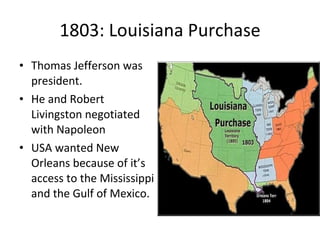
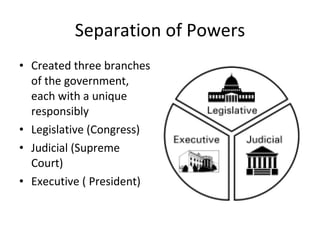
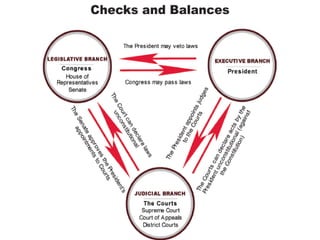
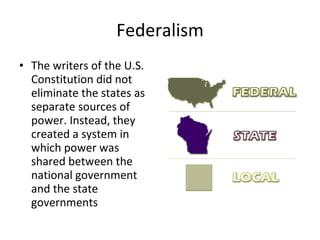
The document provides important dates in American history from 1607 to the 1860s, including the first English settlement at Jamestown in 1607, the Declaration of Independence in 1776, the writing of the Constitution in 1787, and the Civil War from 1861-1865. It also lists key figures from the American Revolution like George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and Benjamin Franklin. The document further discusses principles of the US Constitution such as separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism.