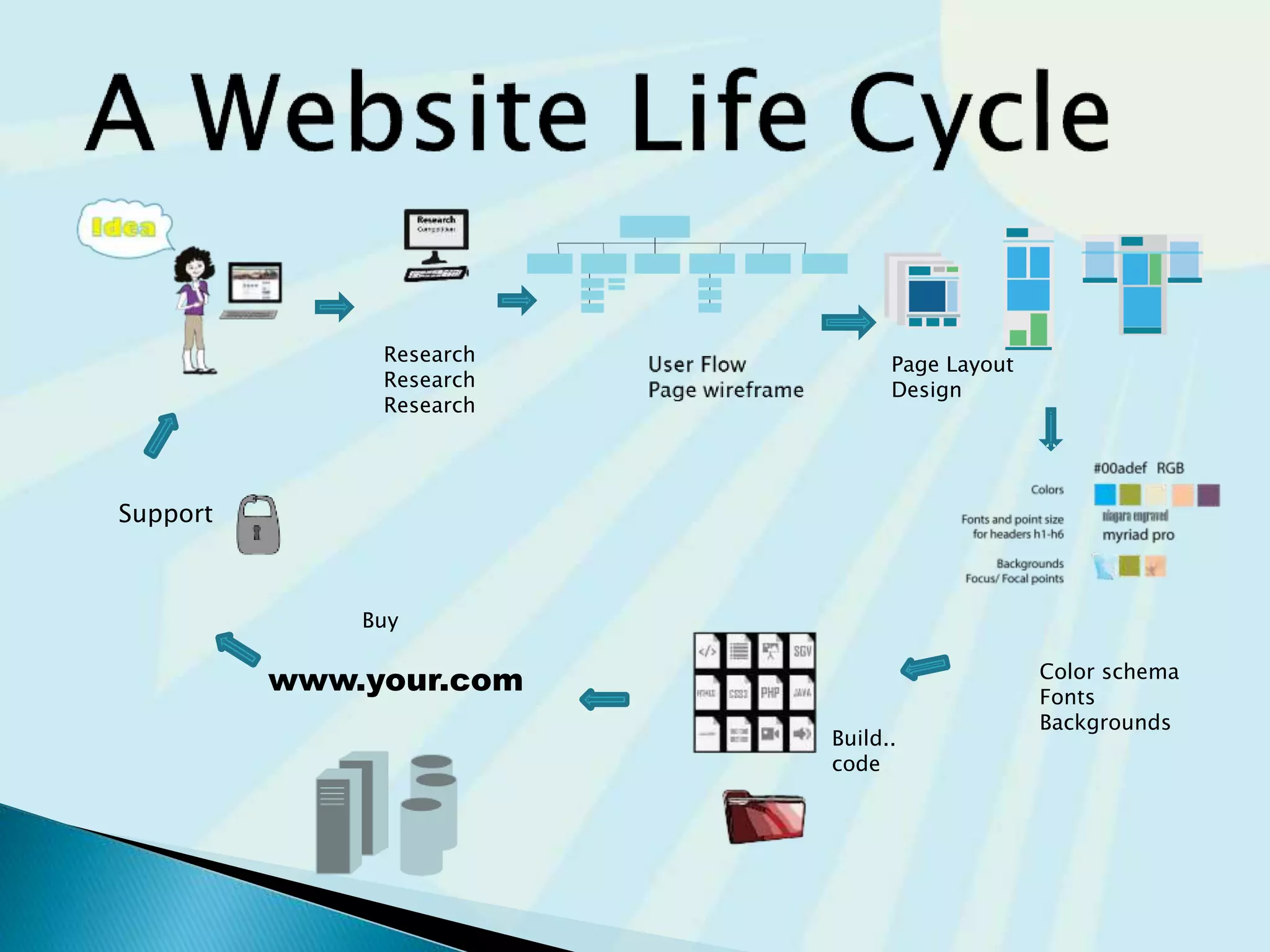
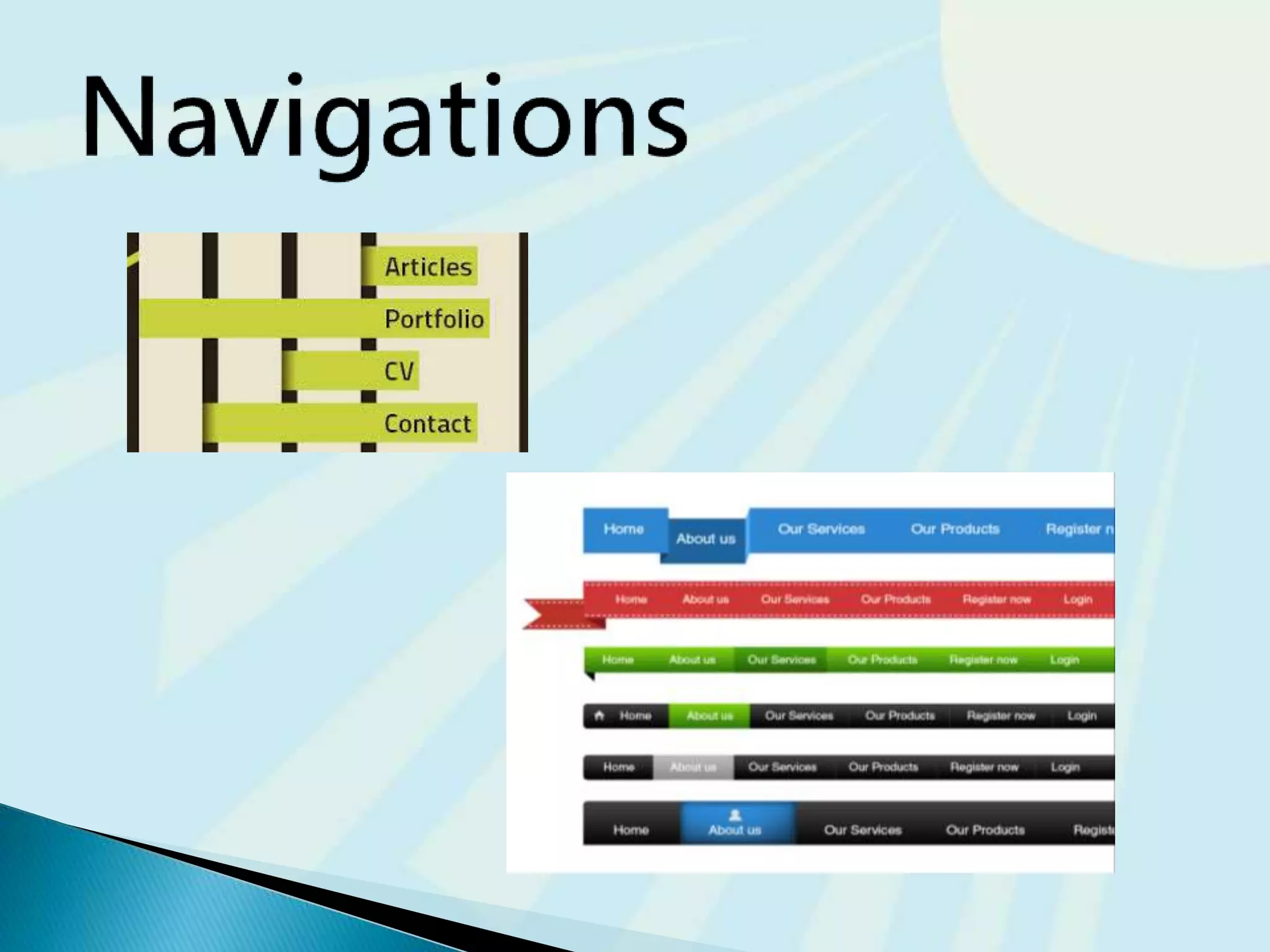
