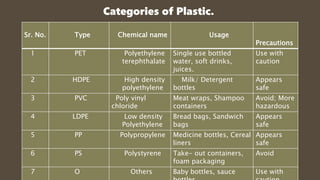
This document discusses plastics and plastic pollution. It begins by defining plastics as a formless material made from natural resources like petroleum and coal that can be molded into various shapes. Plastics are then categorized by type and usage. The document outlines the negative impacts of plastic production and pollution, including releasing toxins during manufacturing and disposal that enter the food chain and cause health problems. It notes plastic pollution spoils land, water and air. The summary concludes by providing the "4 R's" approach to prevent plastic pollution: refuse, reduce, reuse, and recycle.