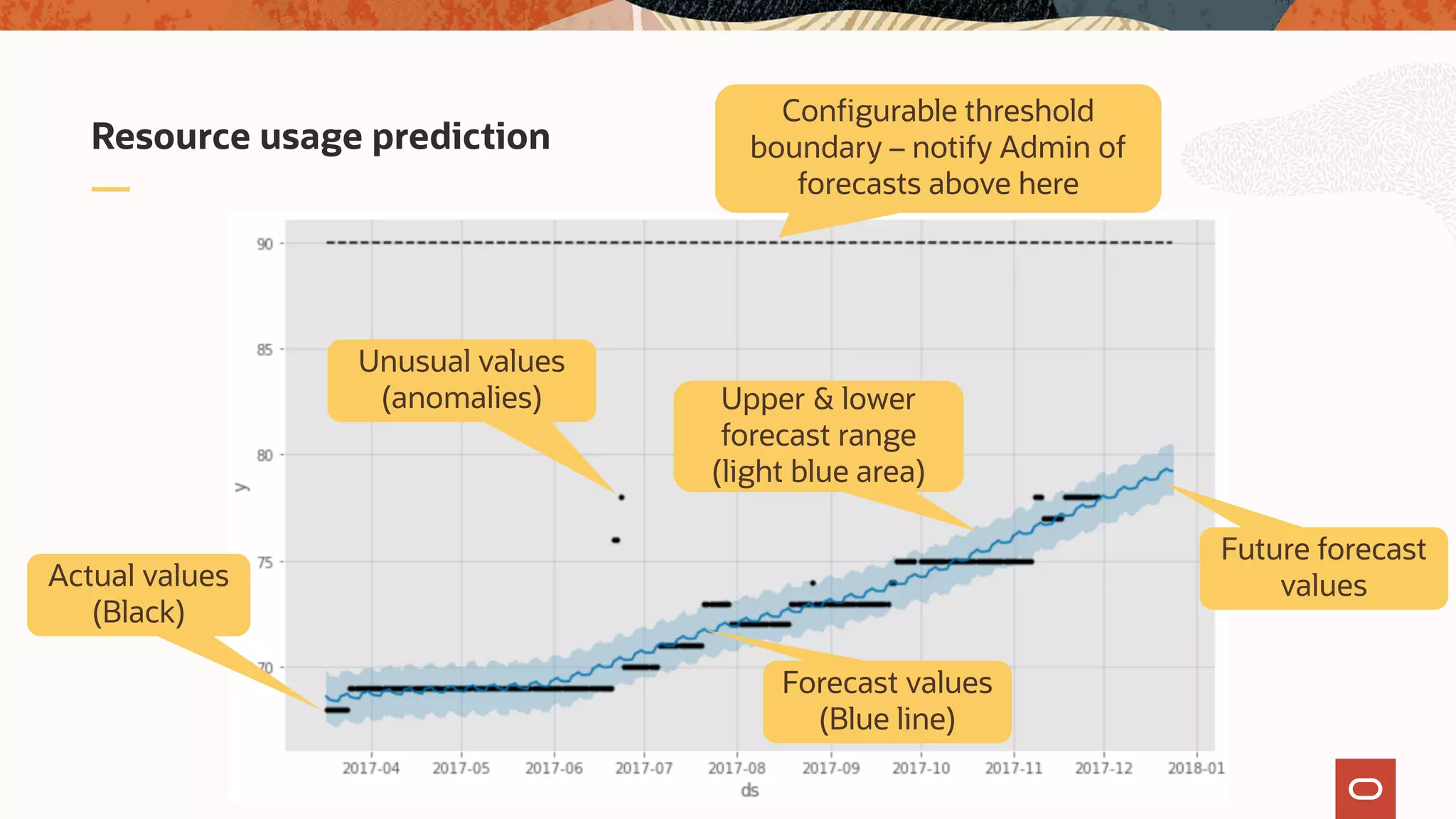
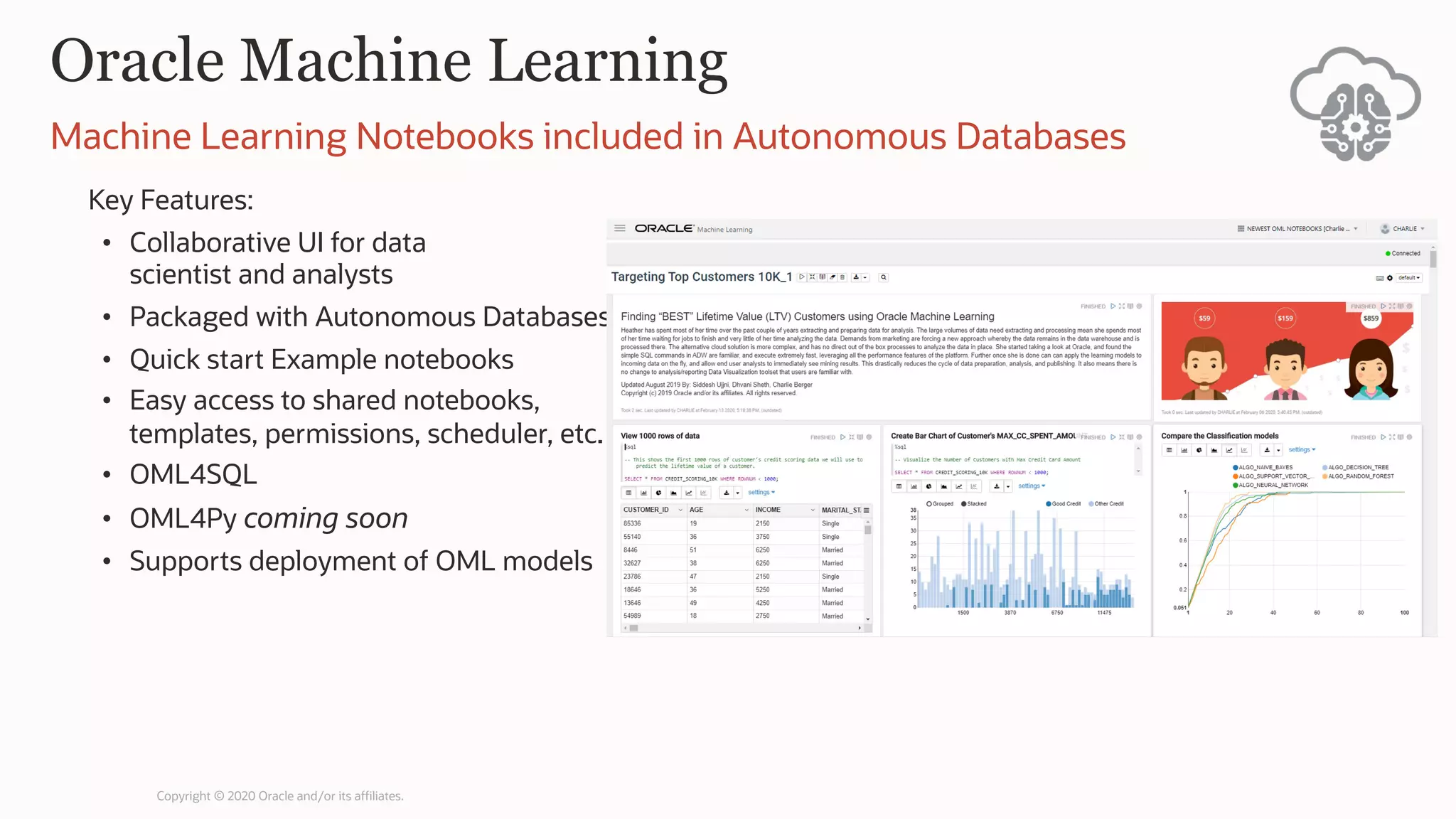
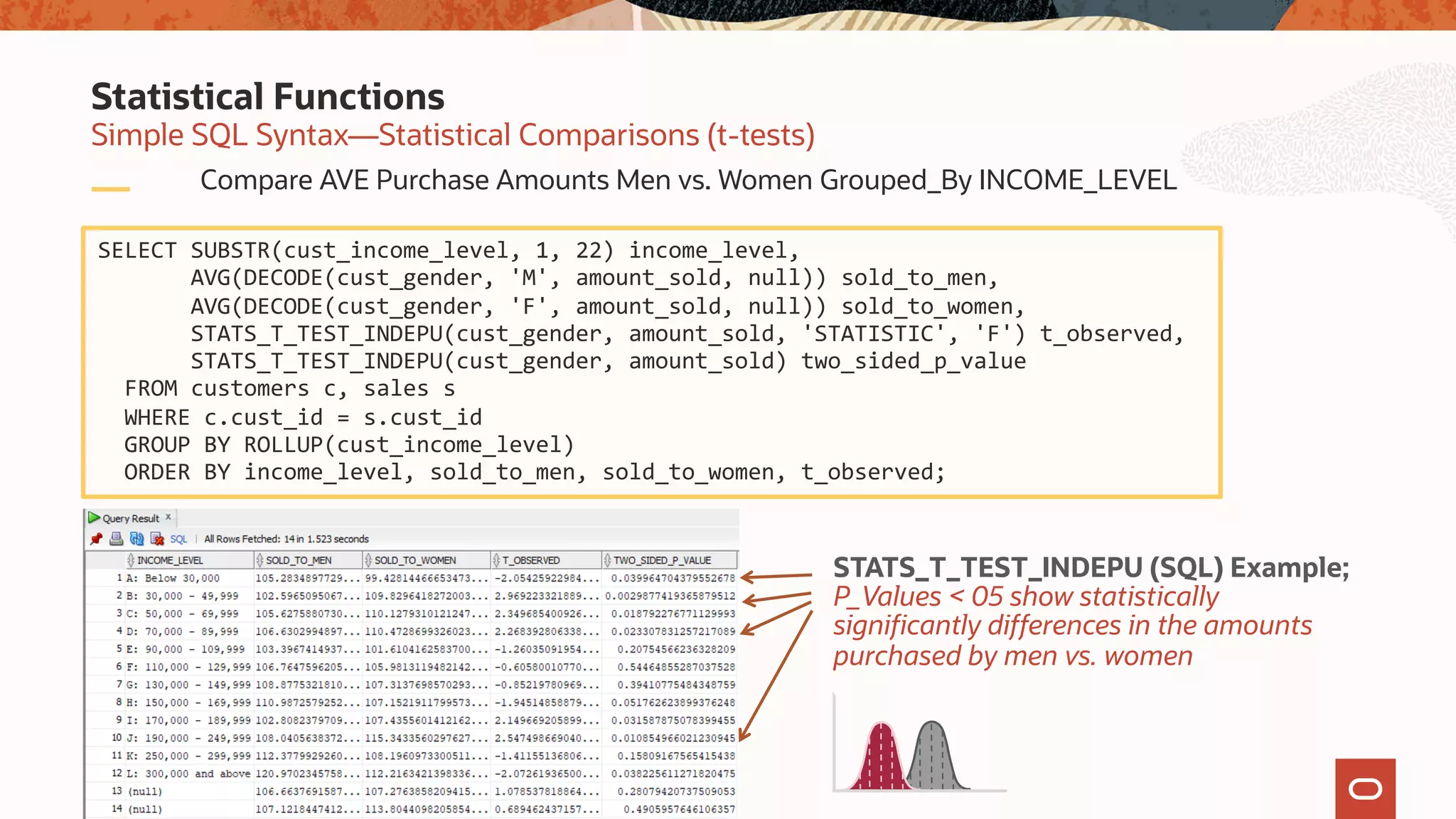
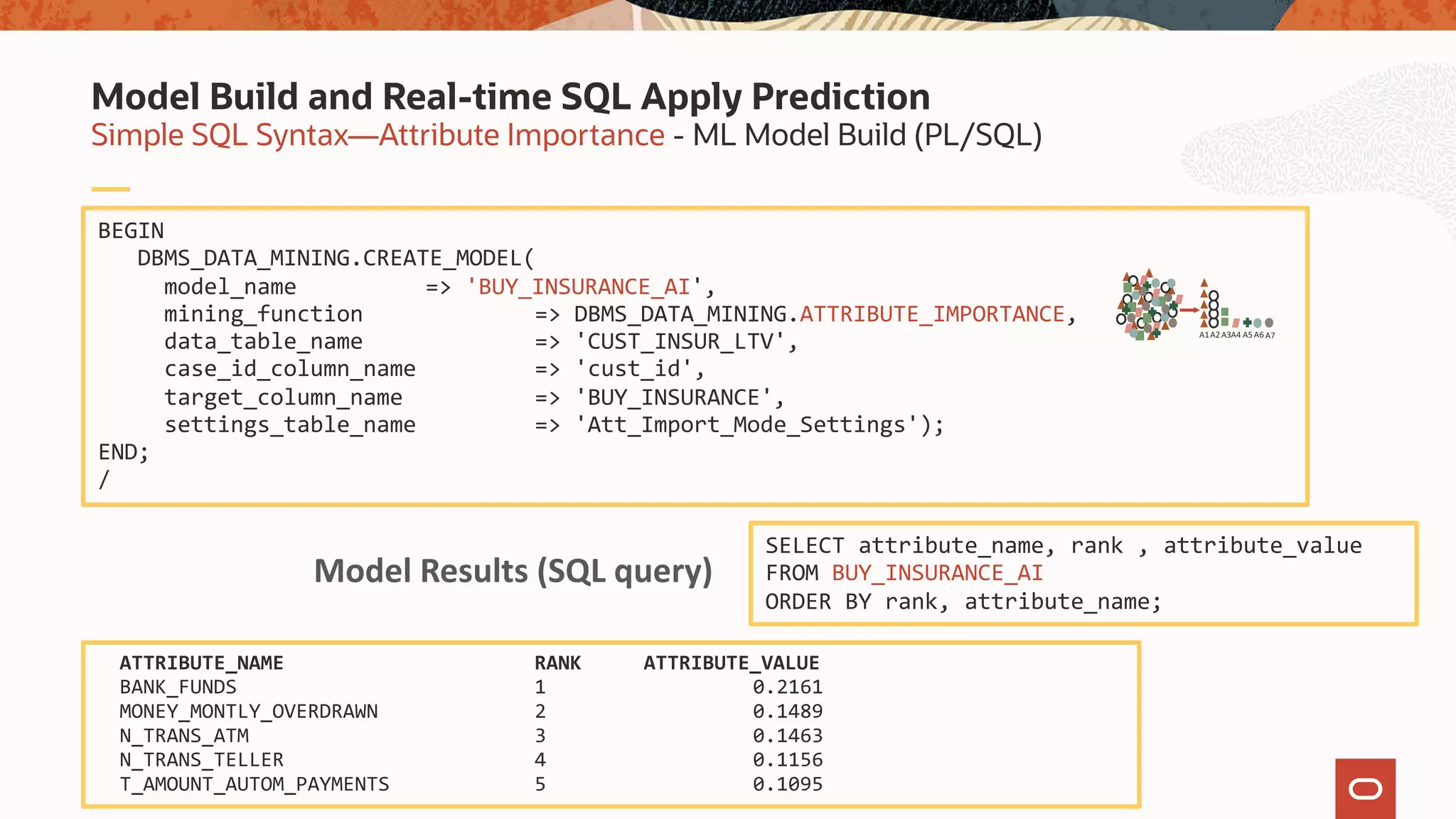