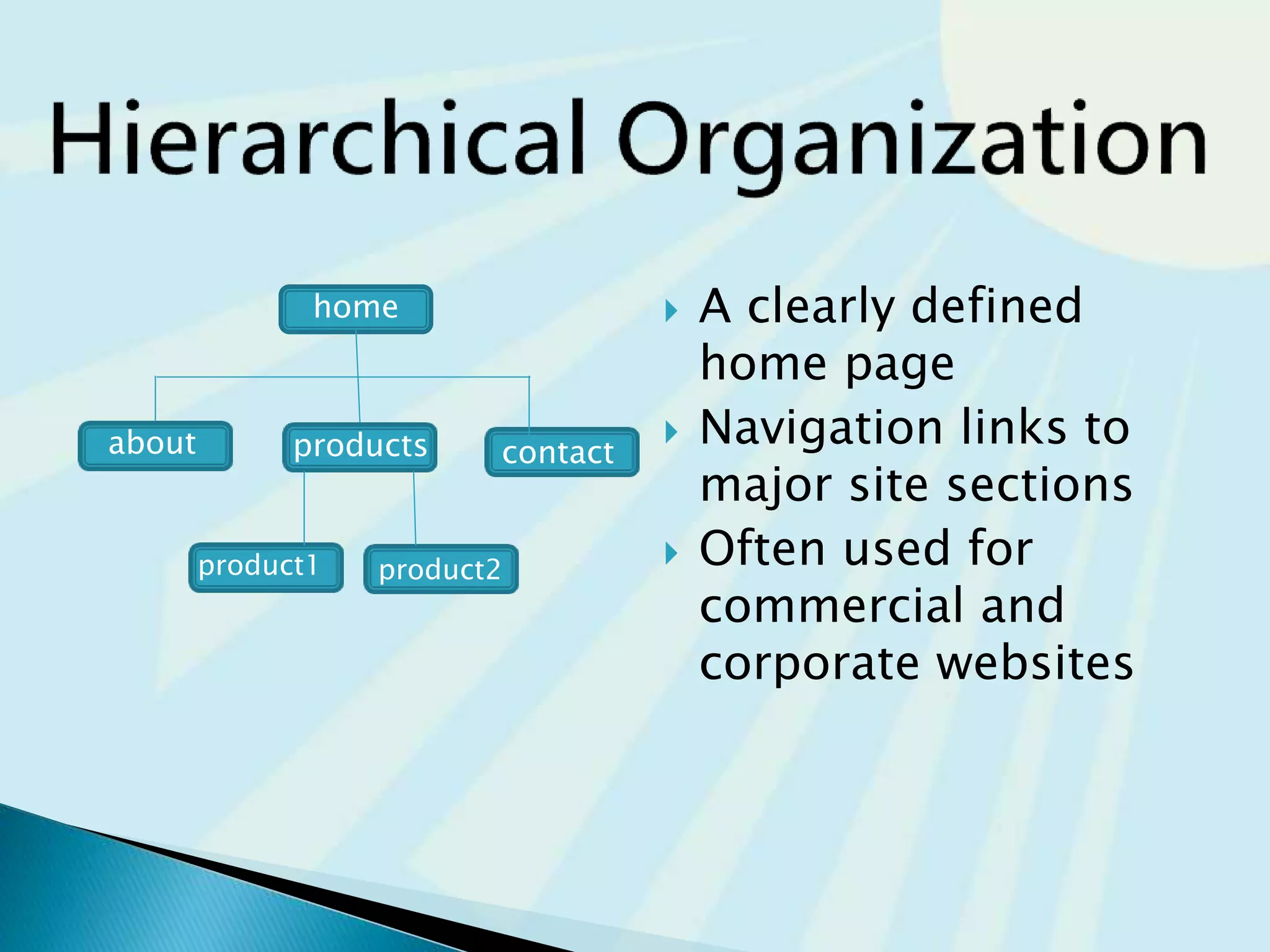
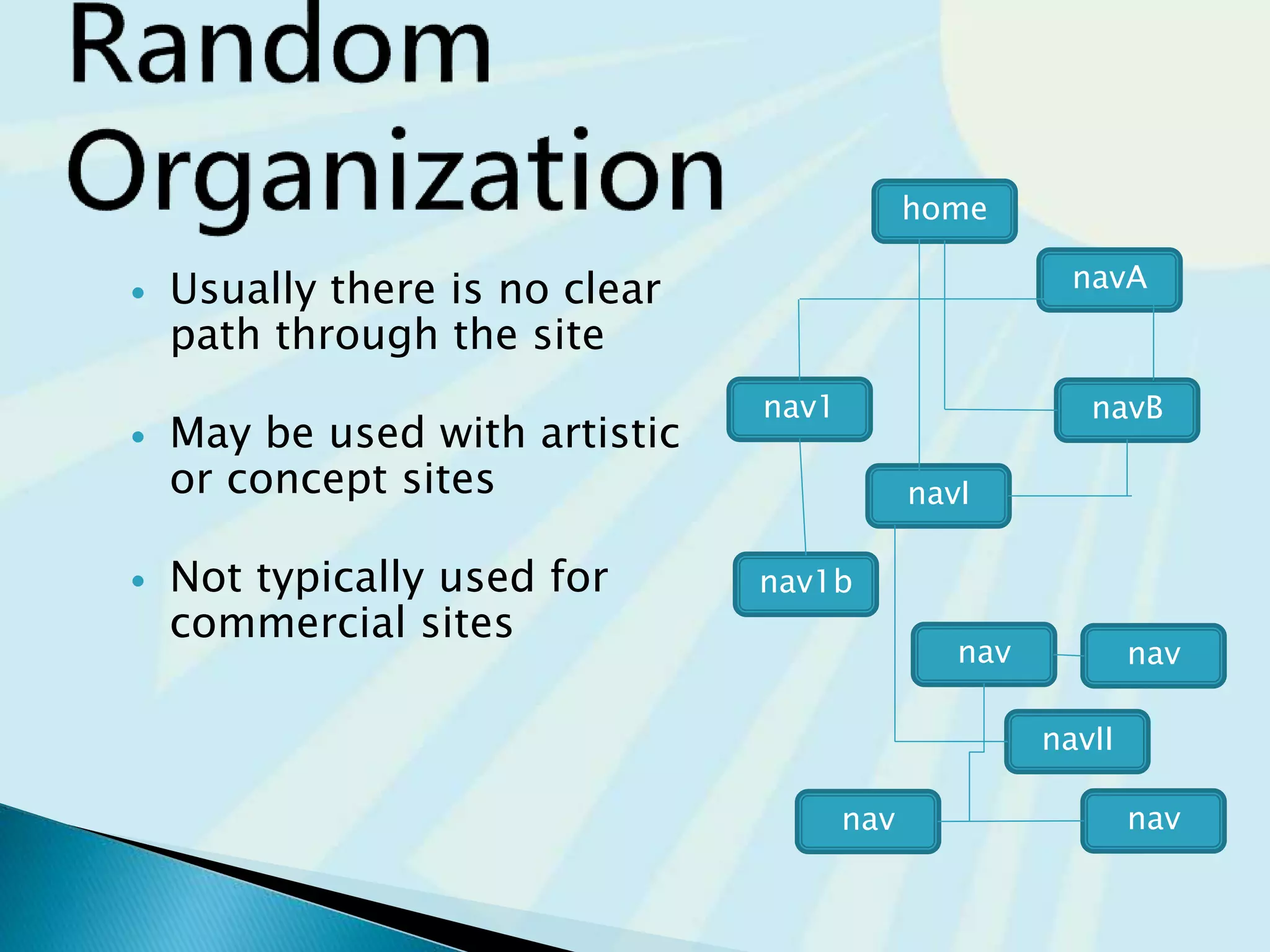
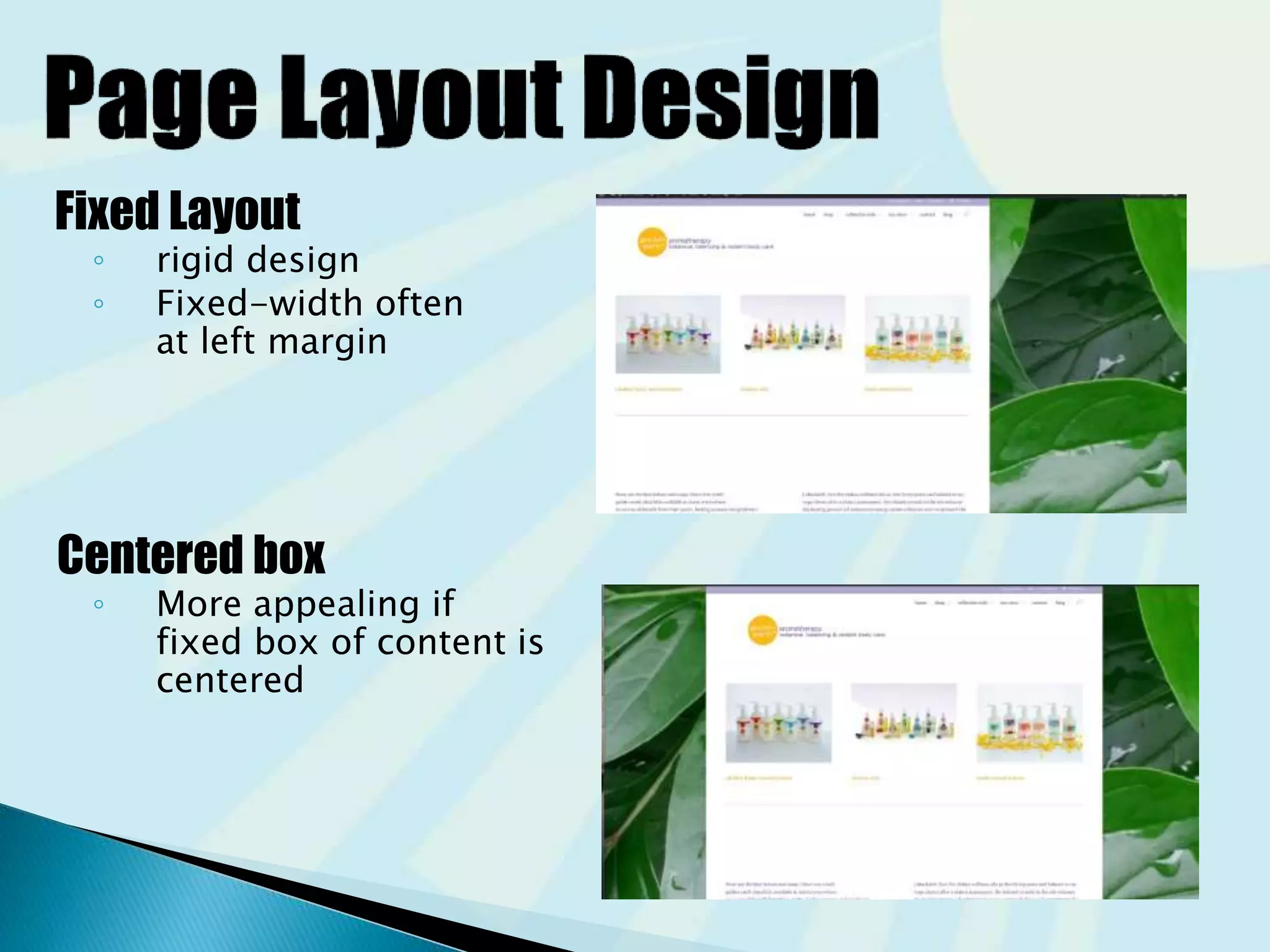
