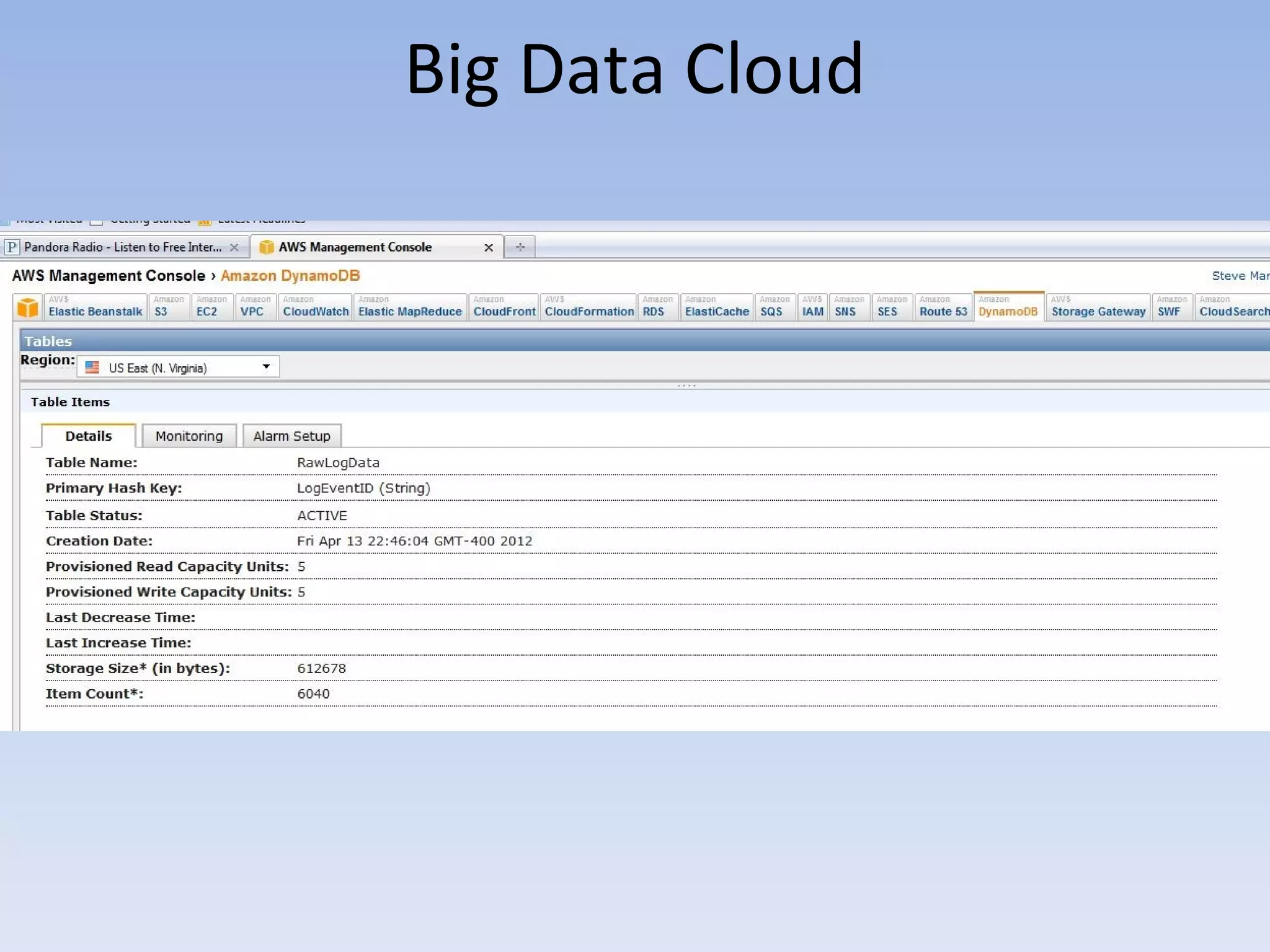
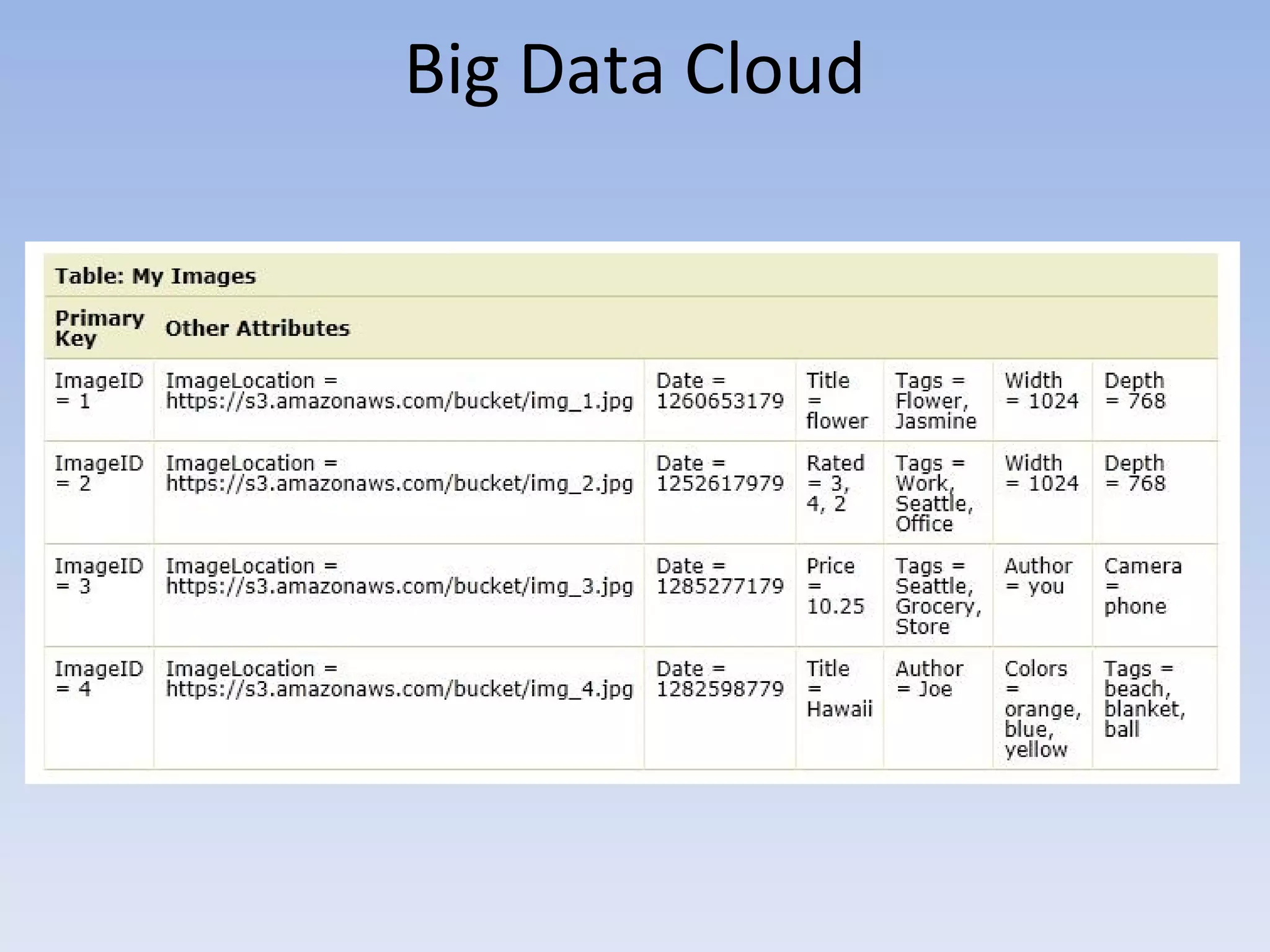
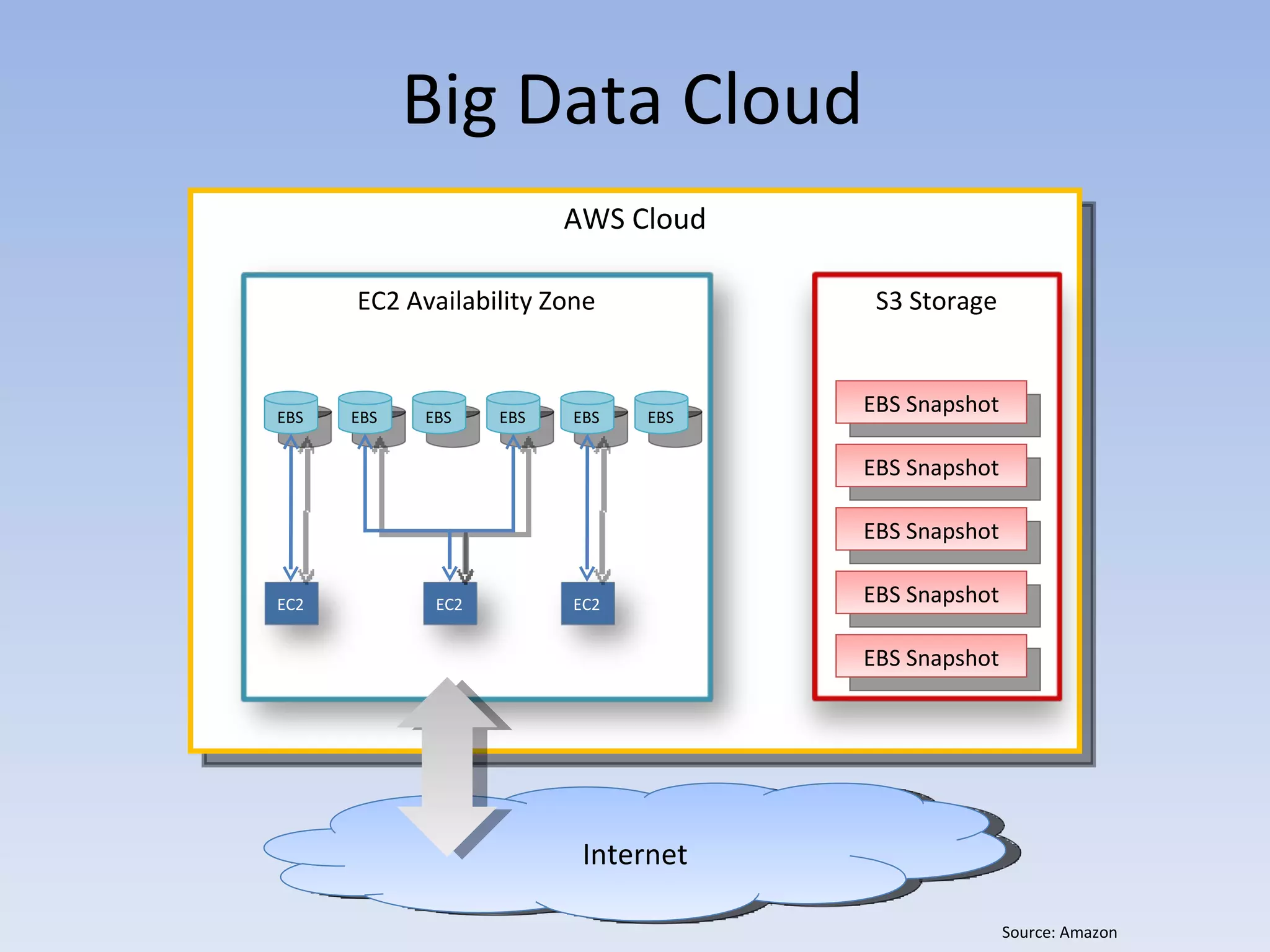
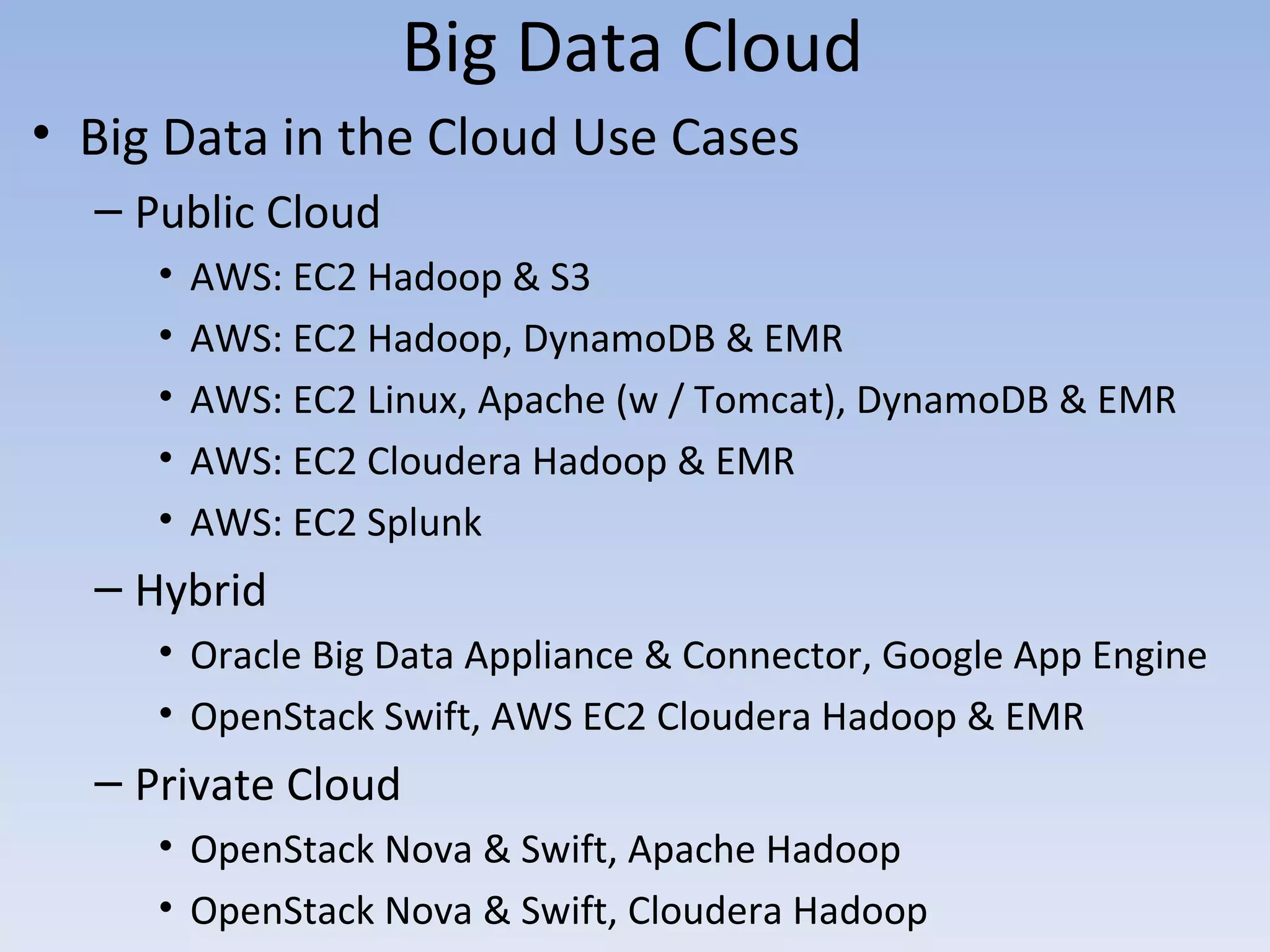
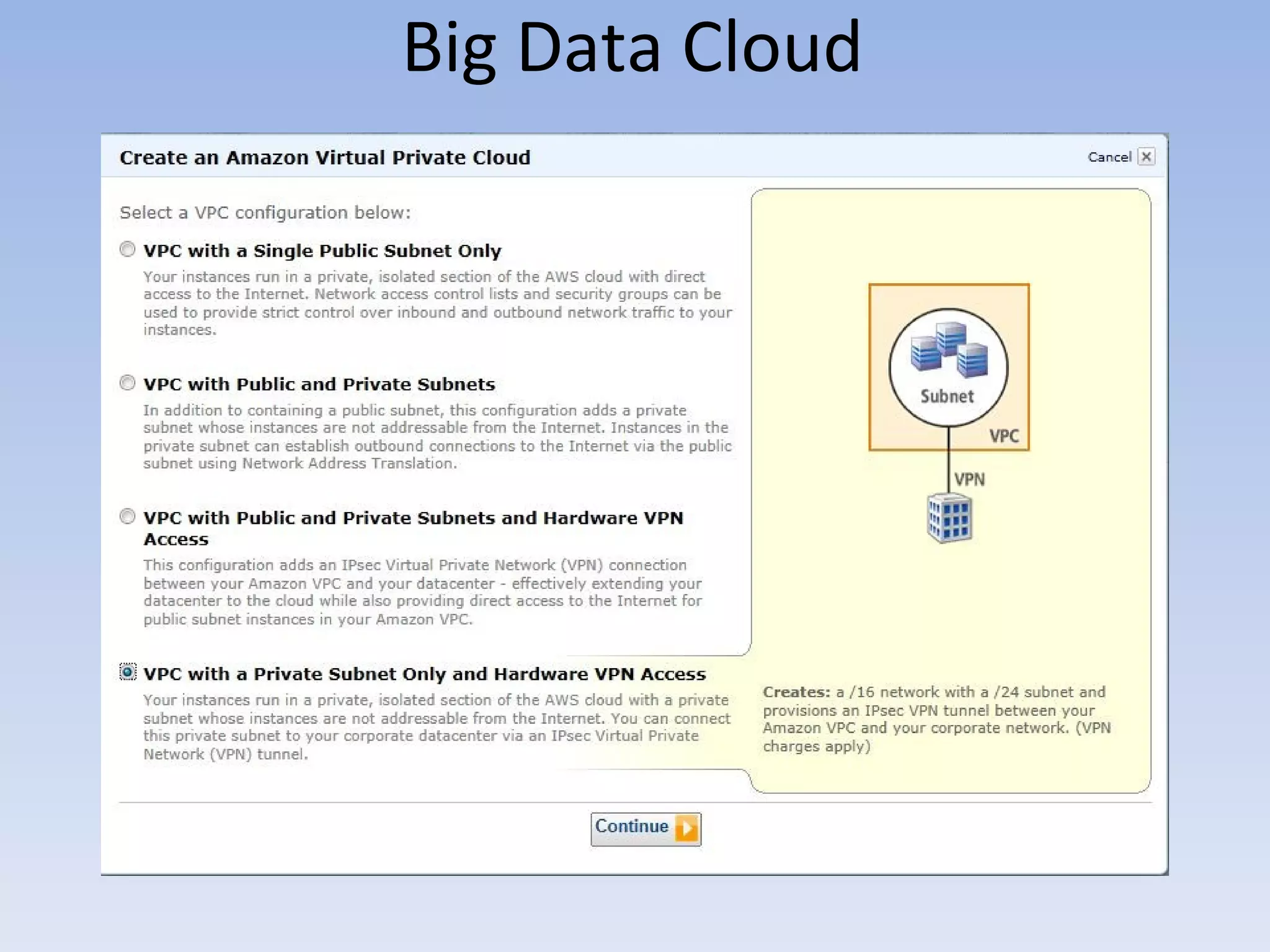
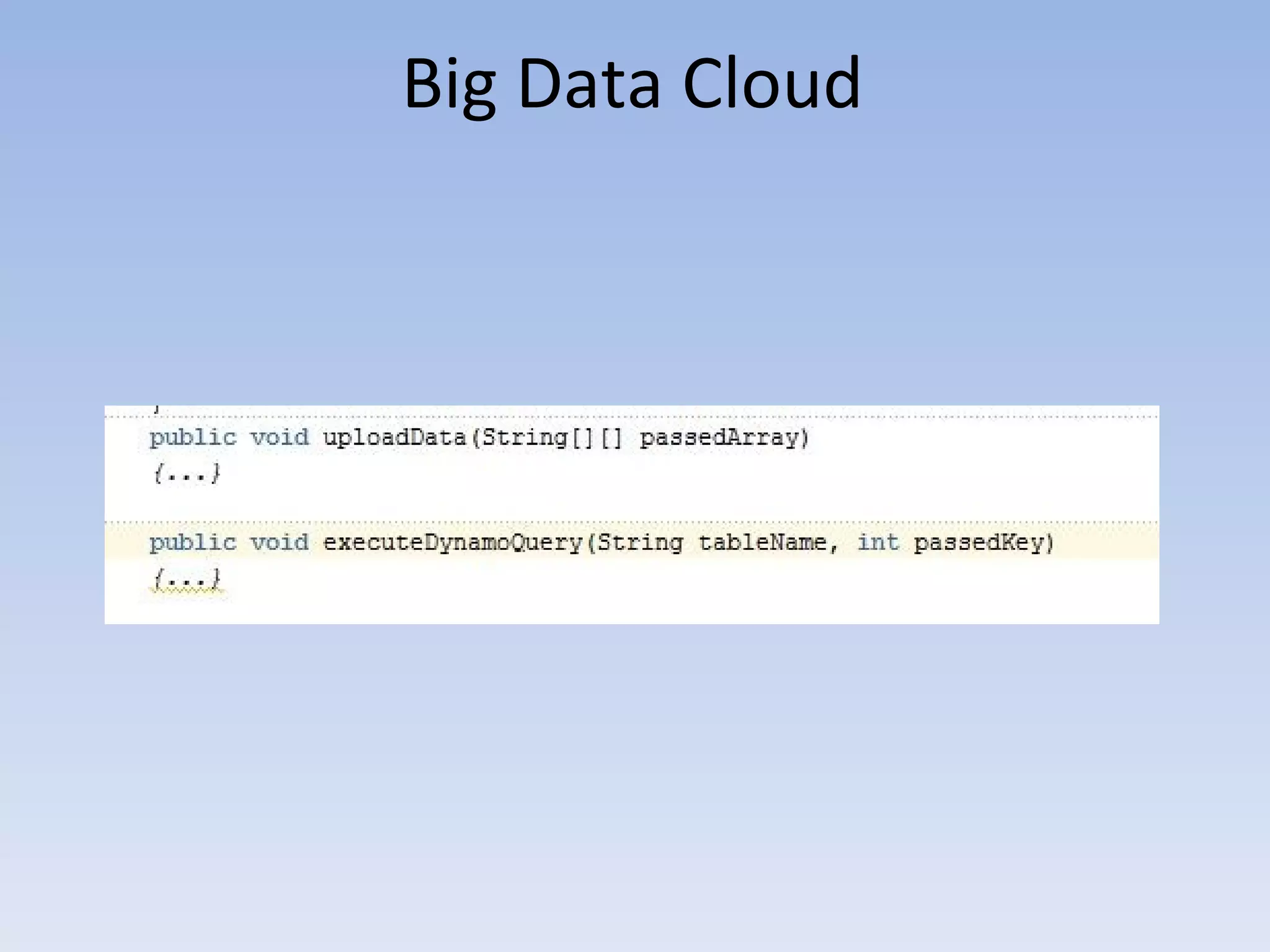
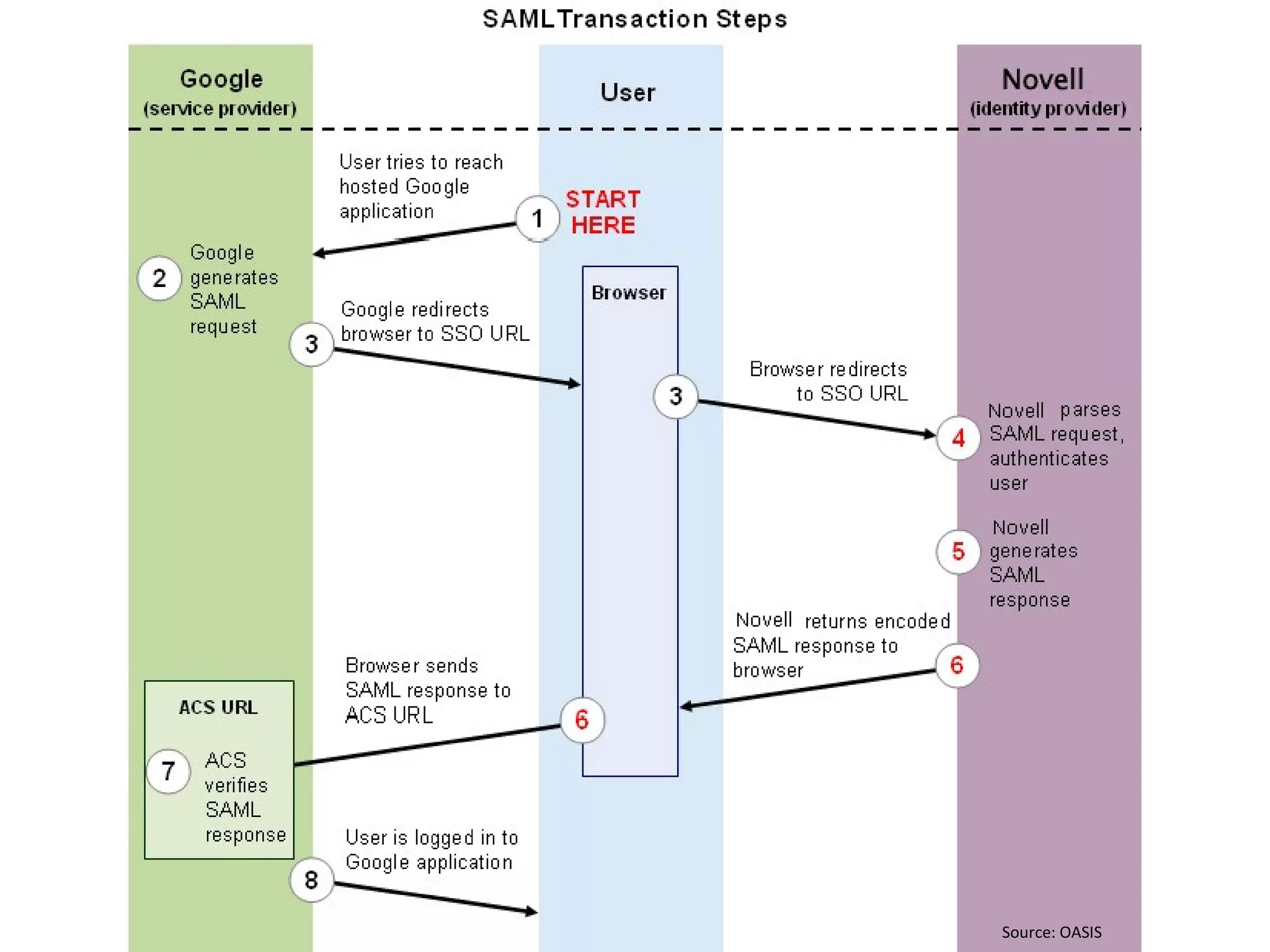
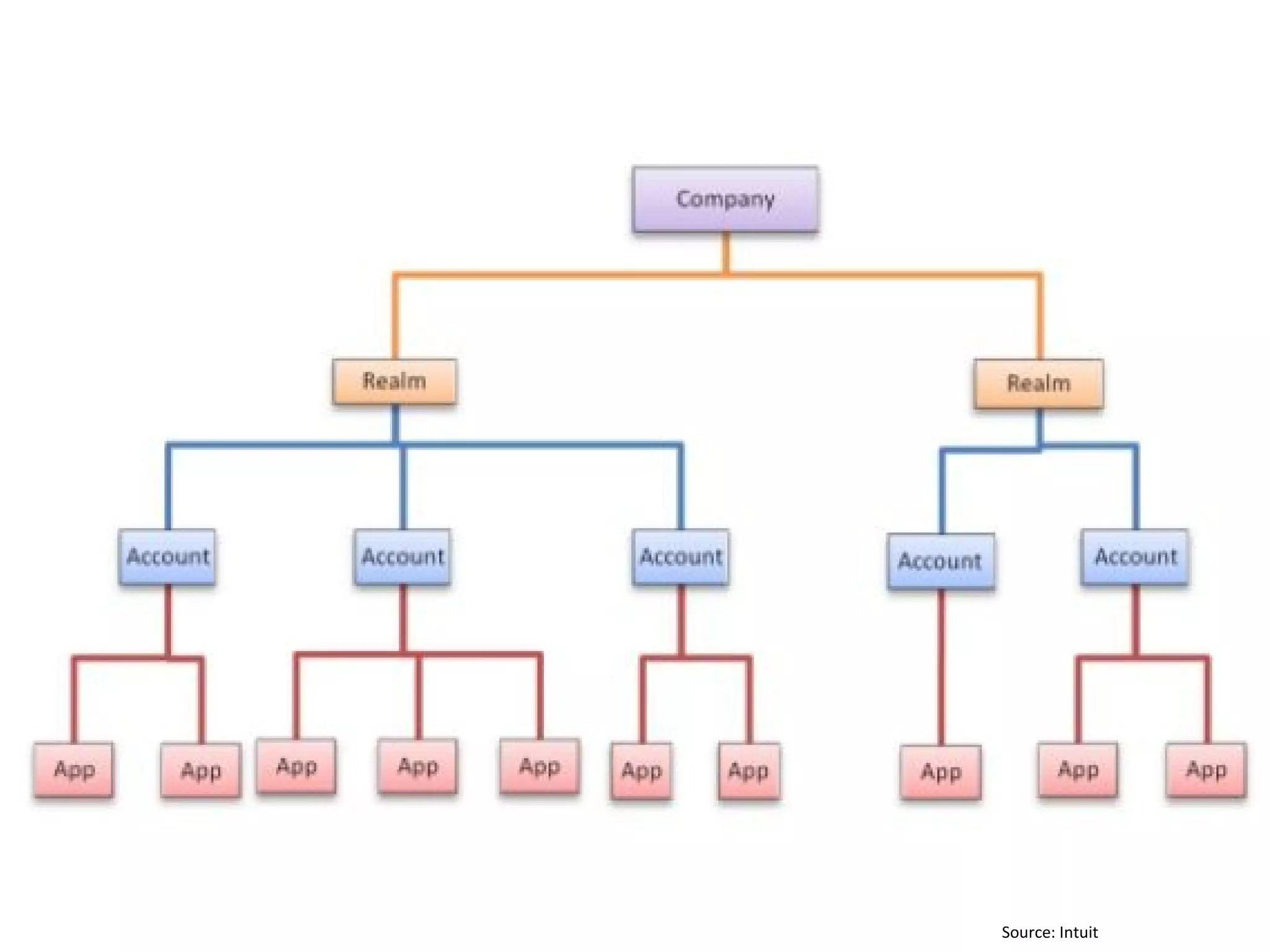
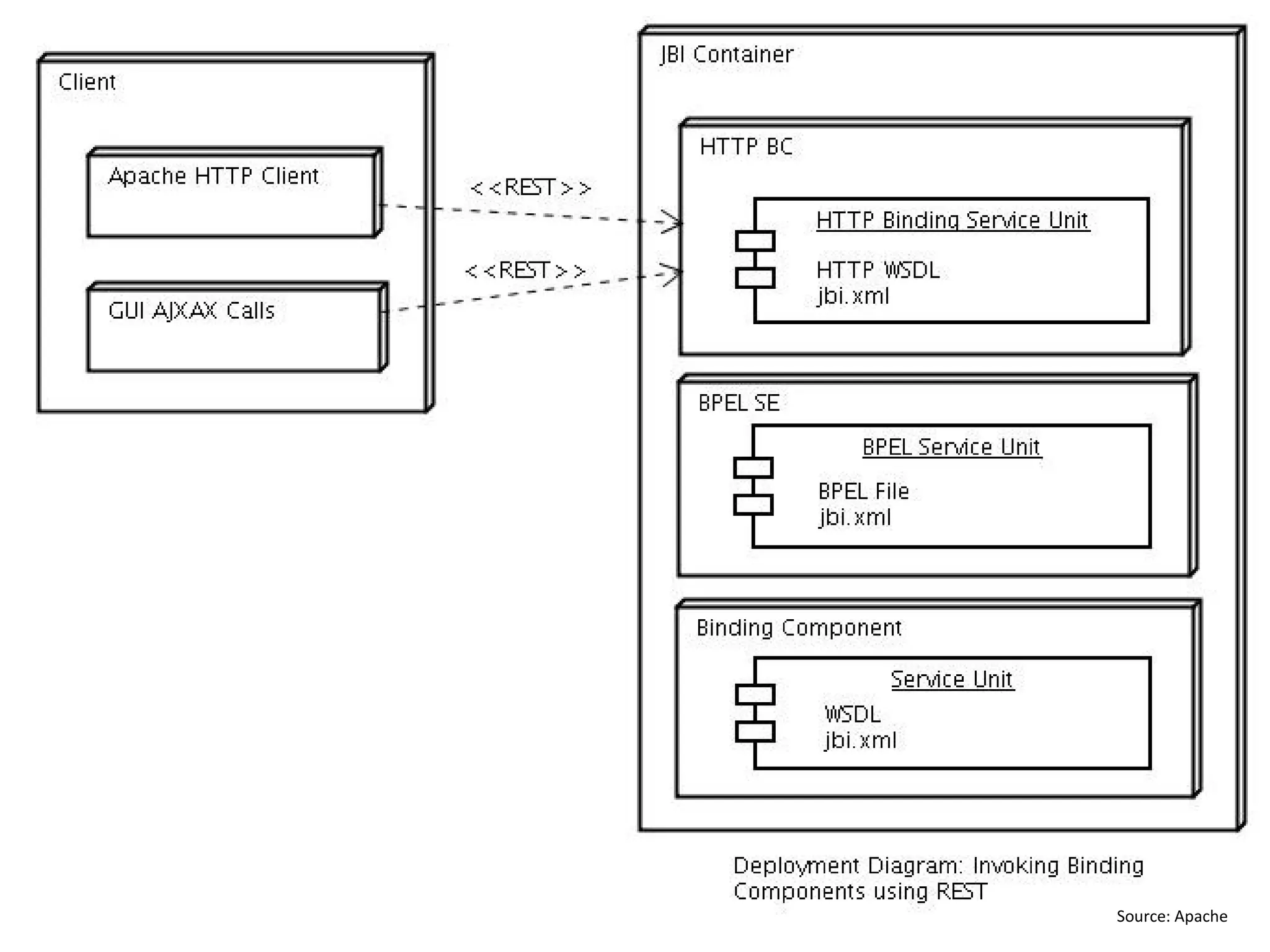