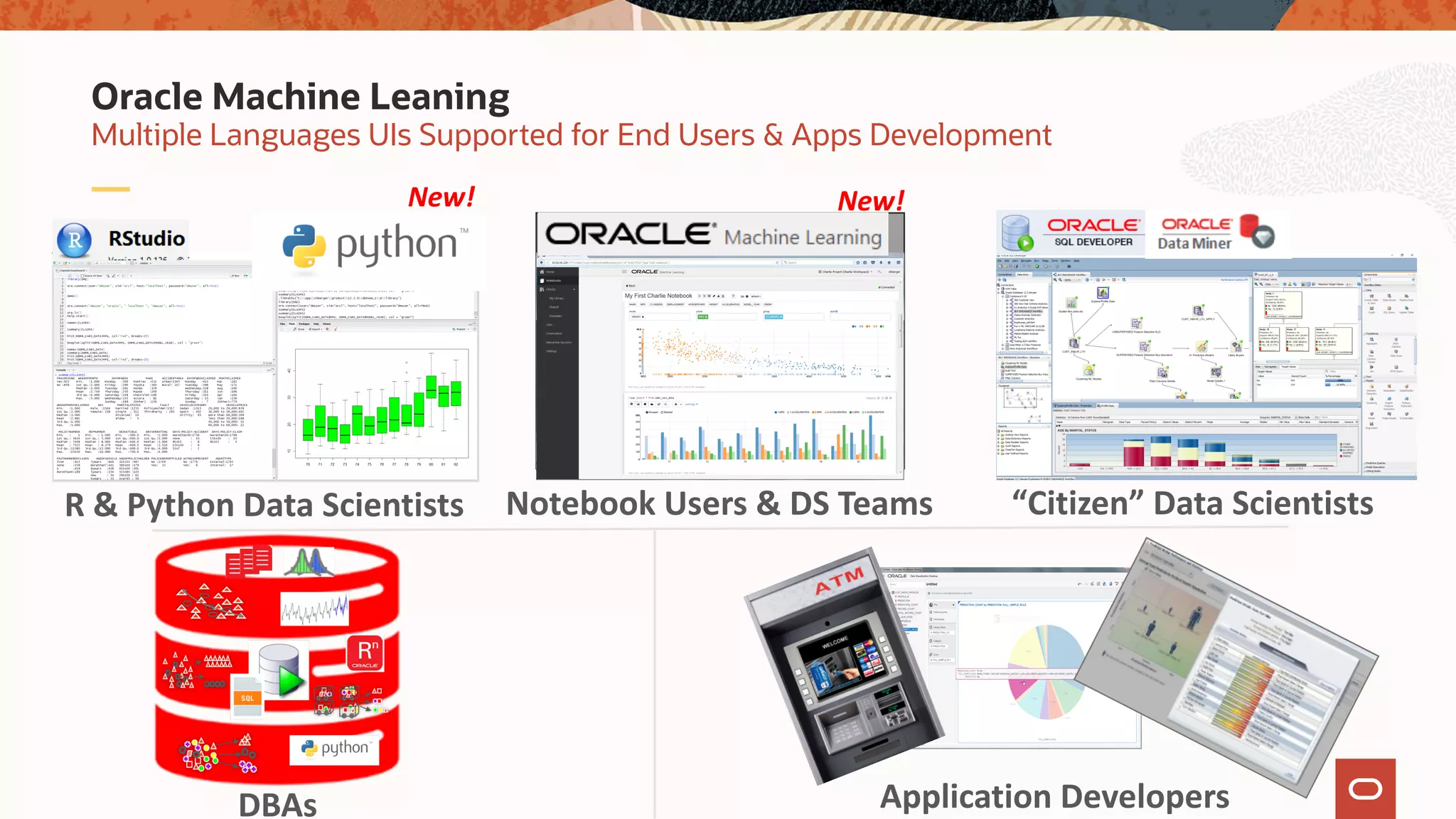
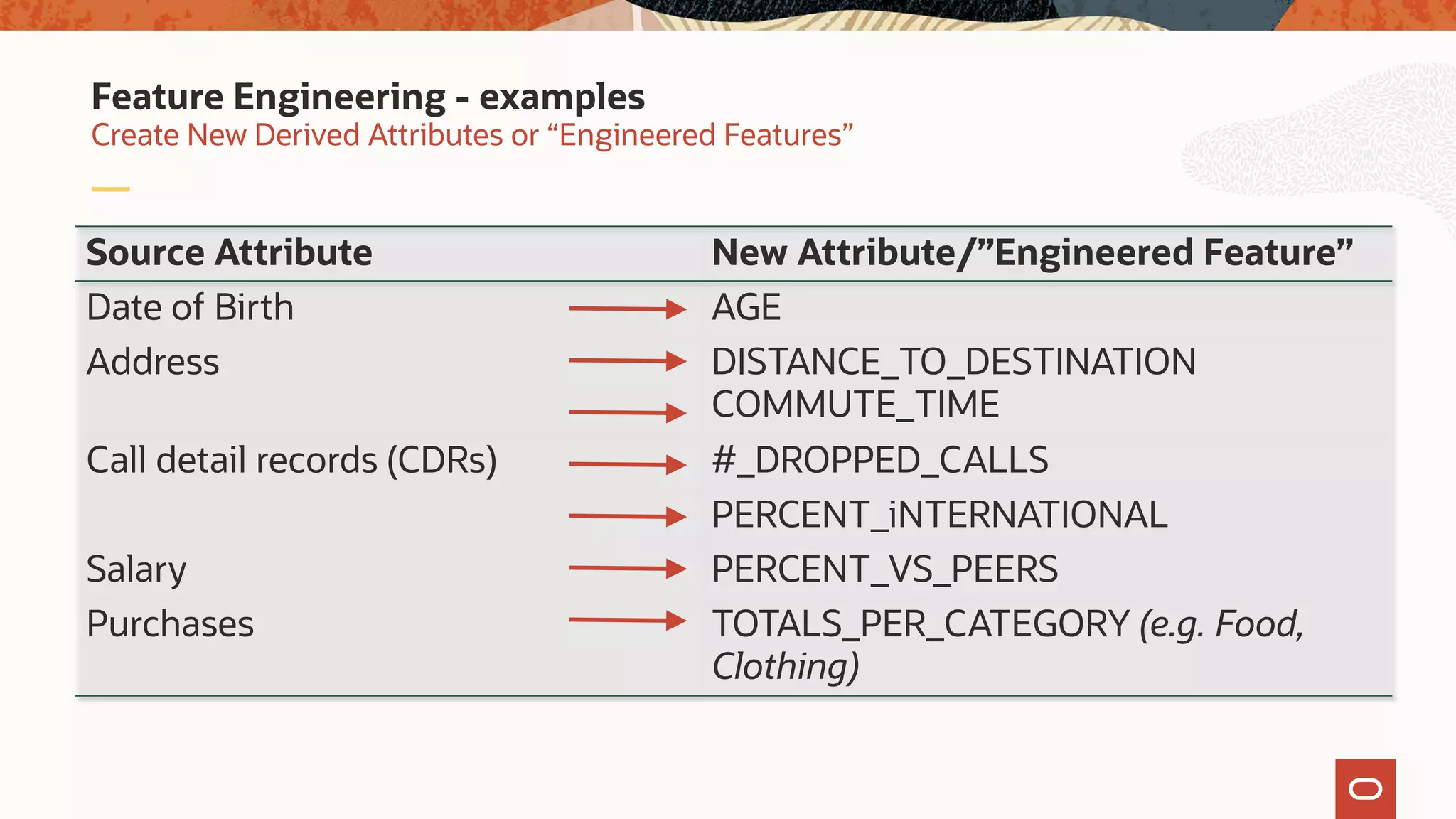
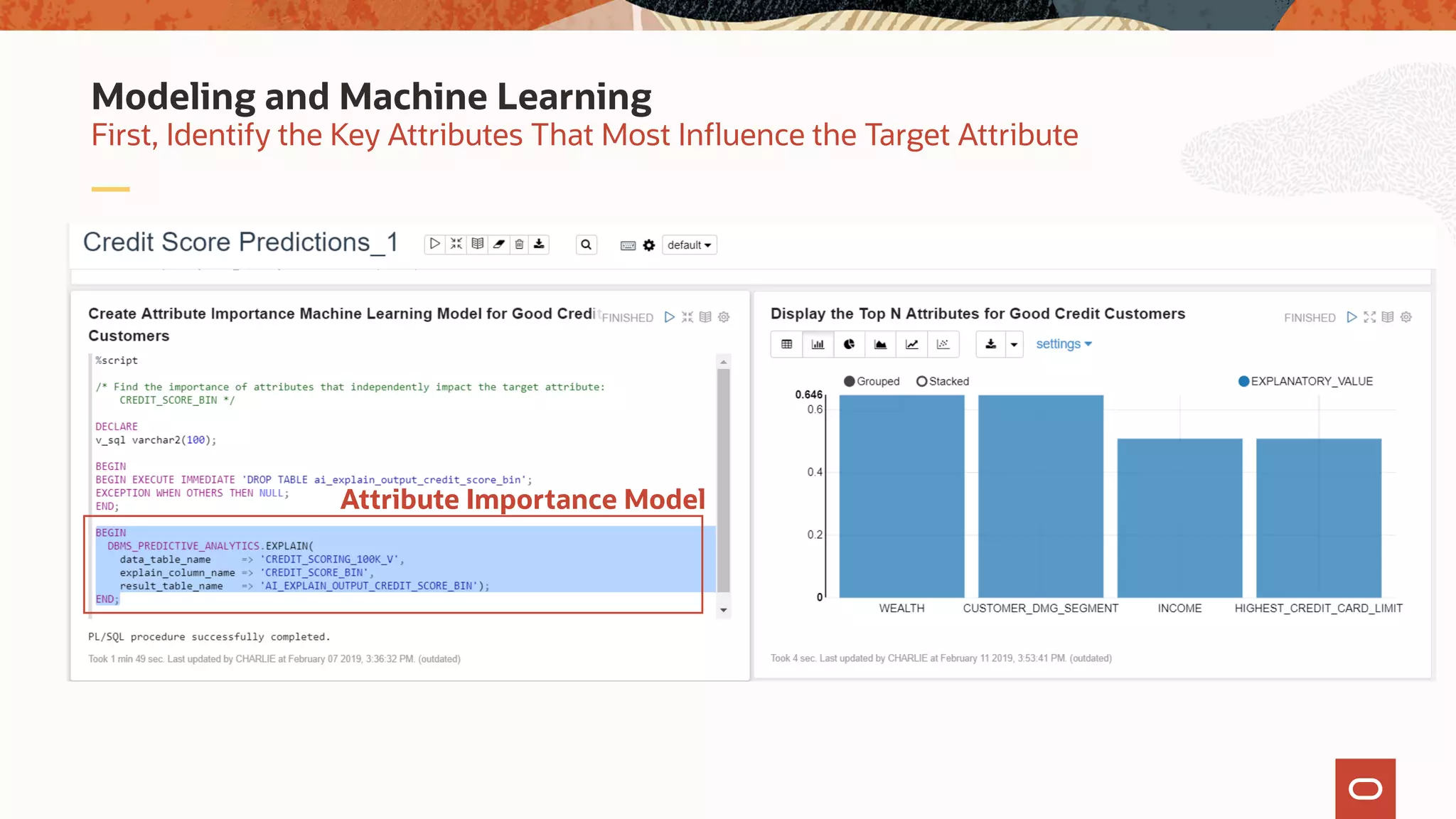