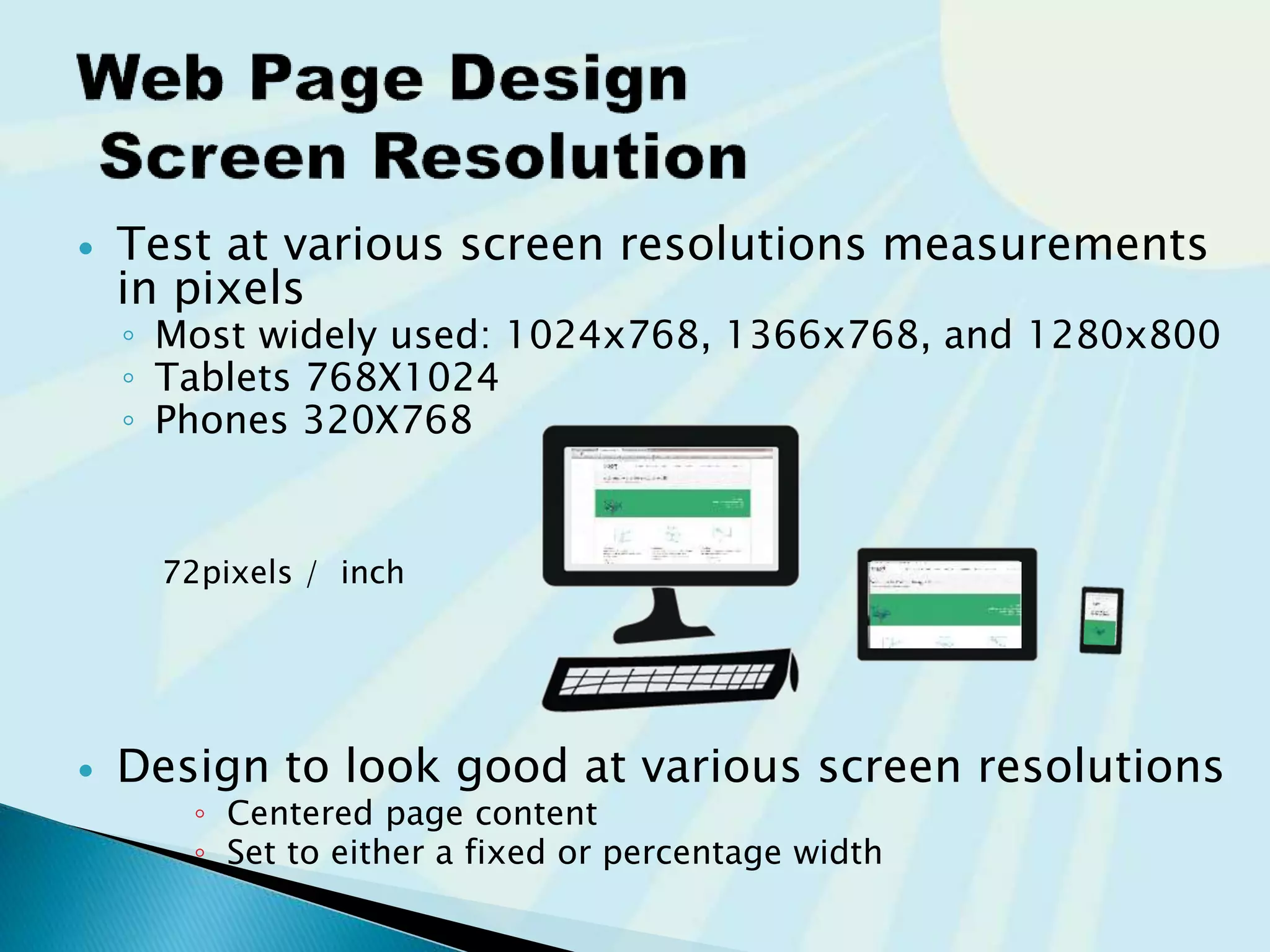
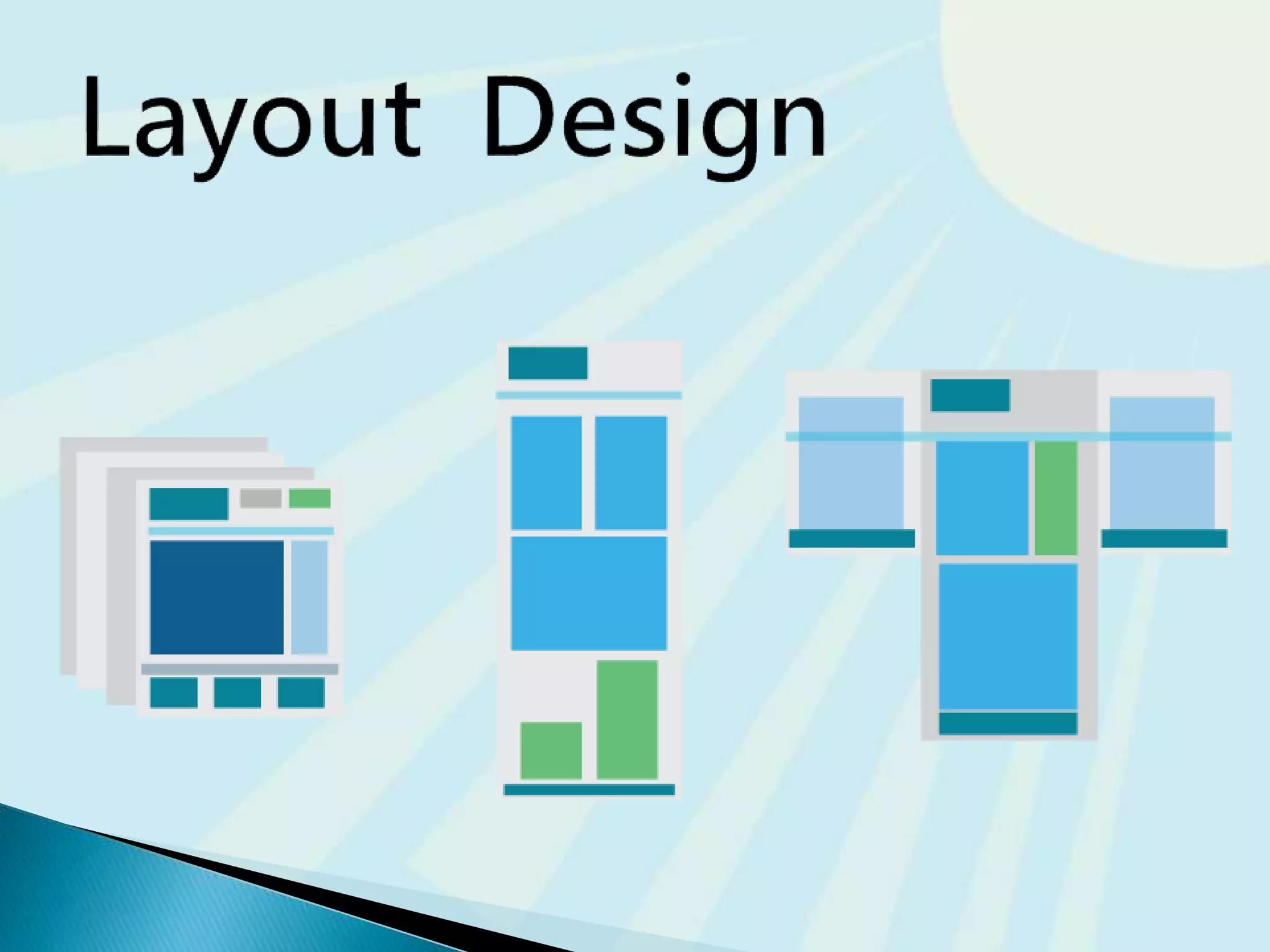