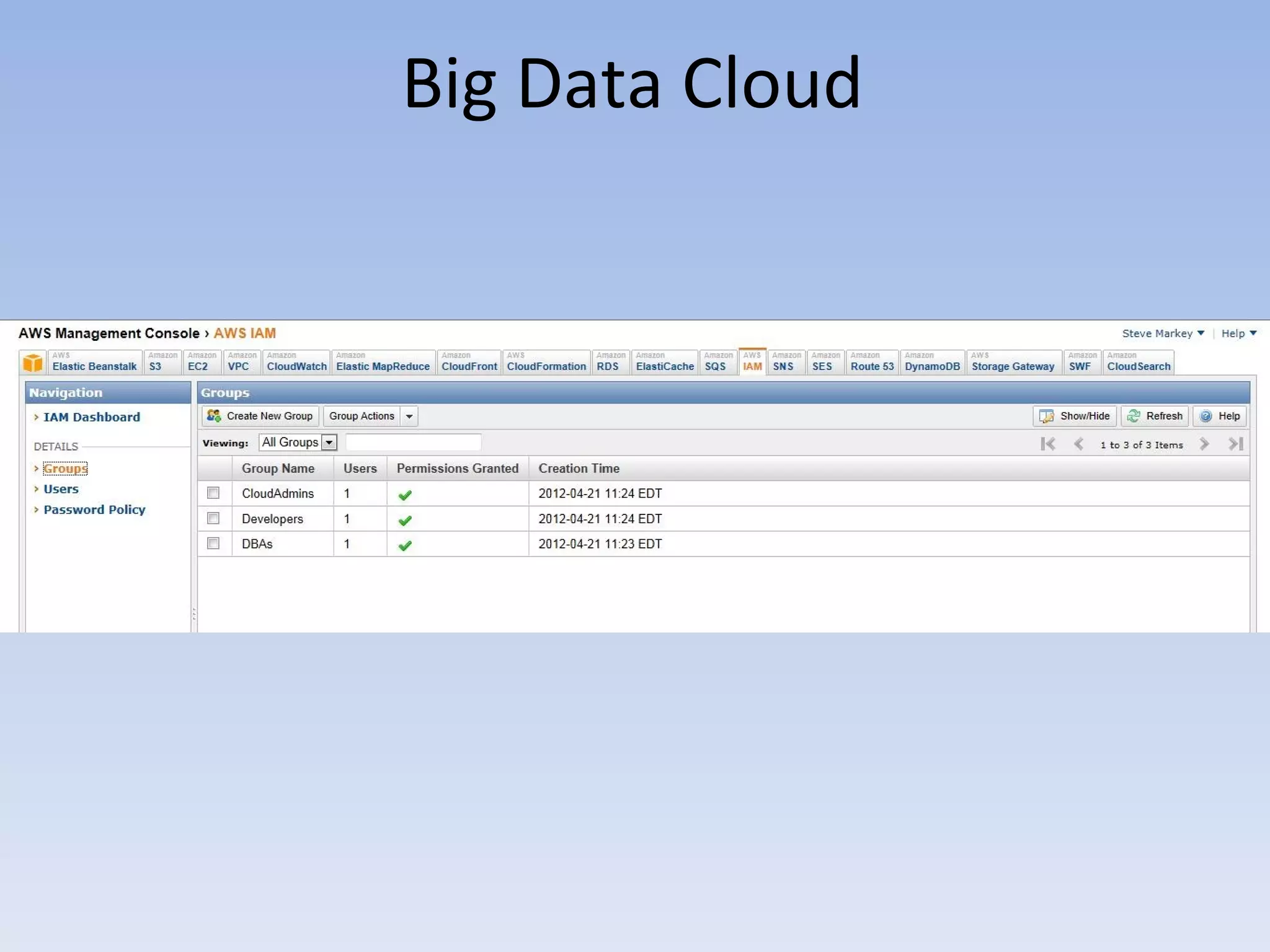
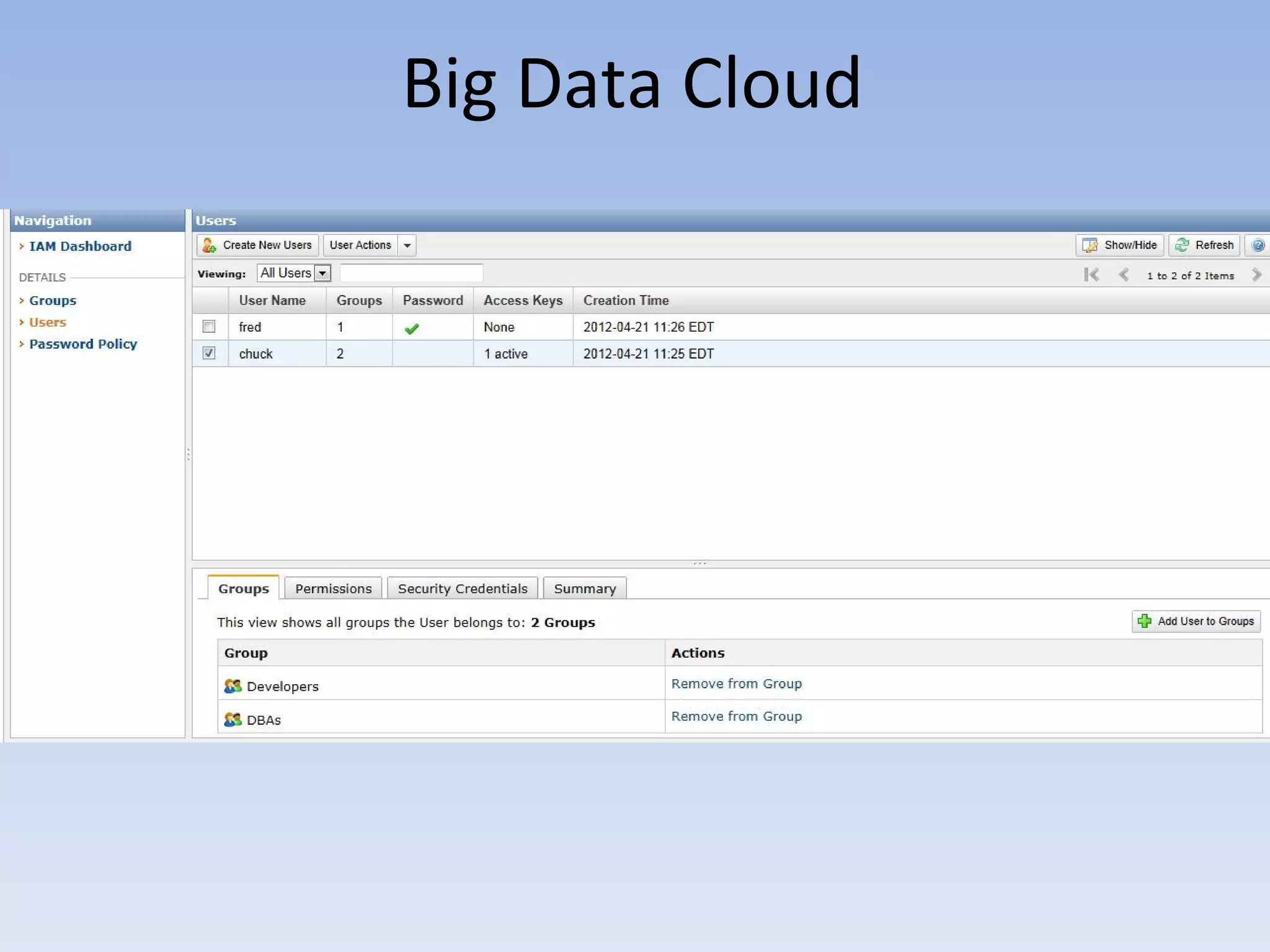