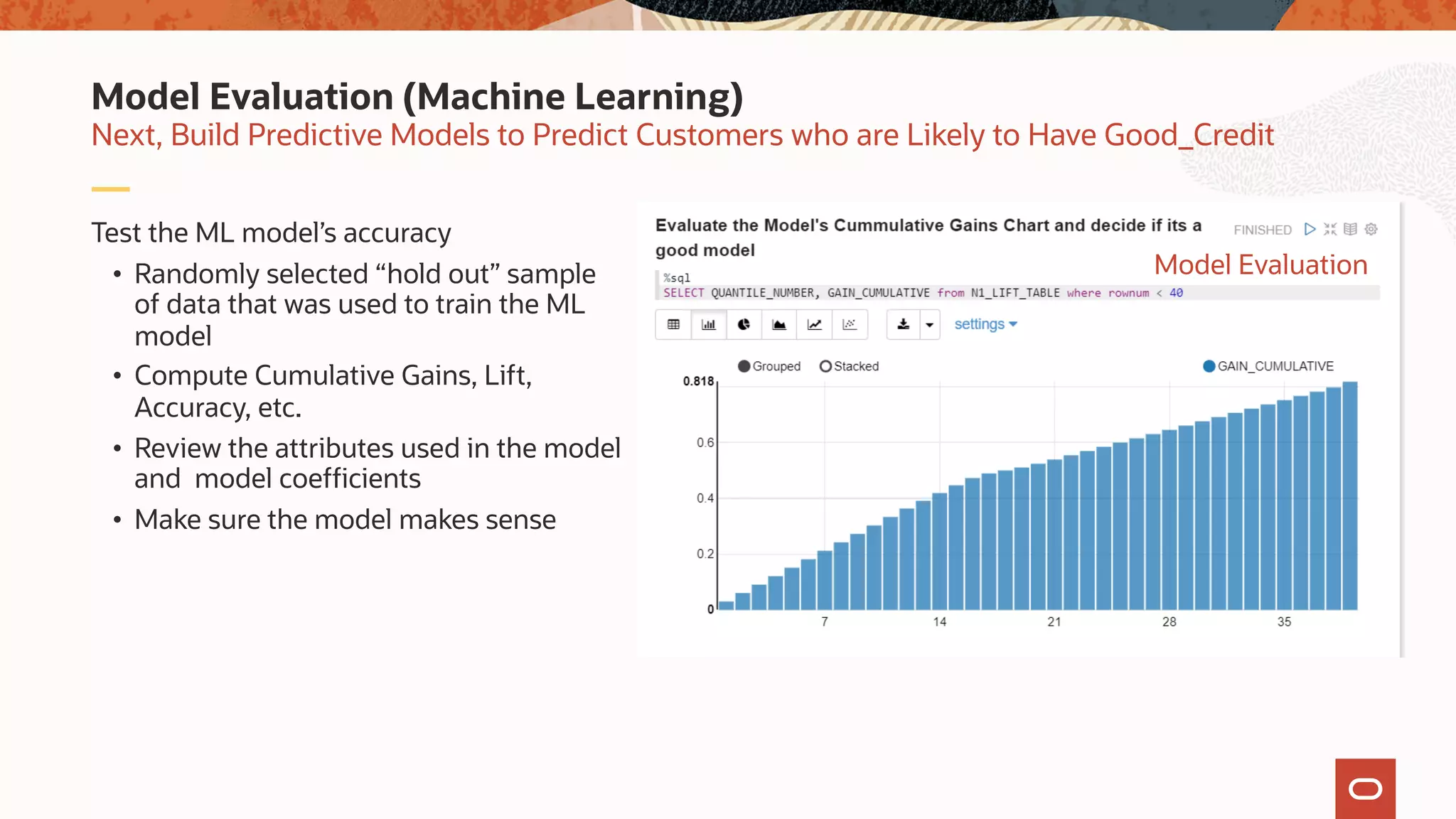
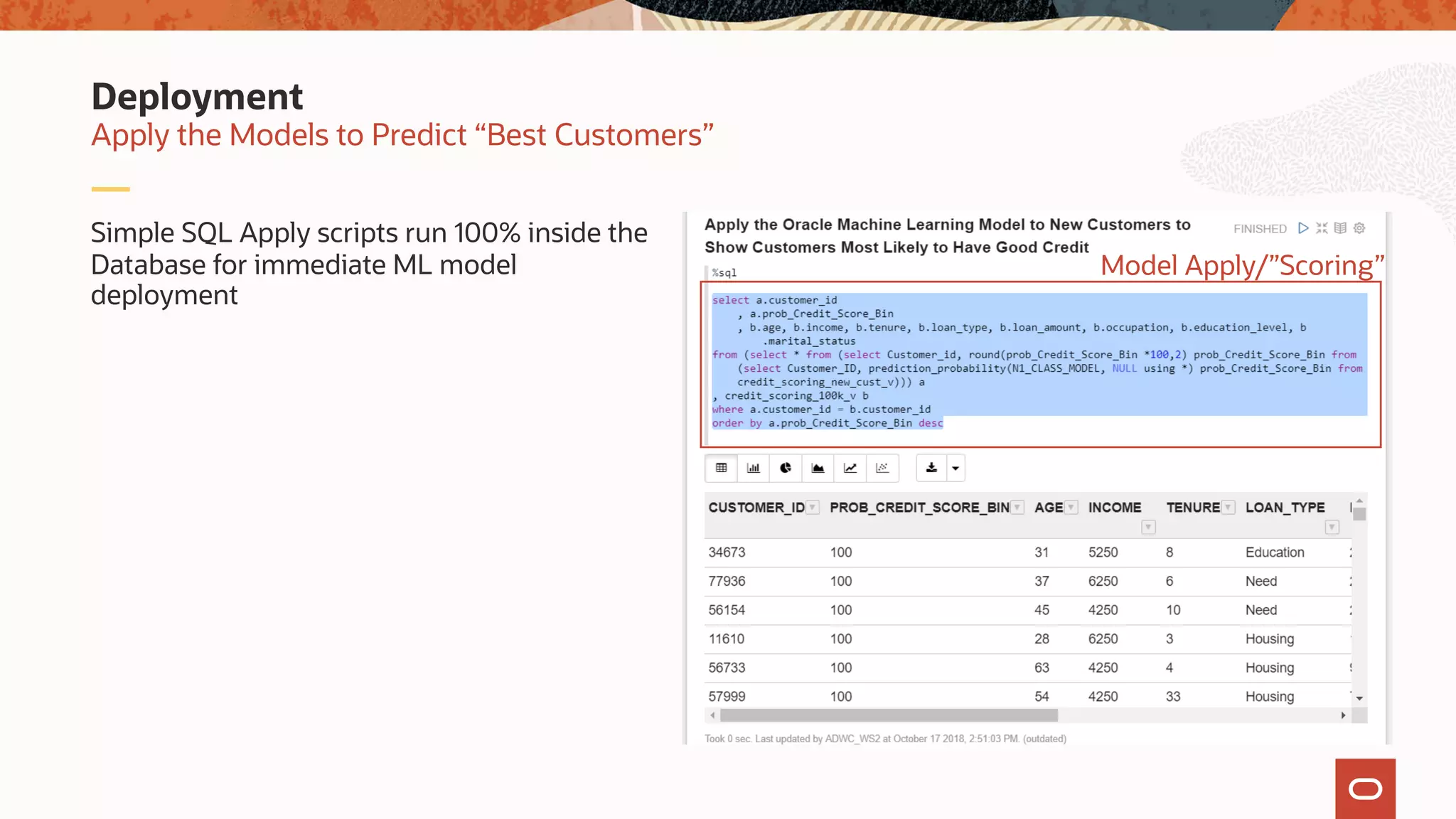
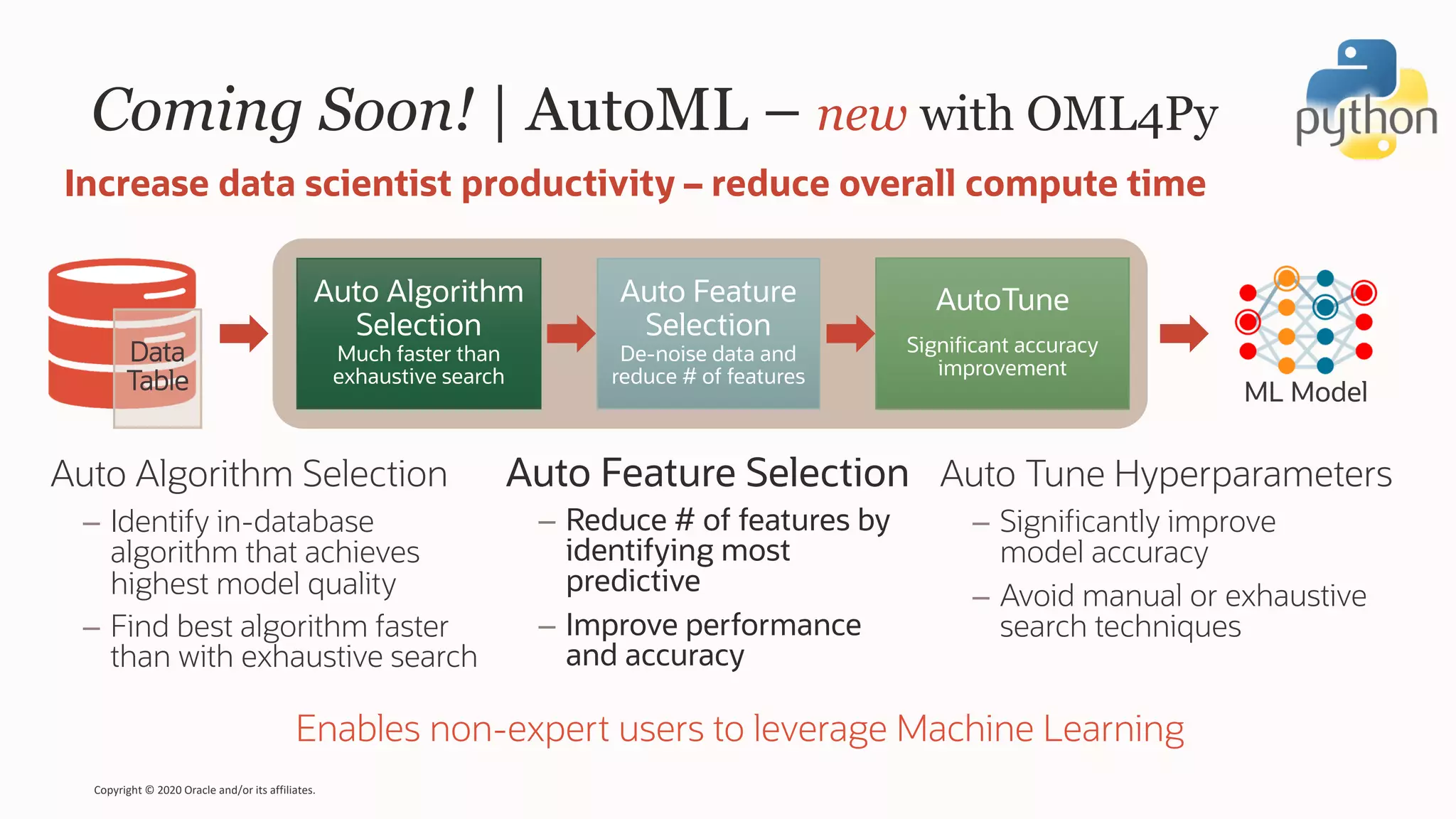
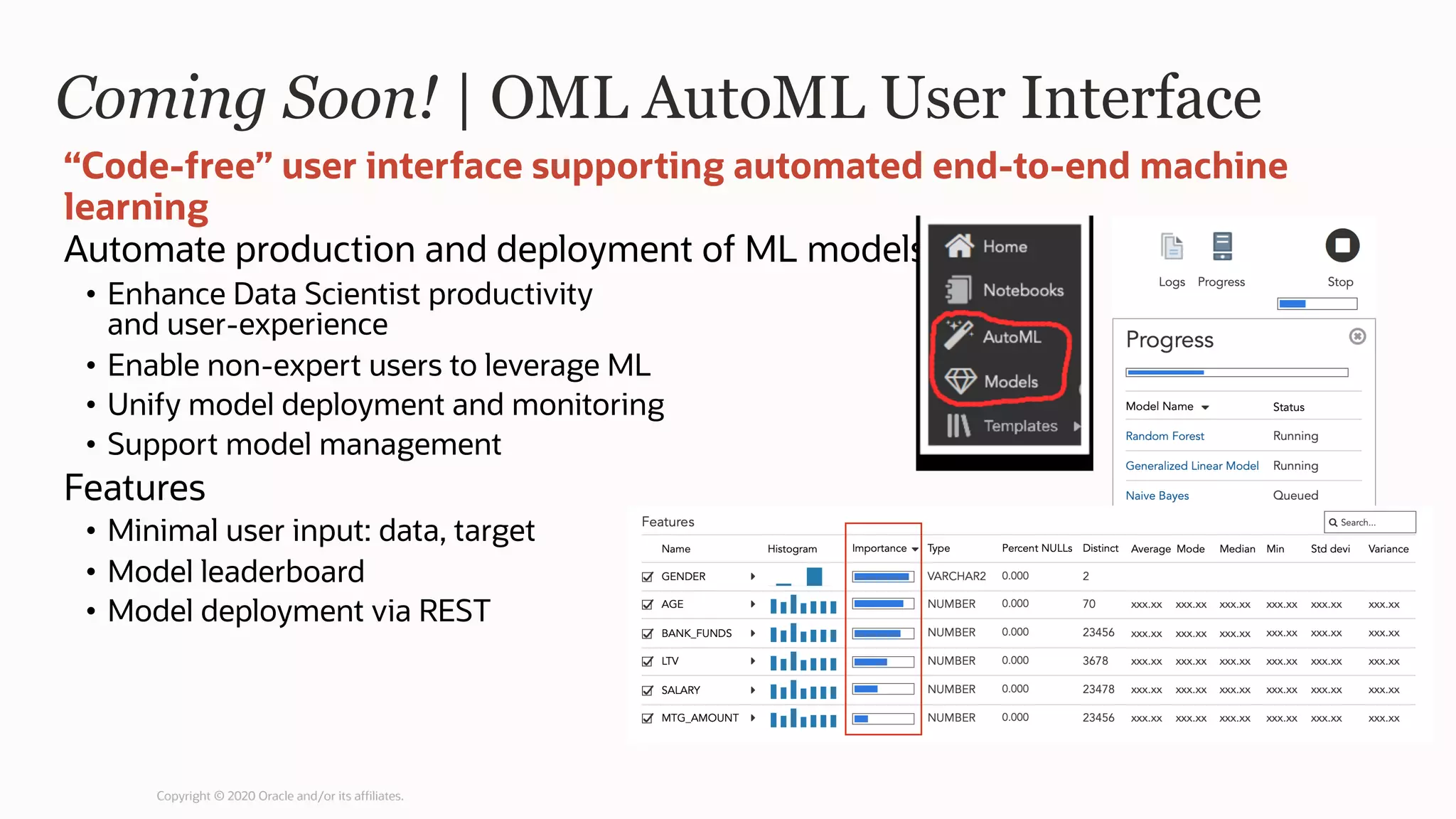
