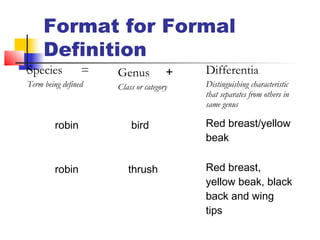
This document outlines best practices for creating and documenting definitions in technical writing, emphasizing the importance of clarity for various audiences. It discusses the purpose of definitions, types of definitions such as formal and informal ones, as well as different approaches like expanded definitions and operational definitions. Additionally, it provides guidance on placement of definitions within texts to enhance comprehension.