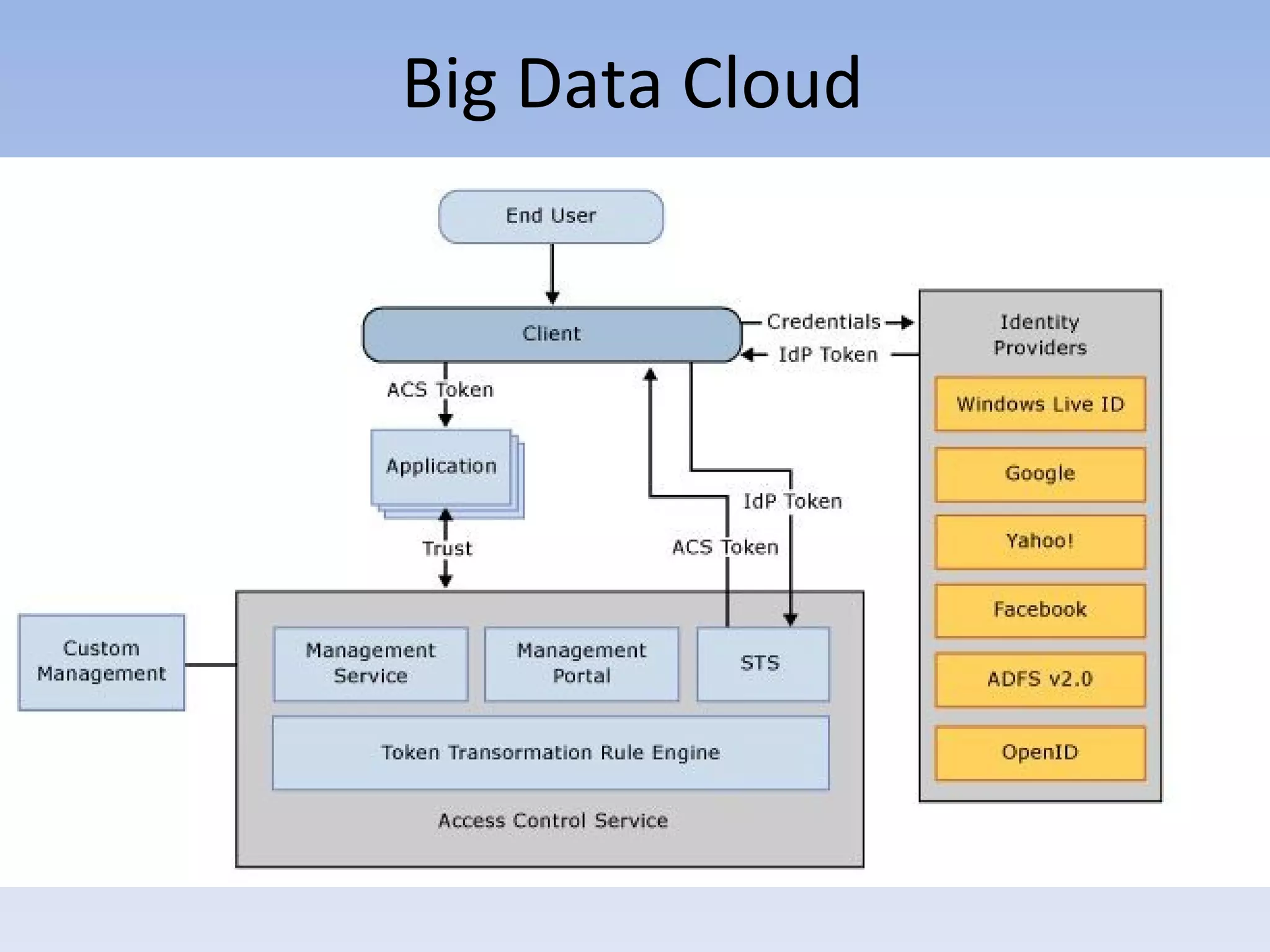
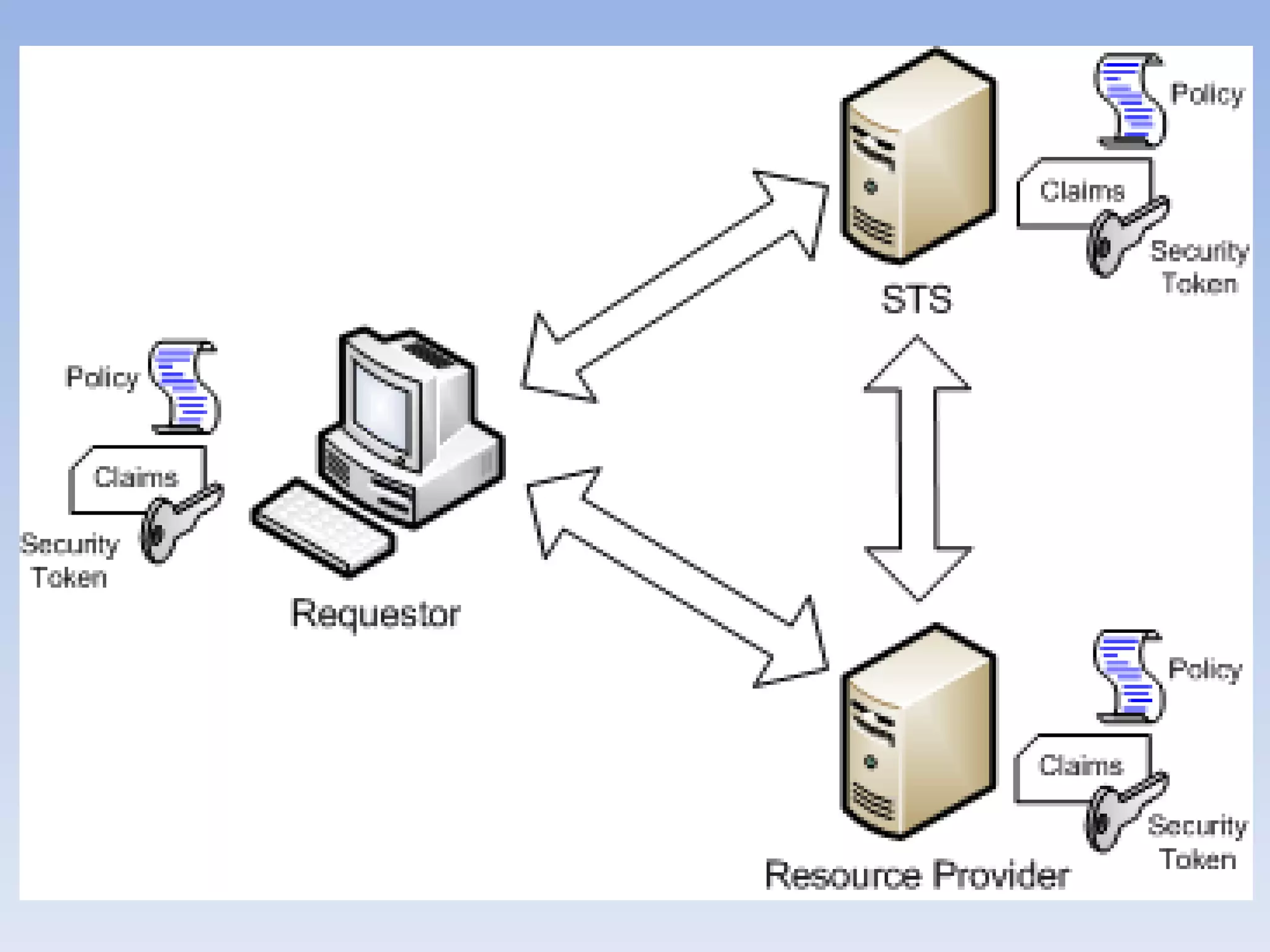
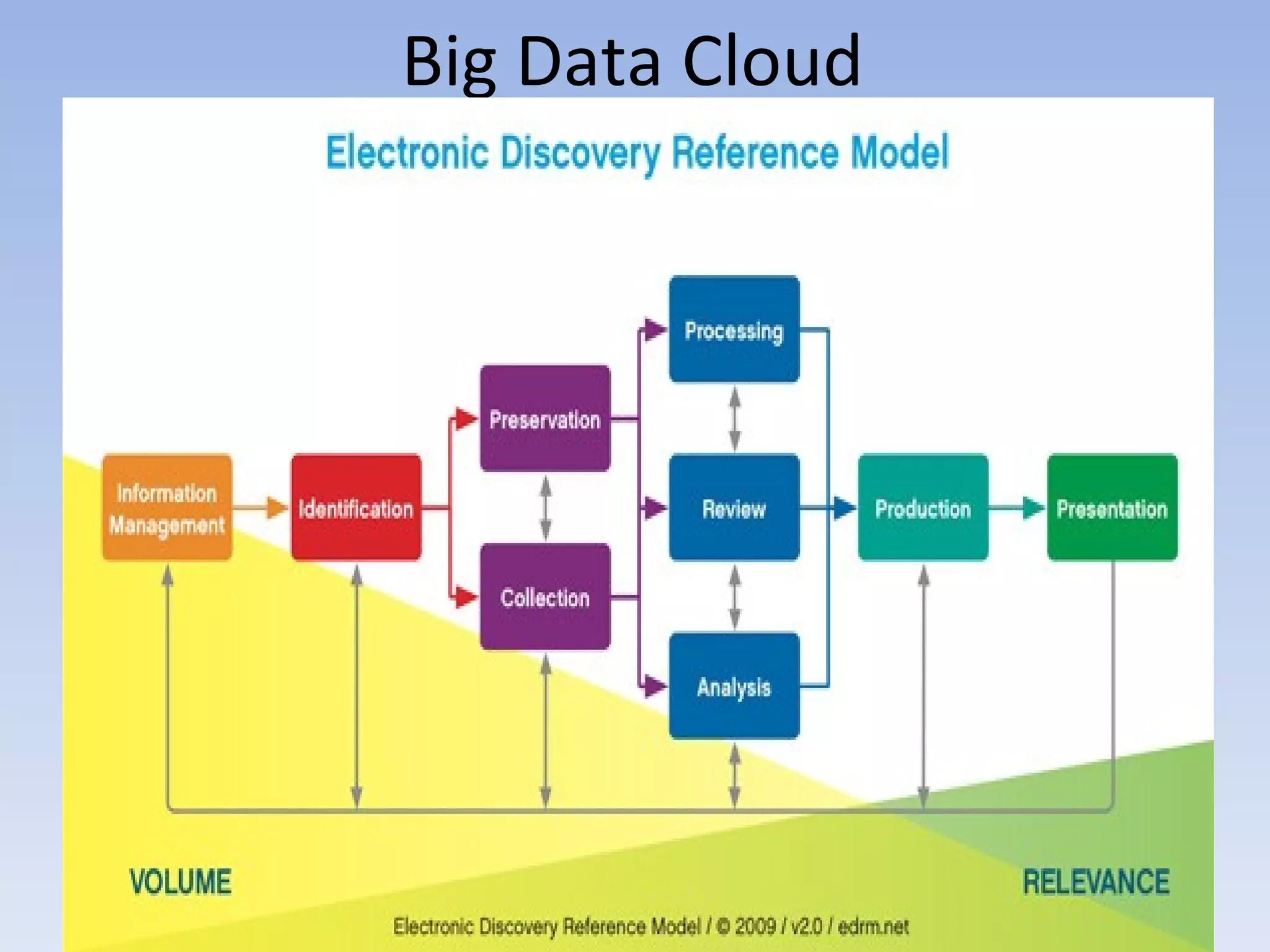