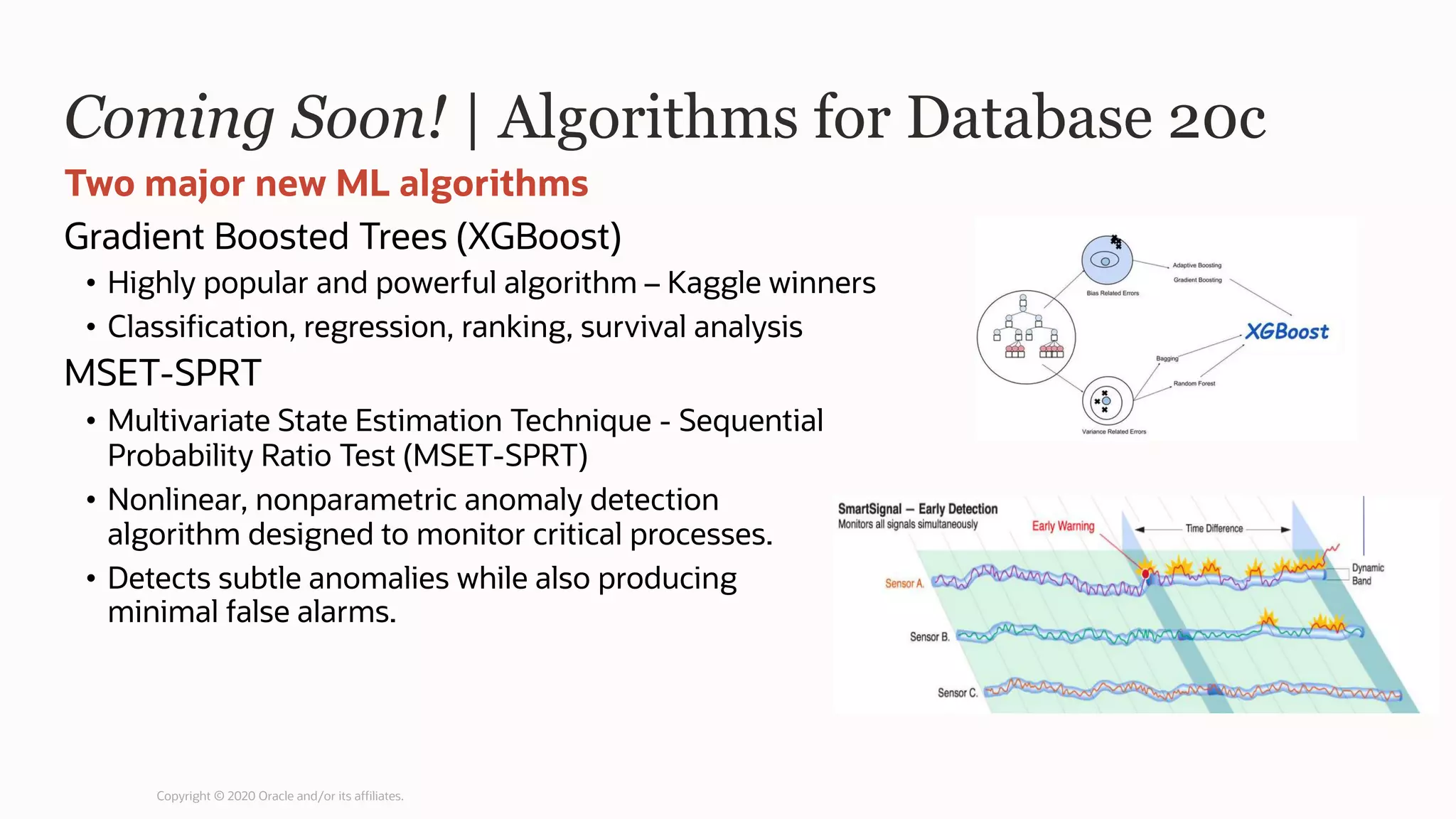
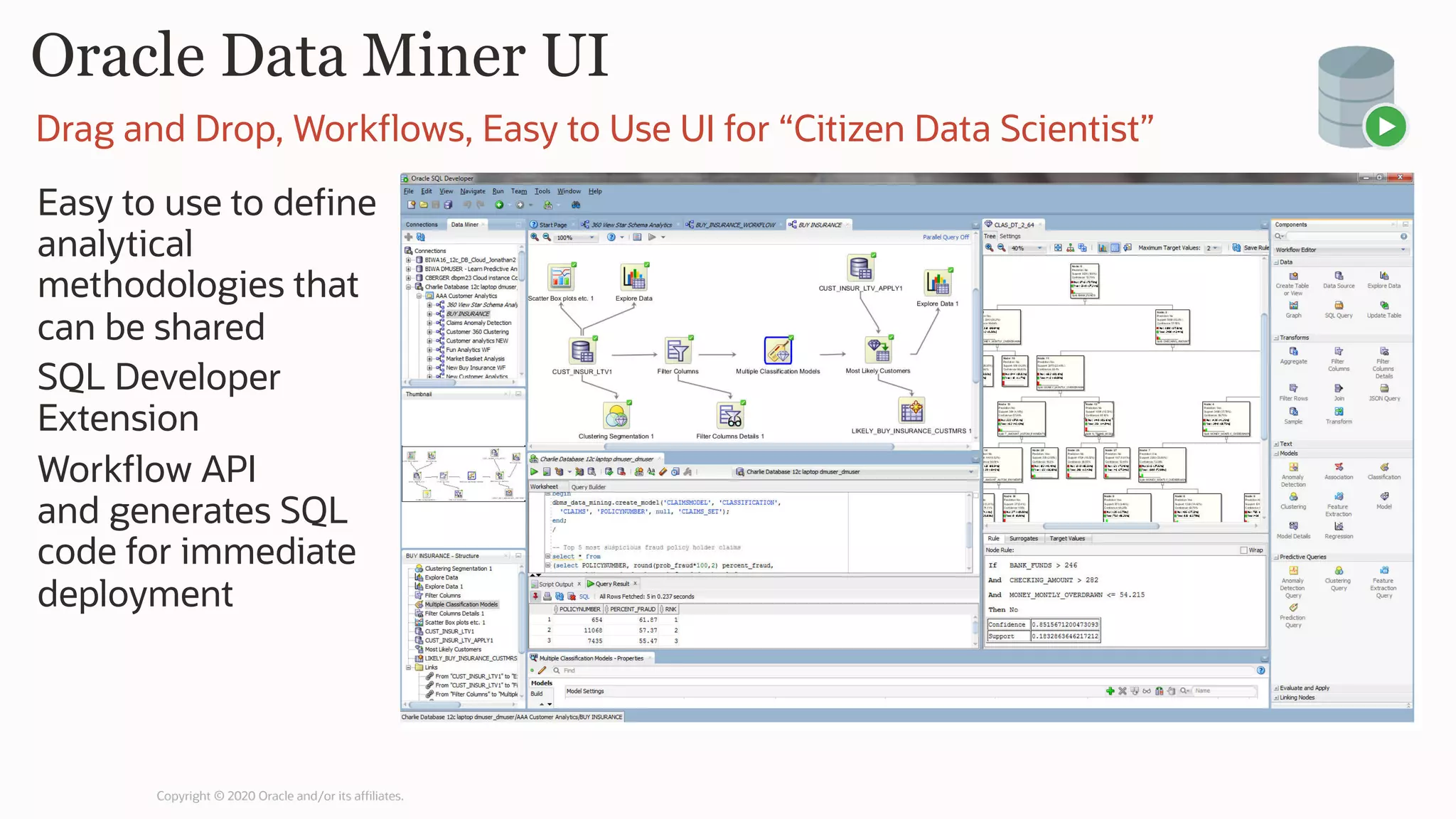
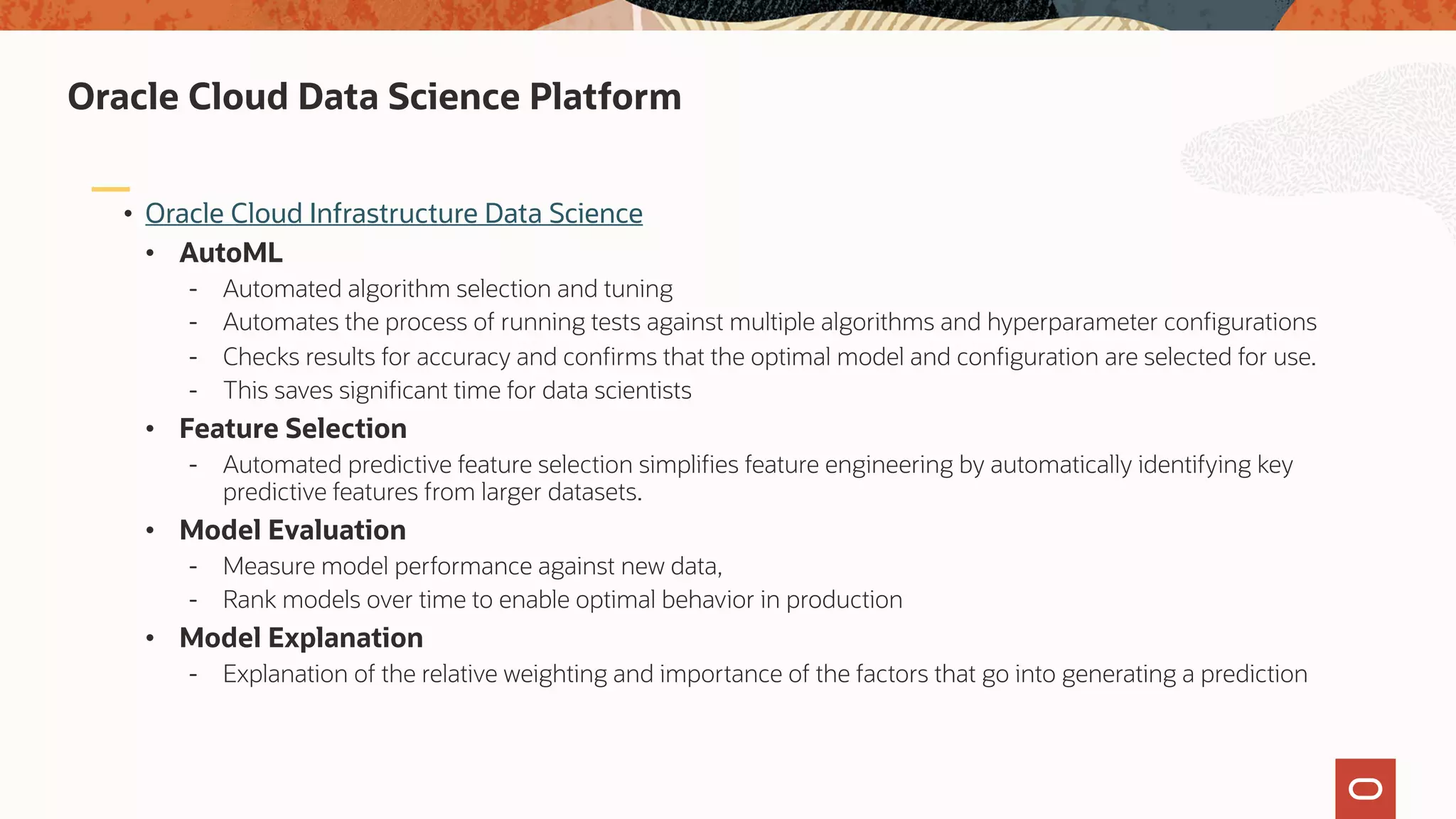
