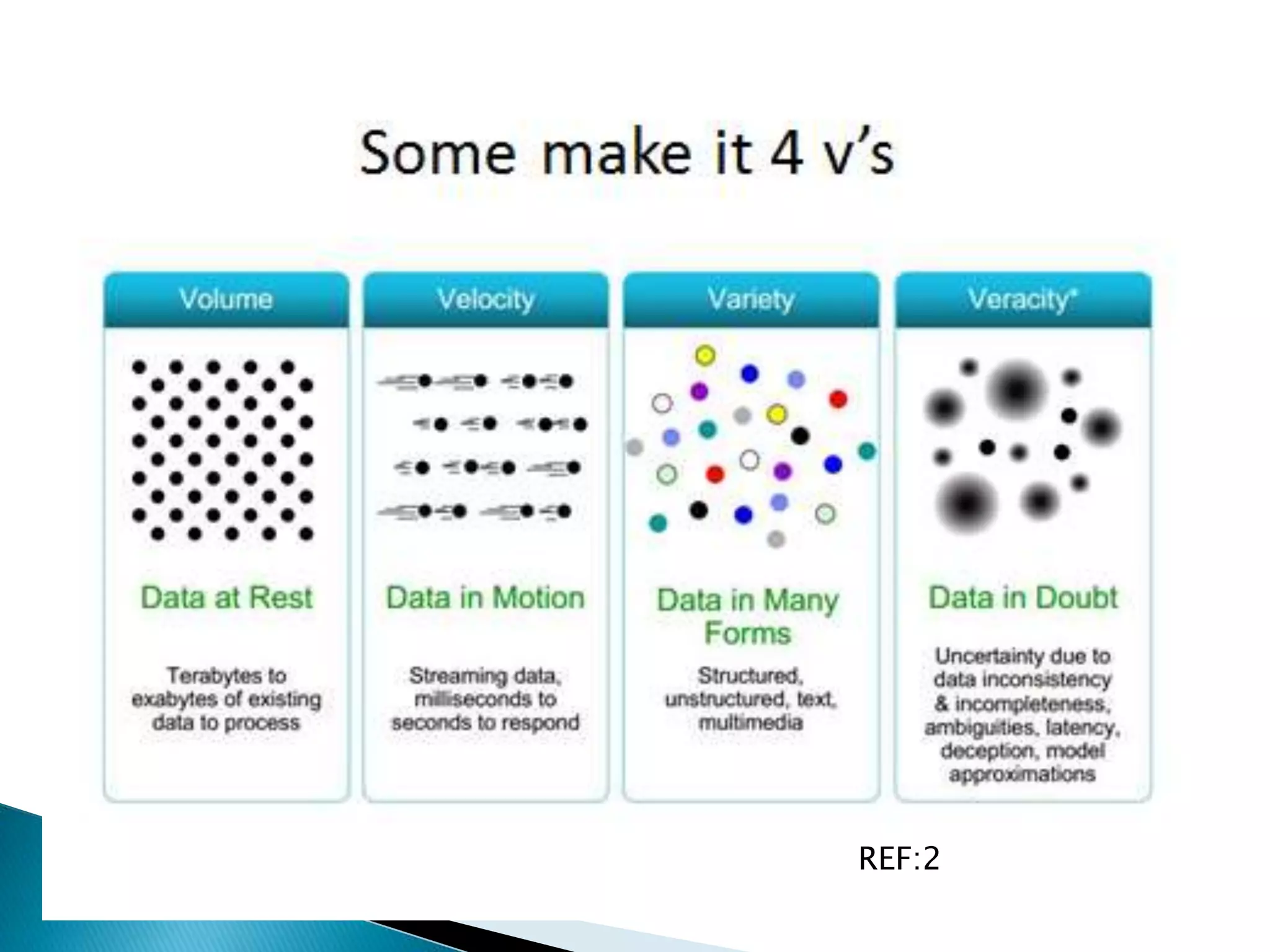
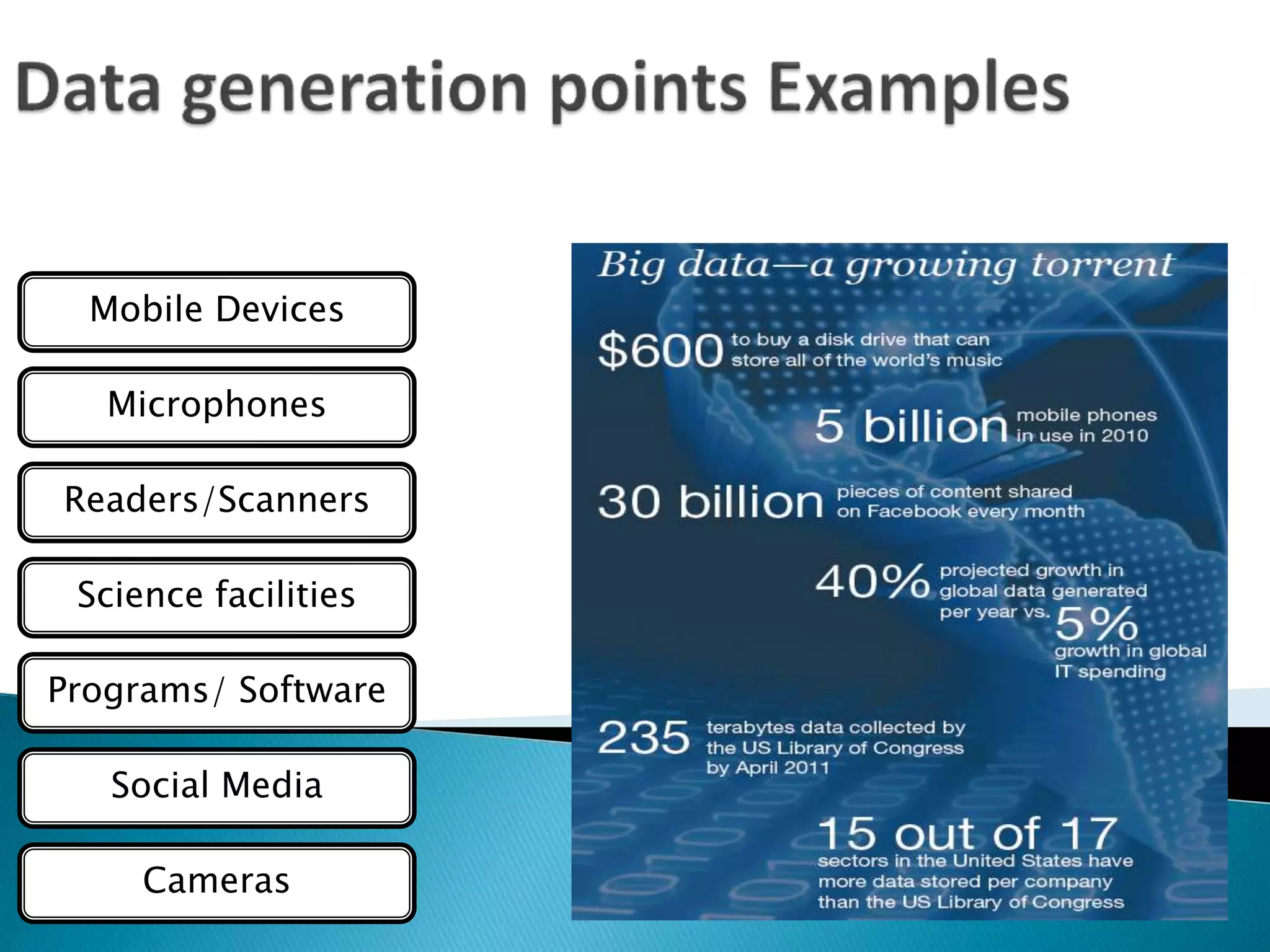
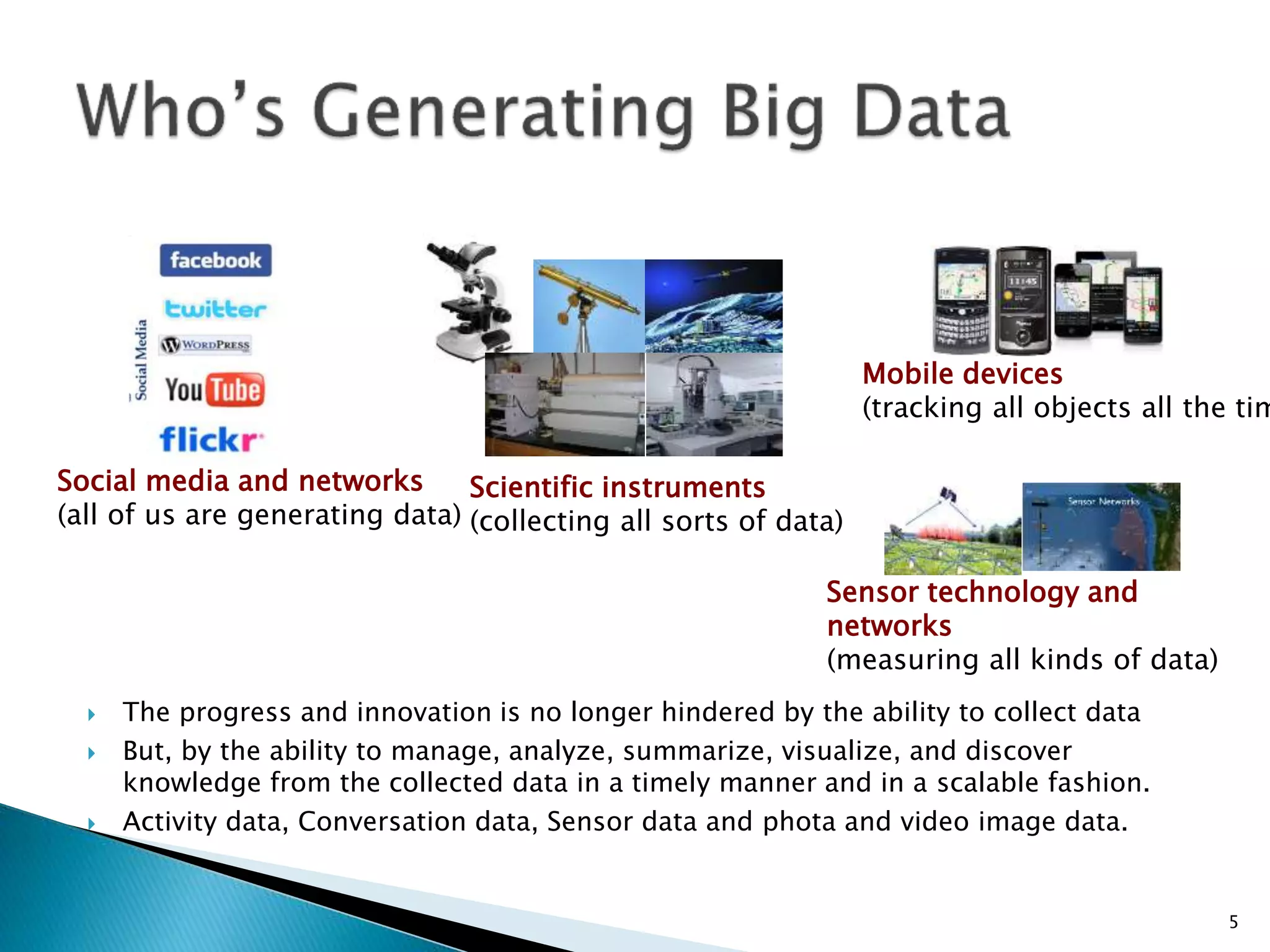
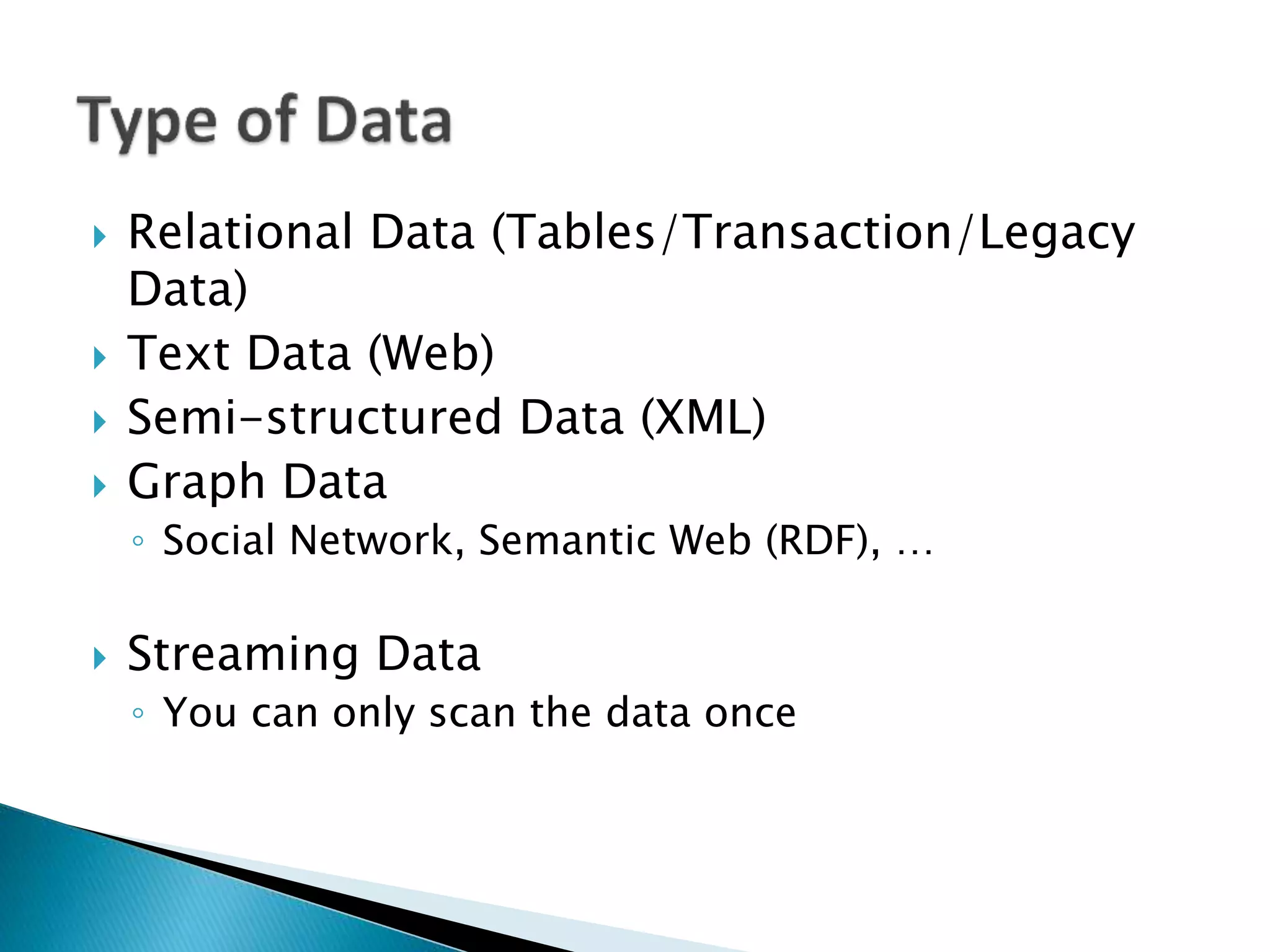
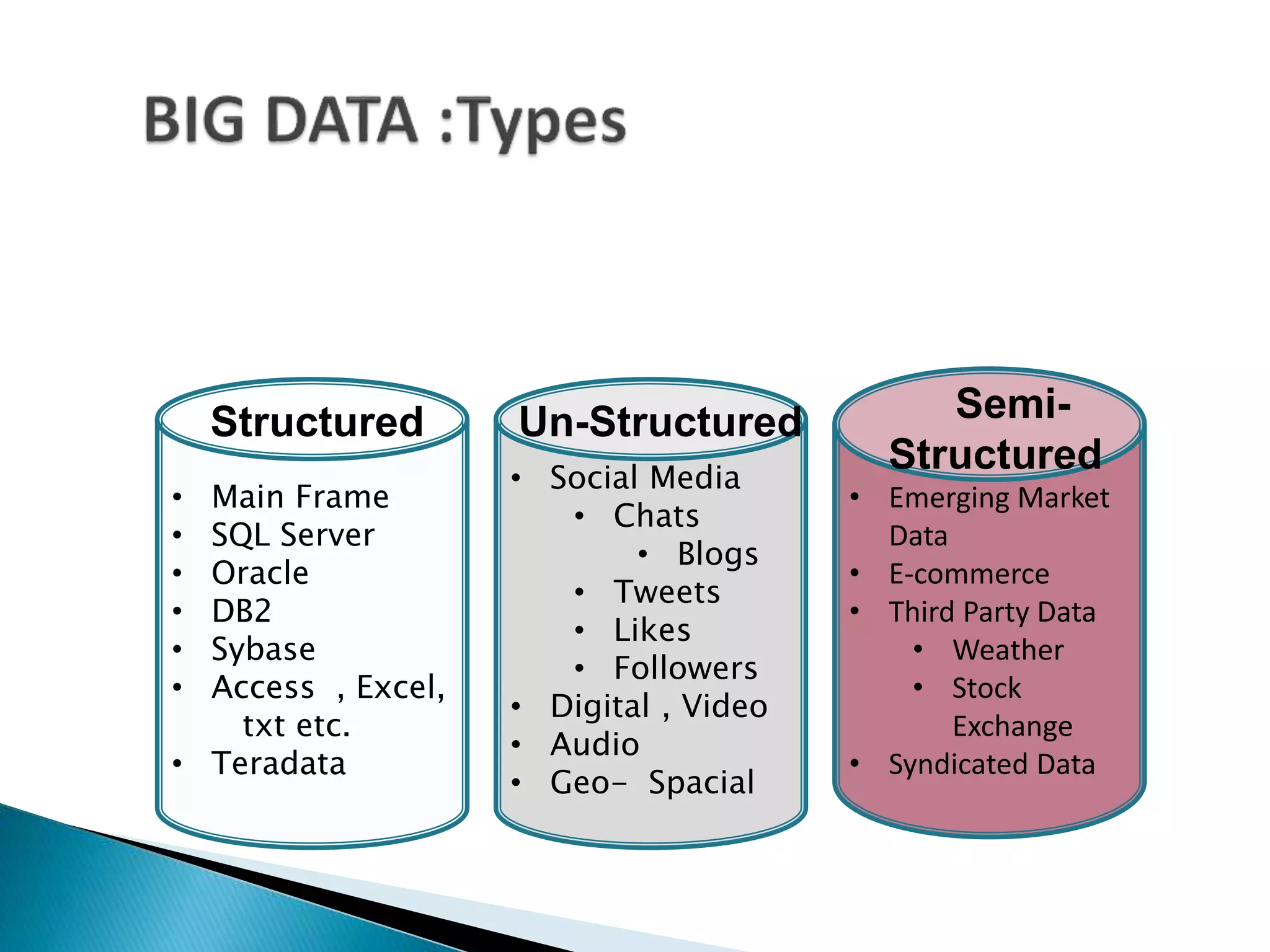
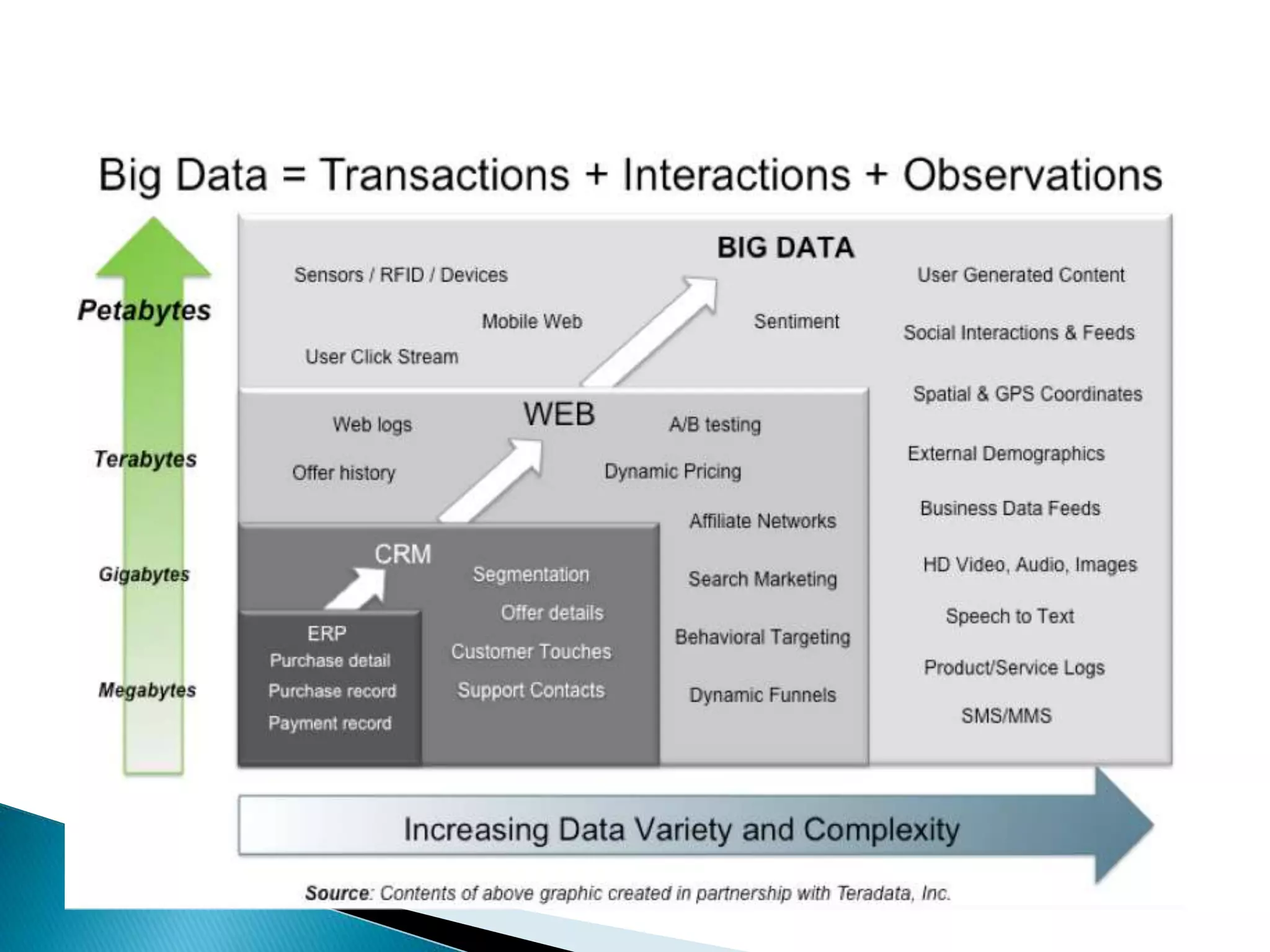