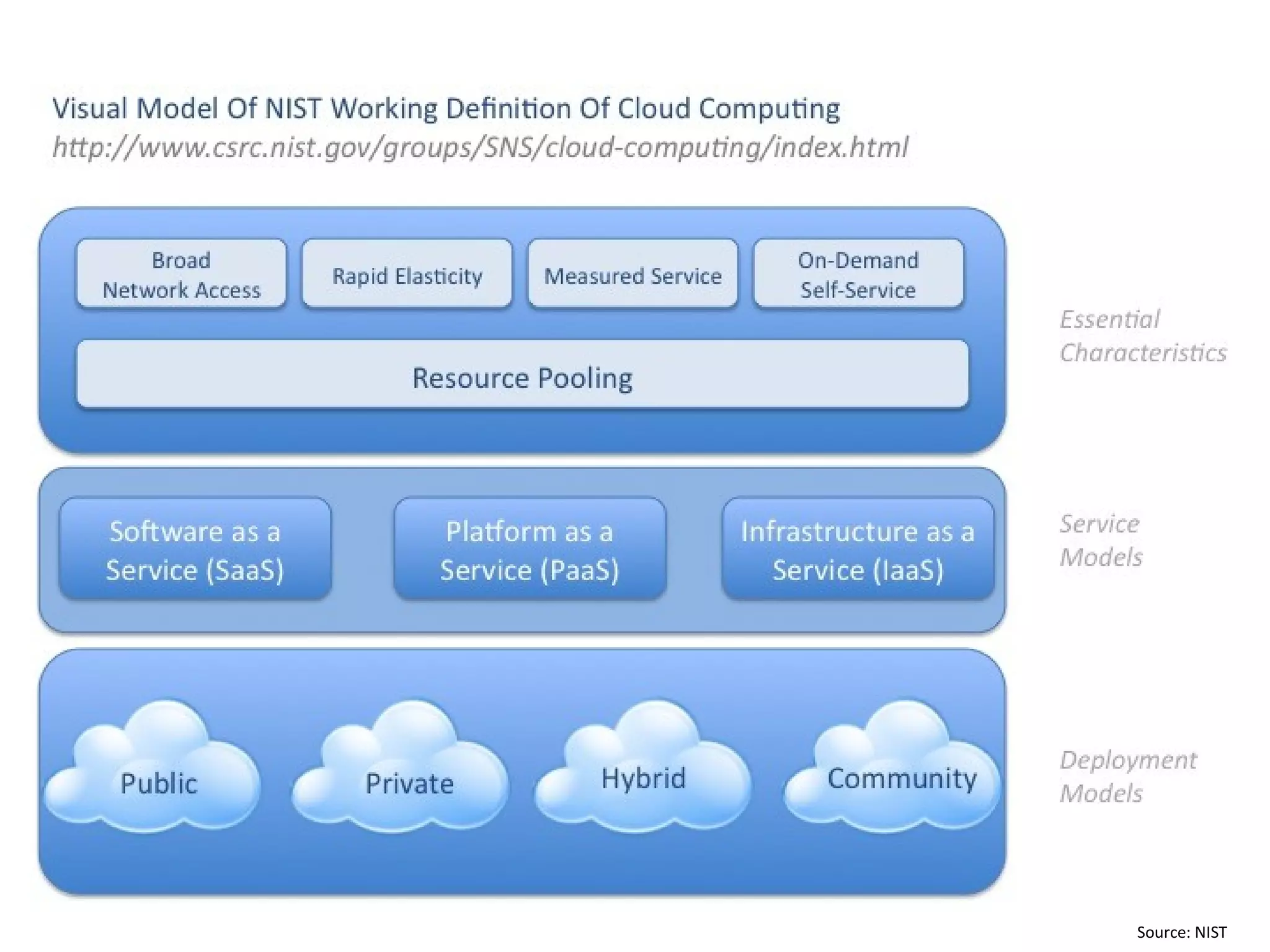
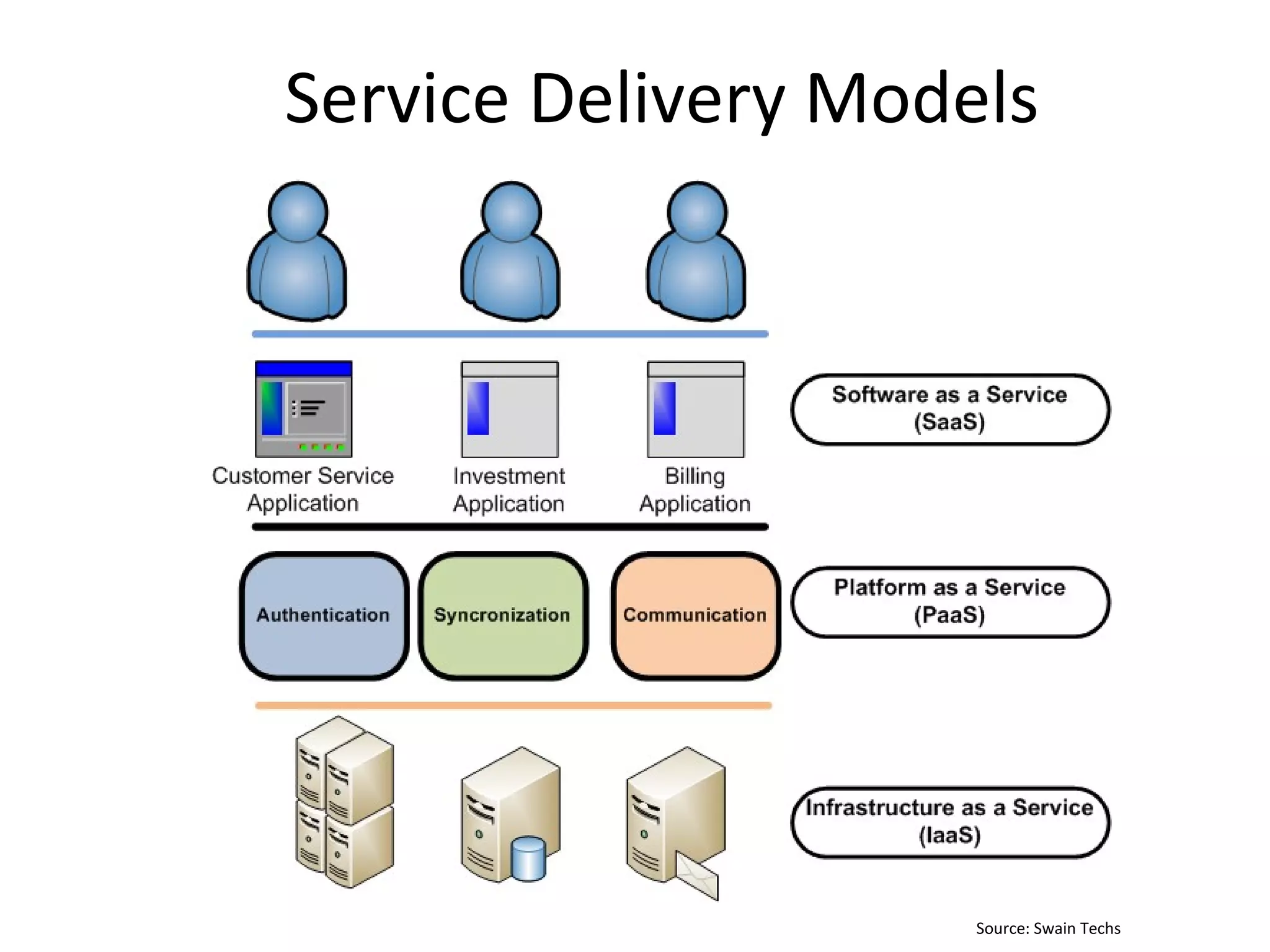
