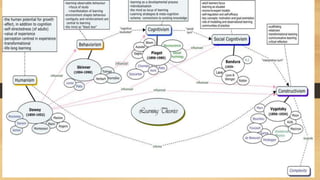
The document provides an overview of behaviorist theory of learning. It discusses some key aspects of behaviorism, including:
- Behaviorist theory uses rewards and punishments to control student behavior and teach new skills. It was popular in the early 20th century but is now less respected than other theories.
- Behaviorism views learning as being shaped by external factors in the environment through conditioning, focusing on observable behaviors rather than internal mental processes.
- Important early behaviorist psychologists who contributed to the theory are mentioned, including Pavlov, Skinner, Thorndike, and Watson.