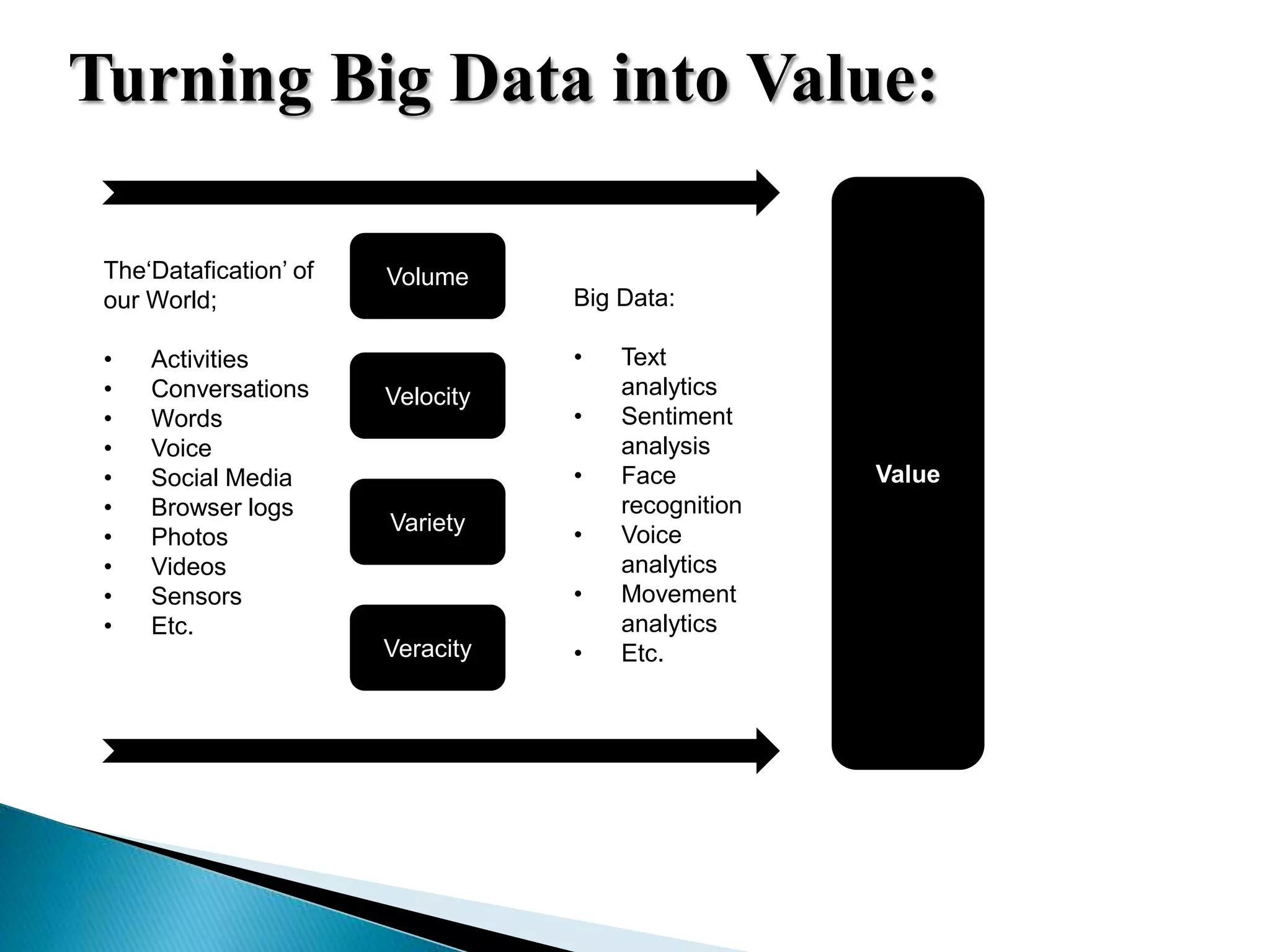
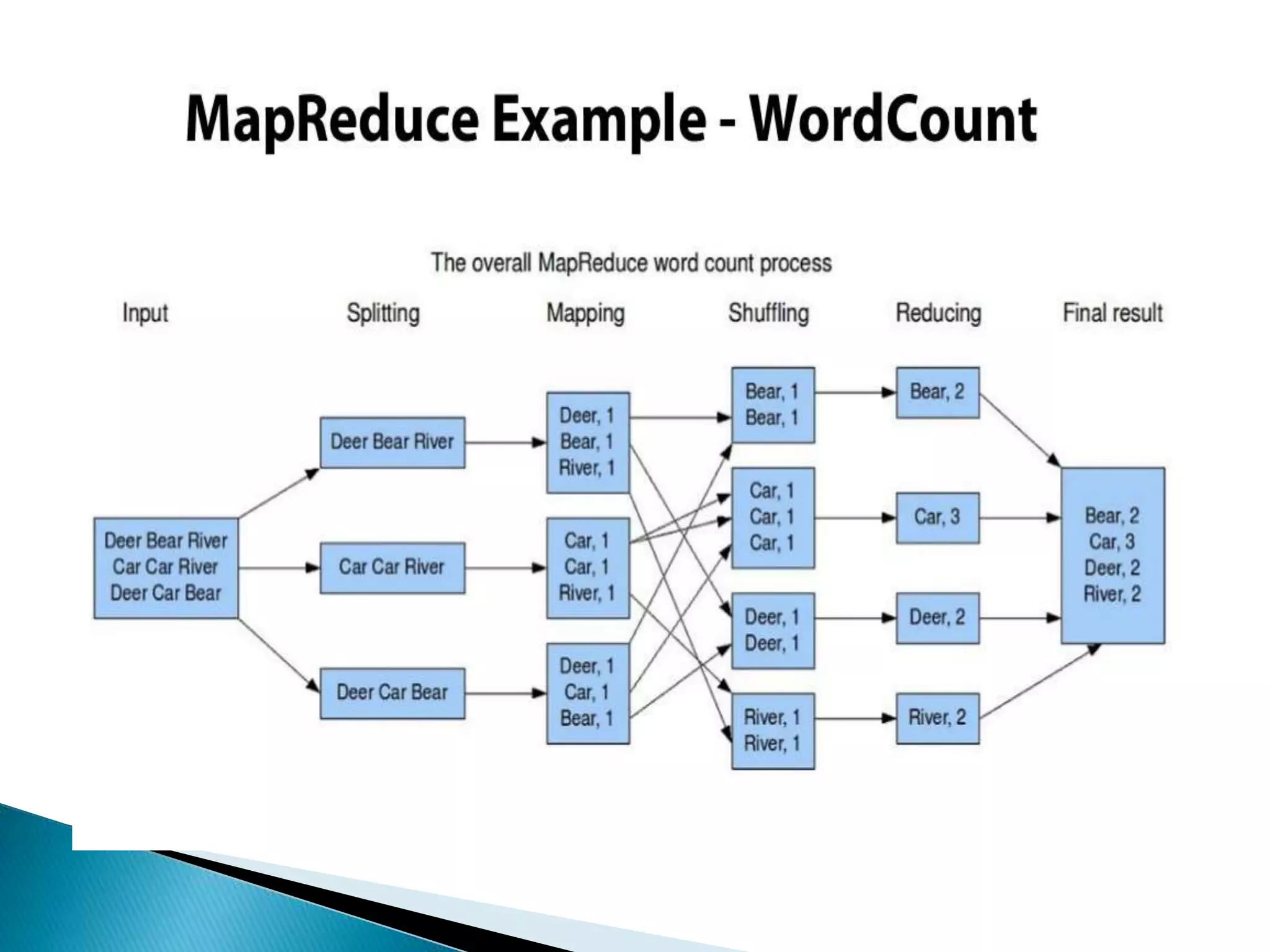
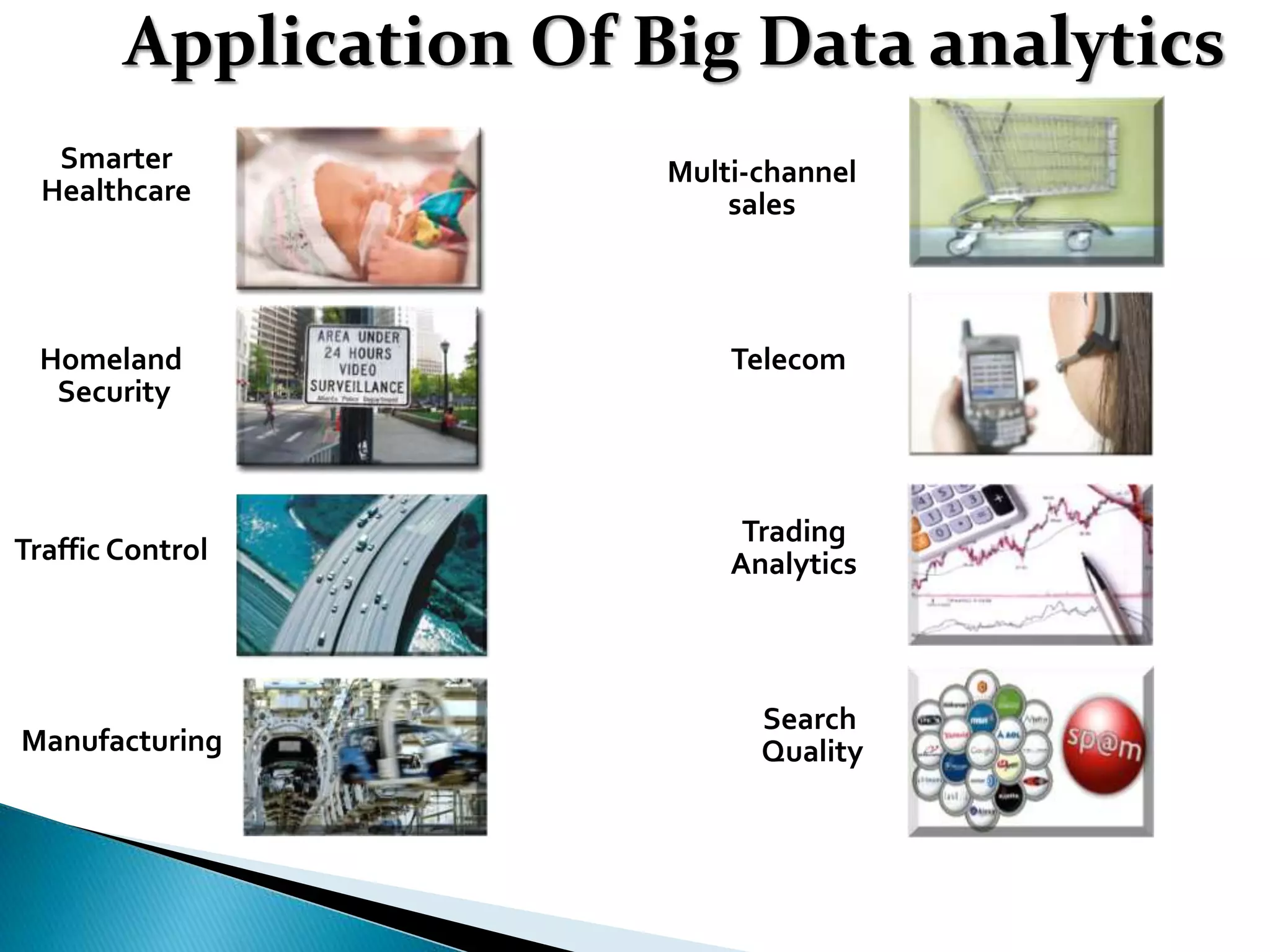
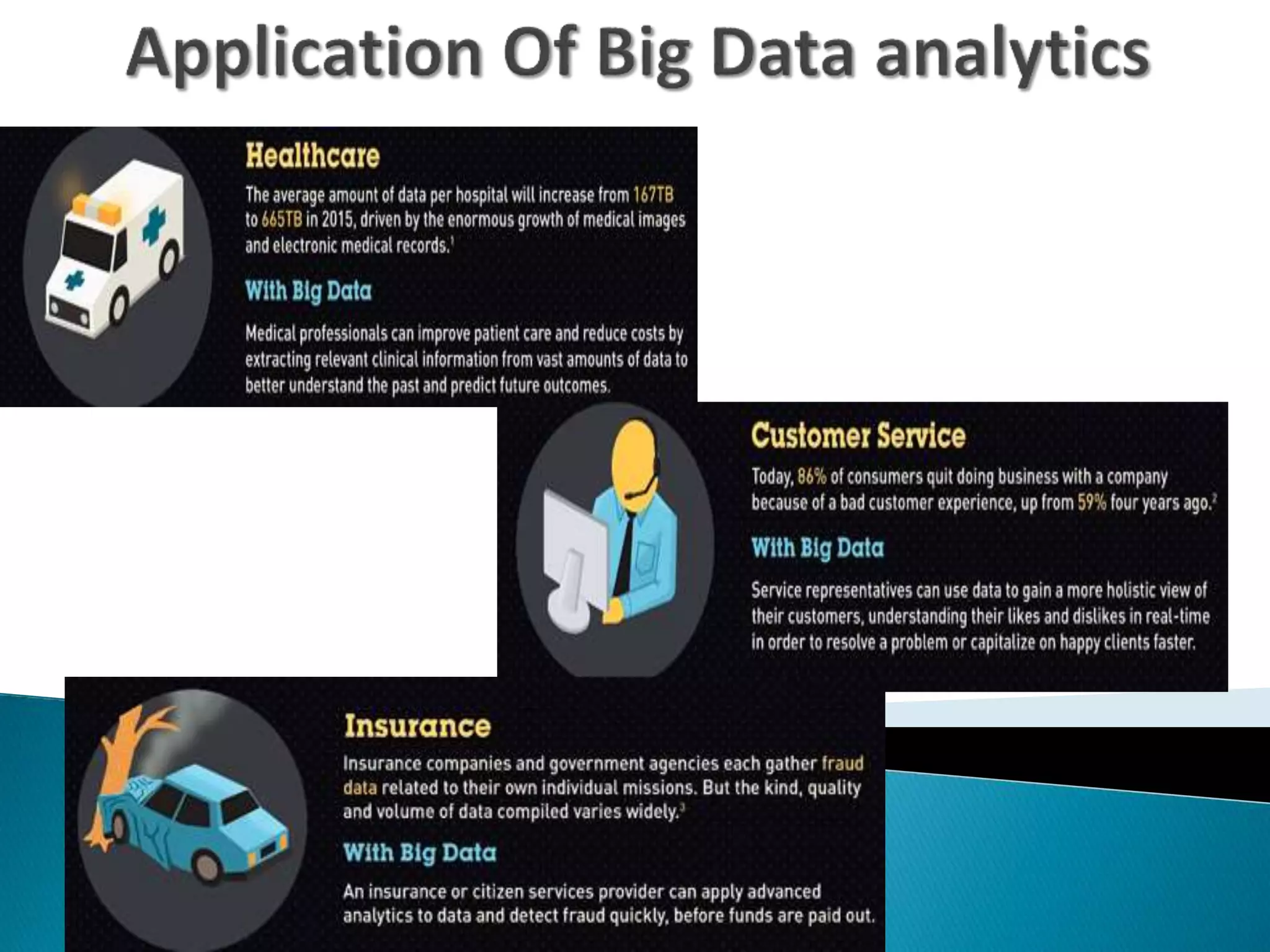
This document discusses big data, including key enablers like increased storage and processing power. It notes that 90% of data today was created in the last two years. Big data comes from sources like mobile devices, sensors, and social media. The challenge is managing and analyzing large amounts of diverse data in a timely way. Common big data types include structured, unstructured, semi-structured, text, graph, and streaming data. Big data analytics can provide value across many domains. Issues include privacy, regulation, and ensuring analysis solves meaningful problems. The big data industry is large and growing rapidly.