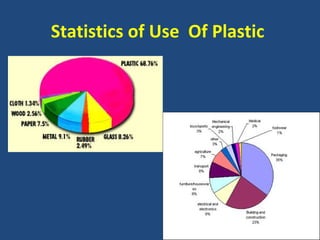
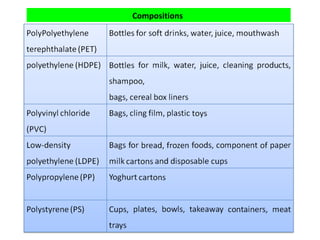
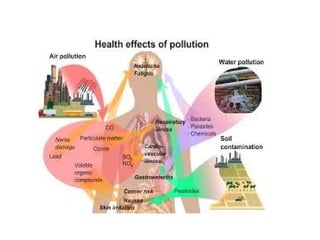
This presentation discusses the growing issue of plastic pollution and its effects on the environment. It notes that human civilization has progressed through Stone, Bronze, and Iron Ages, and are now in the Plastic Age. Plastic is widely used for various domestic, medical, agricultural, and industrial purposes. However, plastic waste pollutes the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Microplastics in particular enter the oceans and aquatic food chains, threatening biodiversity. Burning plastic releases toxic gases that pollute air and contribute to climate change. Potential solutions discussed include banning certain plastics, promoting bioplastics and alternative materials, and developing plastic-degrading enzymes.