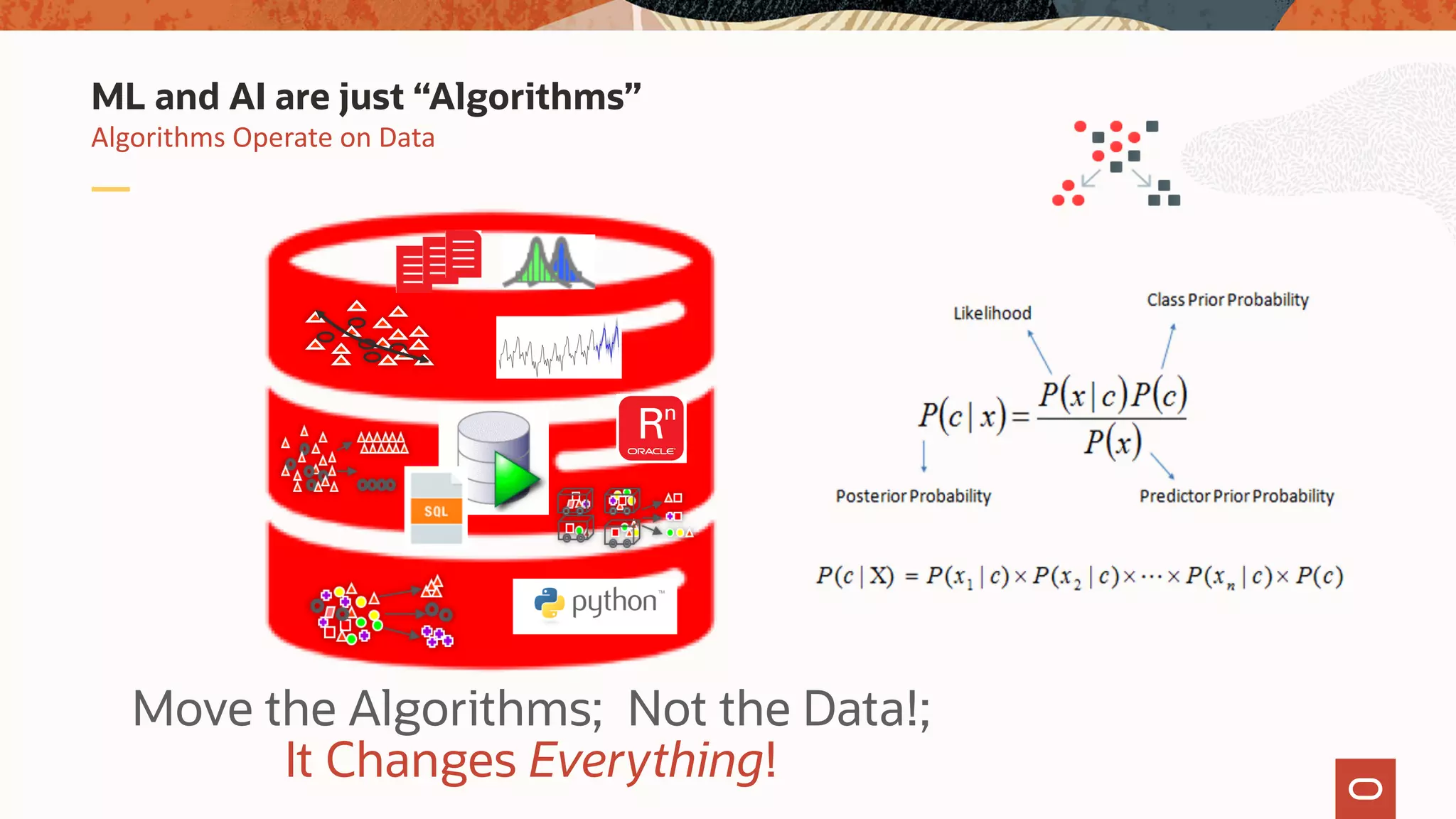
The document discusses the evolution of the database administrator (DBA) role towards incorporating machine learning, emphasizing the transition from traditional database management to data-driven insights and automation. It outlines the significance of machine learning in data processing, model building, and addressing business challenges through predictive analytics. Key features of Oracle's machine learning platform, including automated model selection and deployment, are highlighted to streamline the process for data scientists and non-expert users alike.