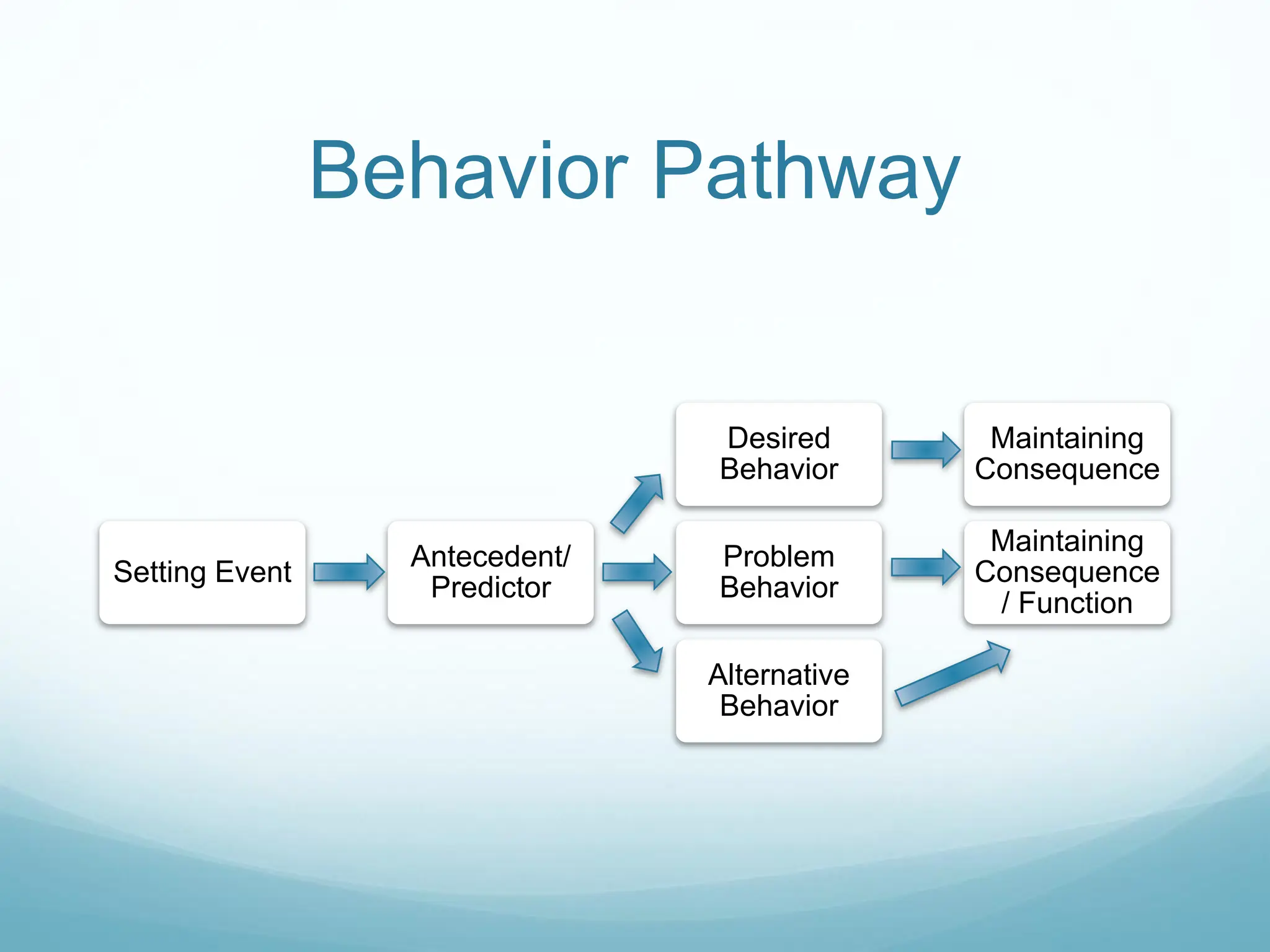
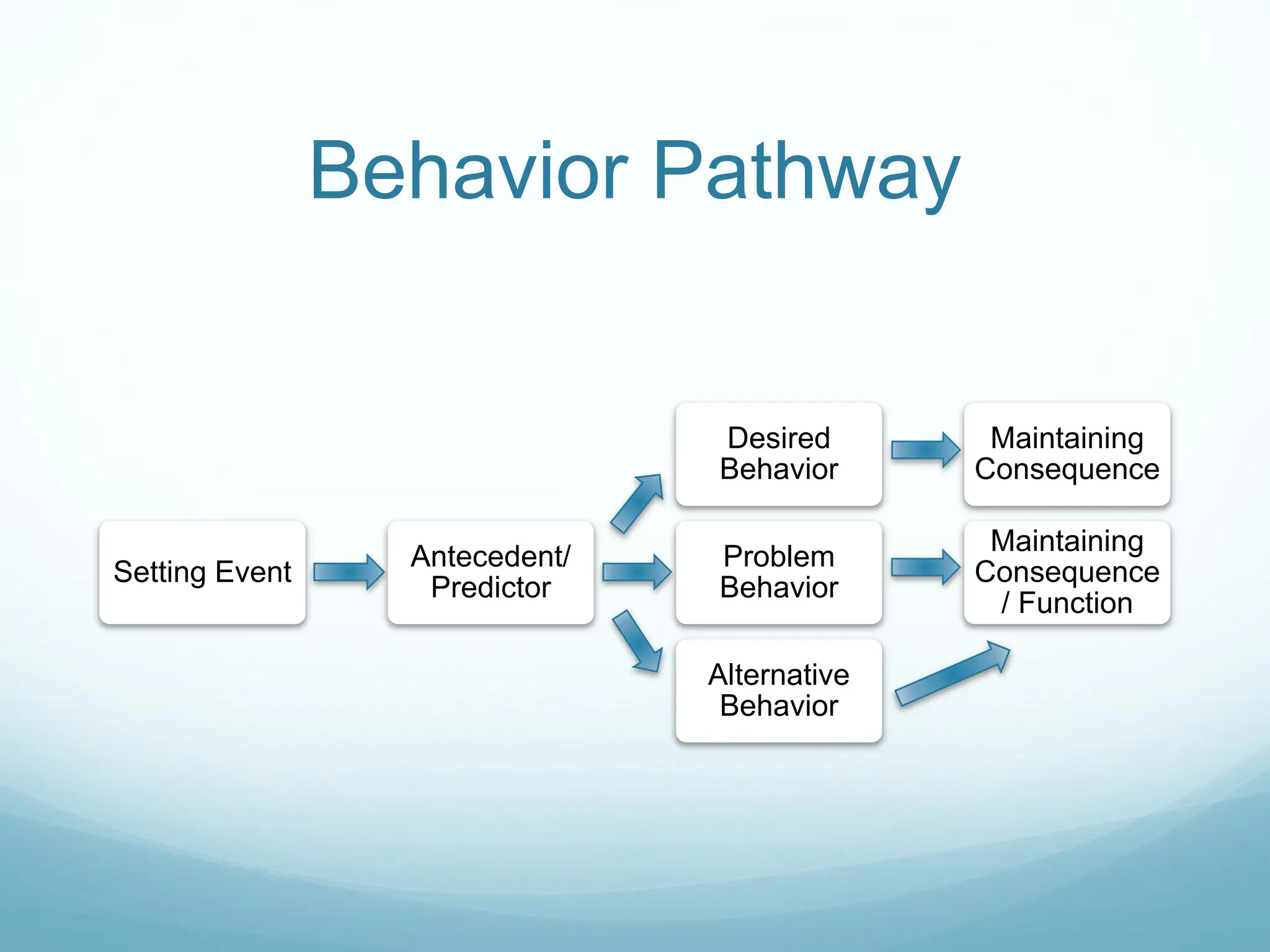
This document provides an introduction to understanding behavior using the behavior pathway model. It explains key concepts like the four functions of behavior (attention, escape/avoidance, access, sensory), and outlines the components of the behavior pathway including setting events, antecedents, problem behavior, maintaining consequences, desired behavior and alternative behavior. Common strategies are discussed for each part of the pathway like using choices, visual schedules and environmental arrangements to influence antecedents and reinforce appropriate behavior. Consistency, persistence and reinforcing the right behaviors are emphasized.