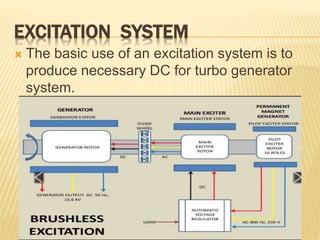
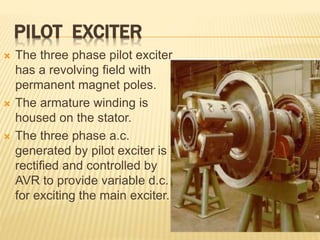
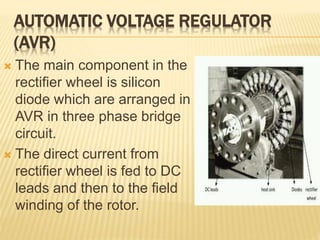
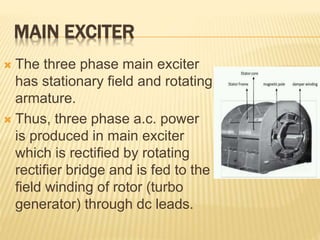
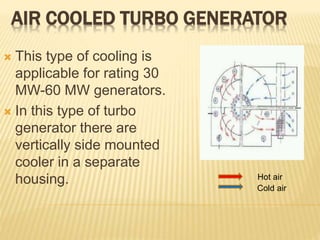
This document provides an overview of an industrial training seminar at Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited. It discusses the need for training, then describes the key components of a turbo generator including the stator, rotor, insulation, excitation system, and cooling systems. Different cooling methods for turbo generators are also explained, such as air cooling, hydrogen cooling, and hydrogen/water cooling.