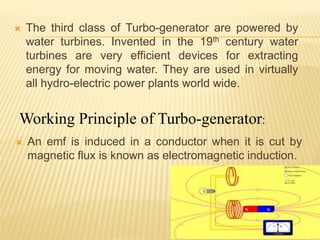
This document provides an introduction and overview of turbo generators and their manufacturing process. It discusses the key components of turbo generators including the rotor, stator, and auxiliary systems. The document also outlines the 12 step design process for constructing turbo generators and their various applications in power generation. Finally, it discusses the advantages of turbo generators in providing reliable and economic power production but also notes their high maintenance and repair costs.