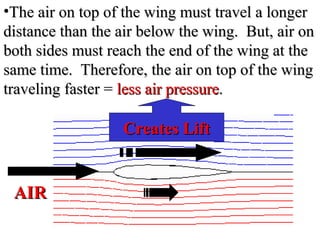
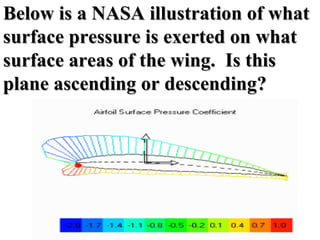
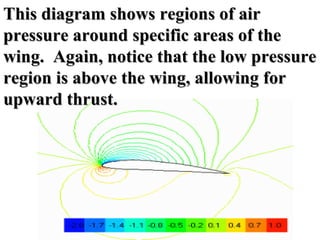
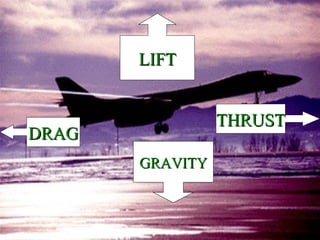
- Bernoulli's Principle states that the air pressure is lower where the air is moving faster, such as over the top of an airplane wing. This lower pressure provides lift, allowing planes and birds to fly.
- The document uses diagrams and examples like a standing tennis ball to illustrate how Bernoulli's Principle works in practice by creating differences in air pressure. It explains that the faster moving air over the top of a wing results in lower pressure than under the wing, providing the upward lift necessary for flight.