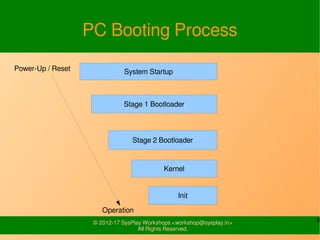
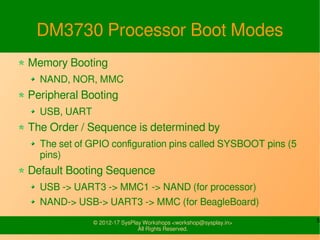
The document discusses the booting process of the BeagleBoard. It explains that the ROM code first loads the x-loader (MLO) which performs external DRAM configuration. The x-loader then loads U-Boot by default from the SD card. U-Boot executes default environment commands which load the kernel by default from the second partition of the SD card. The kernel then reads the root filesystem.



















![23© 2012-14 SysPlay Workshops <workshop@sysplay.in>
All Rights Reserved.
Adding the Command in uboot
Create the file cmd_<file>.c
Fill the Macro 'U_BOOT_CMD()'
name : the name of the command
maxargs: the maximum number of arguments this function takes
command : function pointer (*cmd)(struct cmd_tbl_s *, int, int, char
*[])
usage : Short Description
help : Long description
Add the entry into common/Makefile
COBJS-$(CONFIG_CMD_<NAME>) += cmd_<file>.o
Include the macro CONFIG_CMD_<NAME> in board.h file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beaglebootloaderbasic-170810110348/85/BeagleBoard-xM-Booting-Process-23-320.jpg)