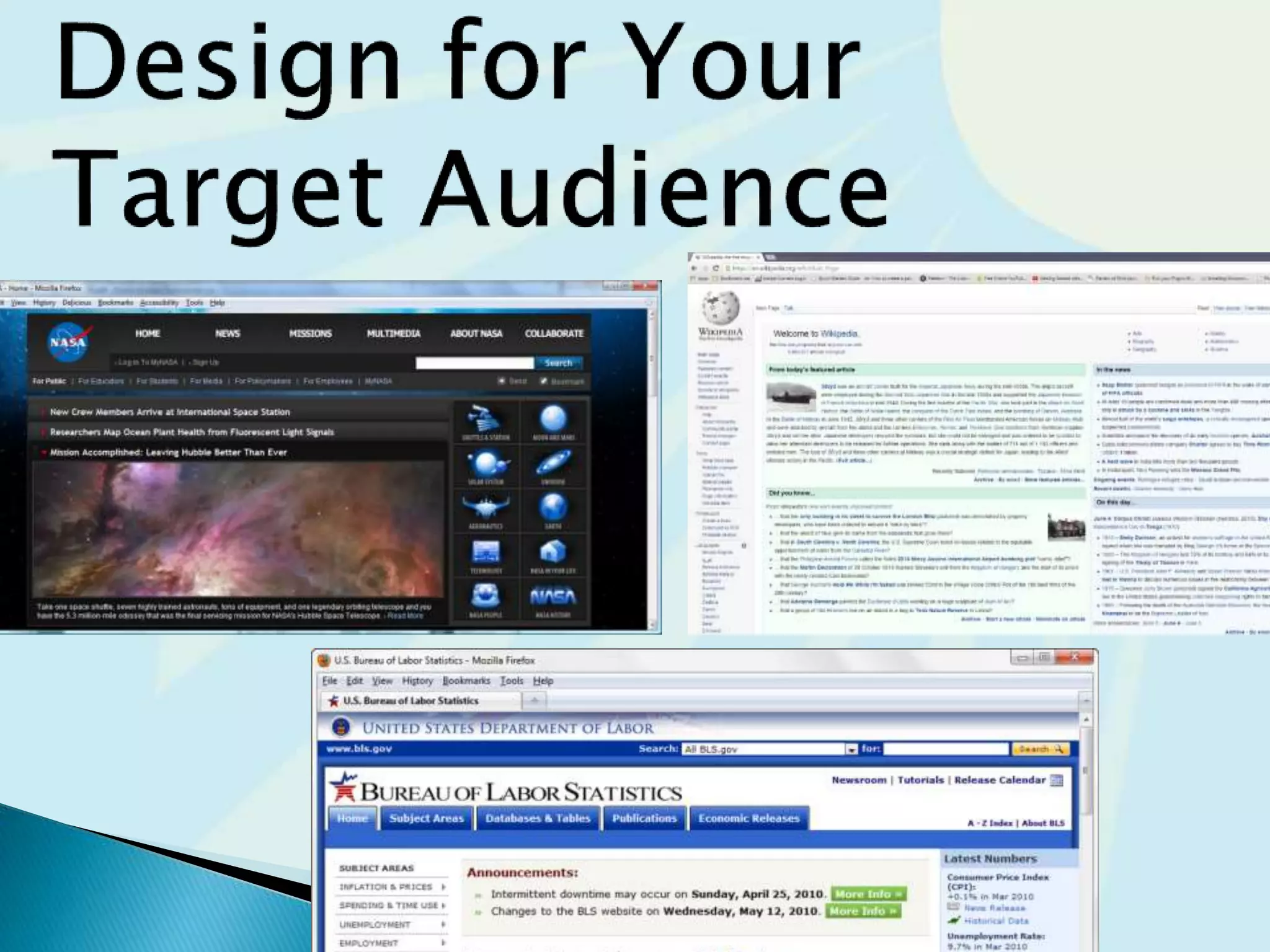
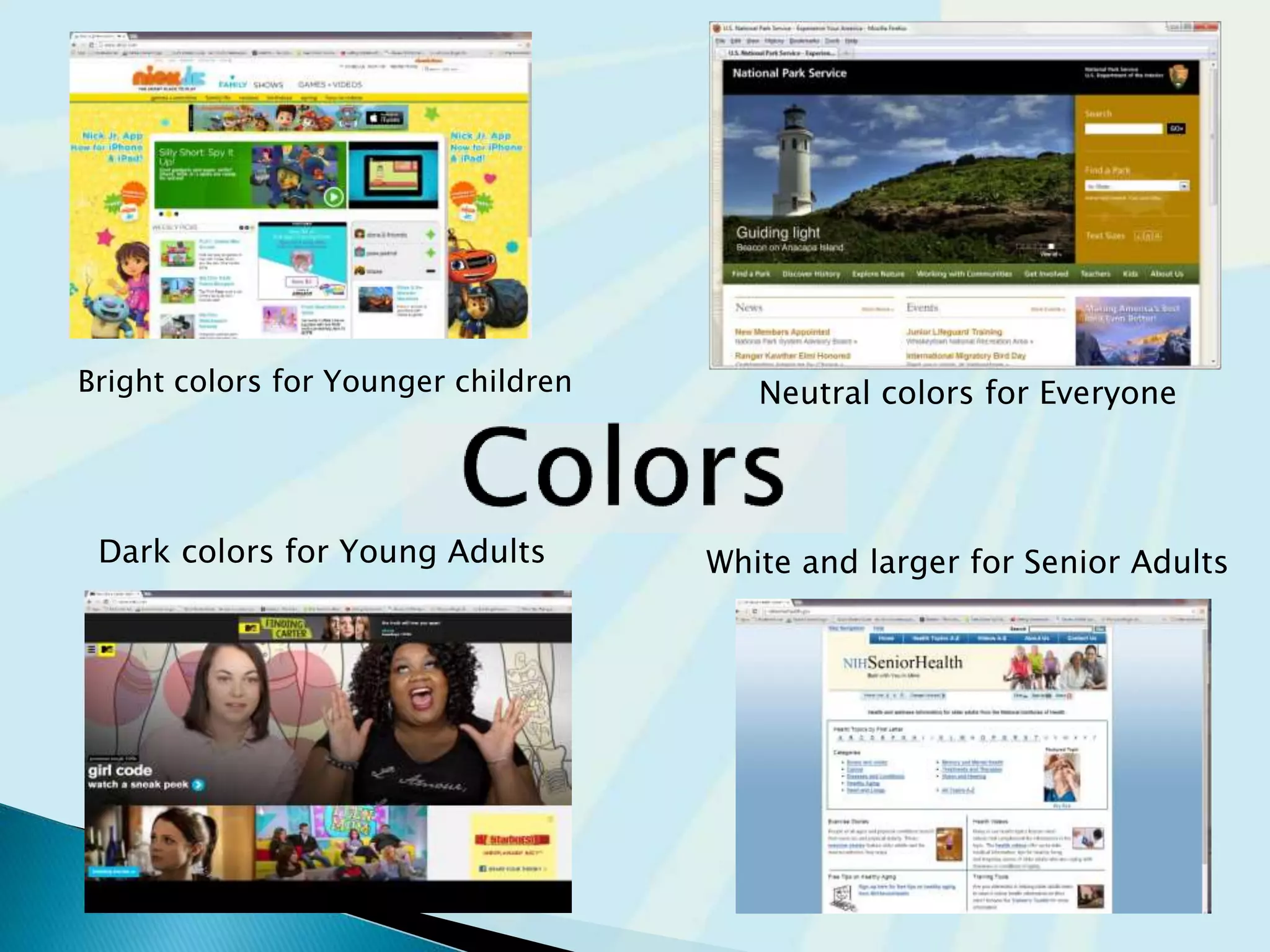
This document provides guidance on questions to answer and considerations to make before building a website. It discusses researching the target audience and goals for the site. Key topics covered include page layout, design elements, content types, navigation structures, and usability best practices. The document emphasizes planning content before design and ensuring the site is accessible on different devices.