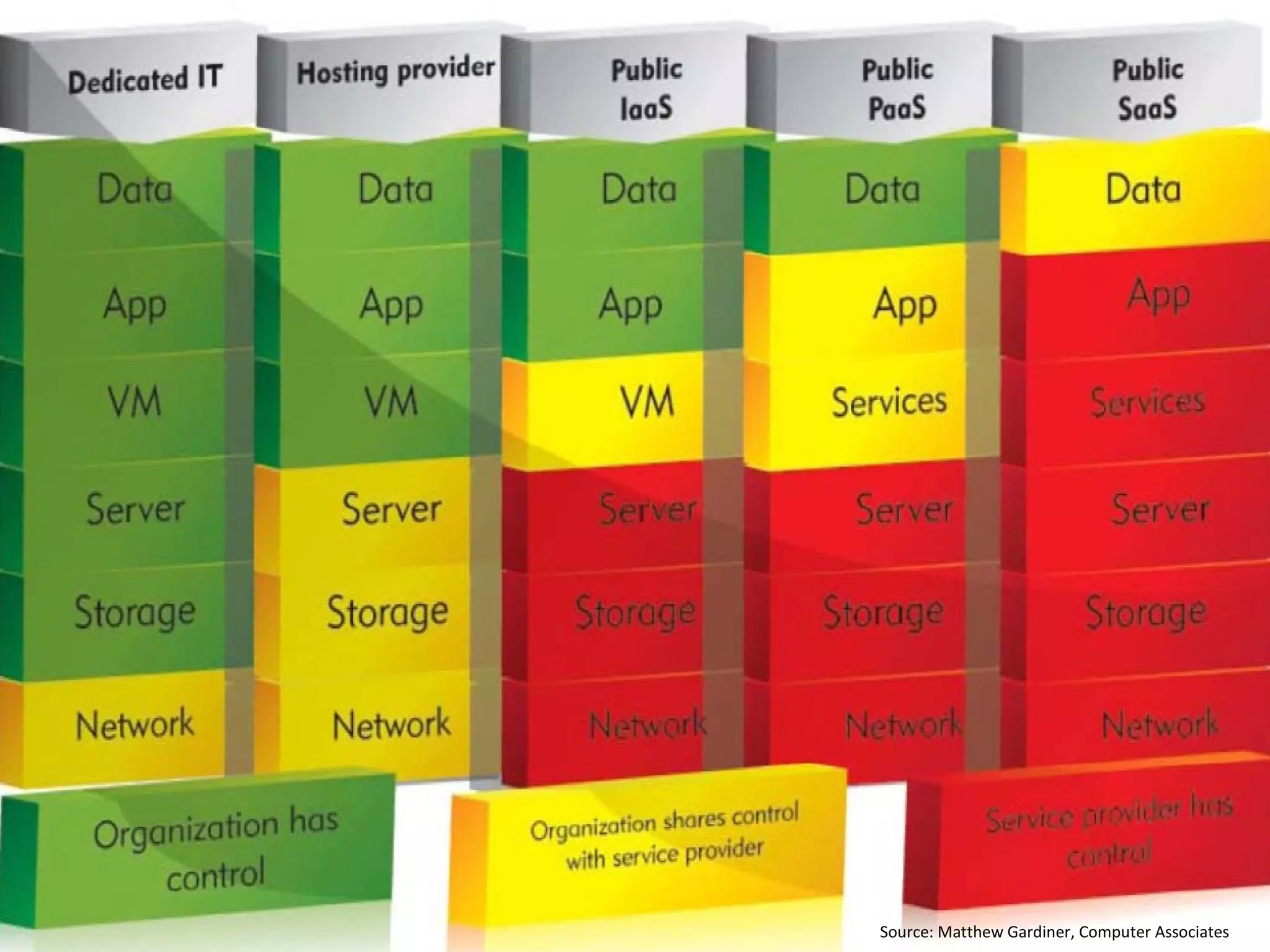
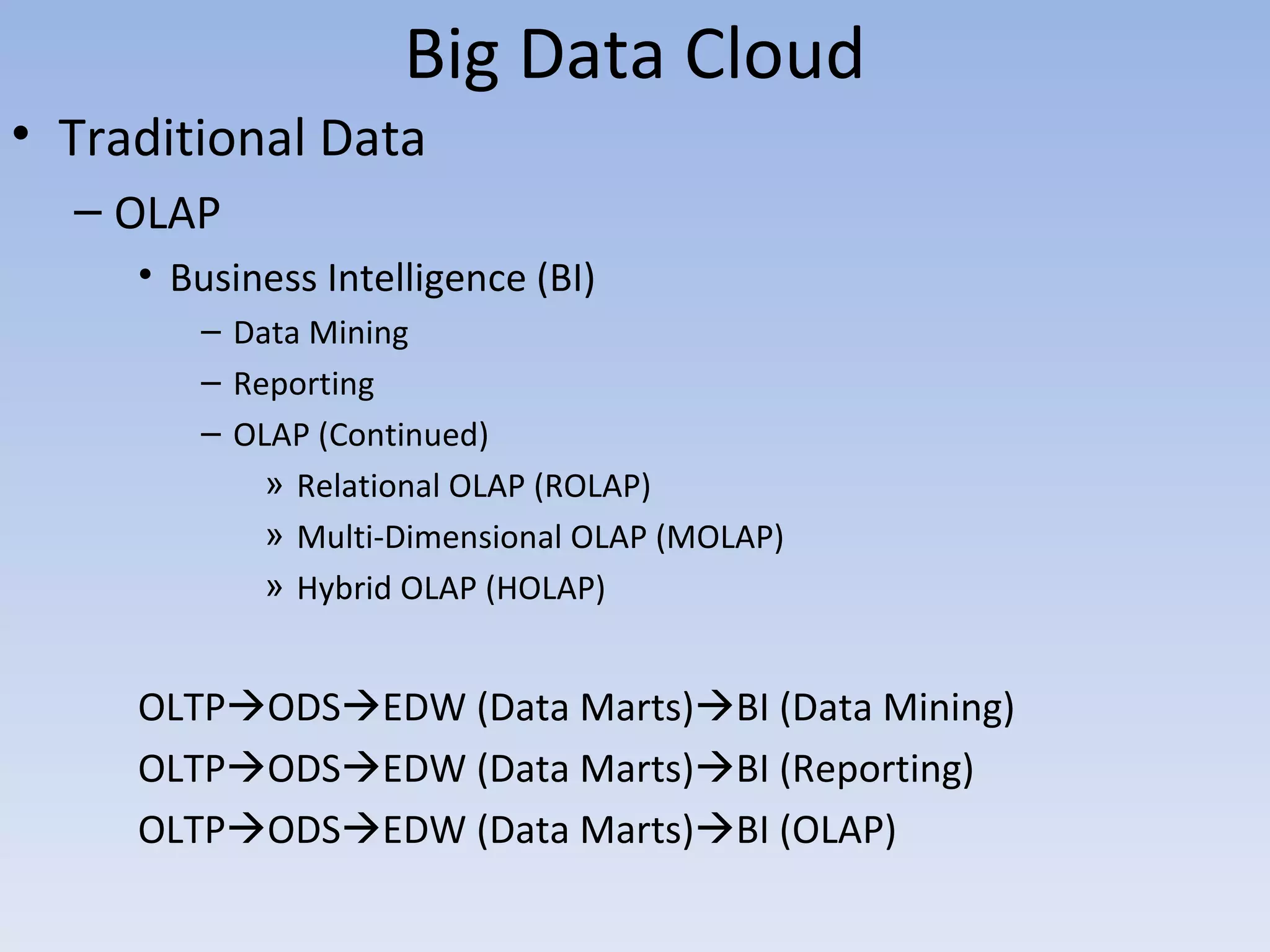
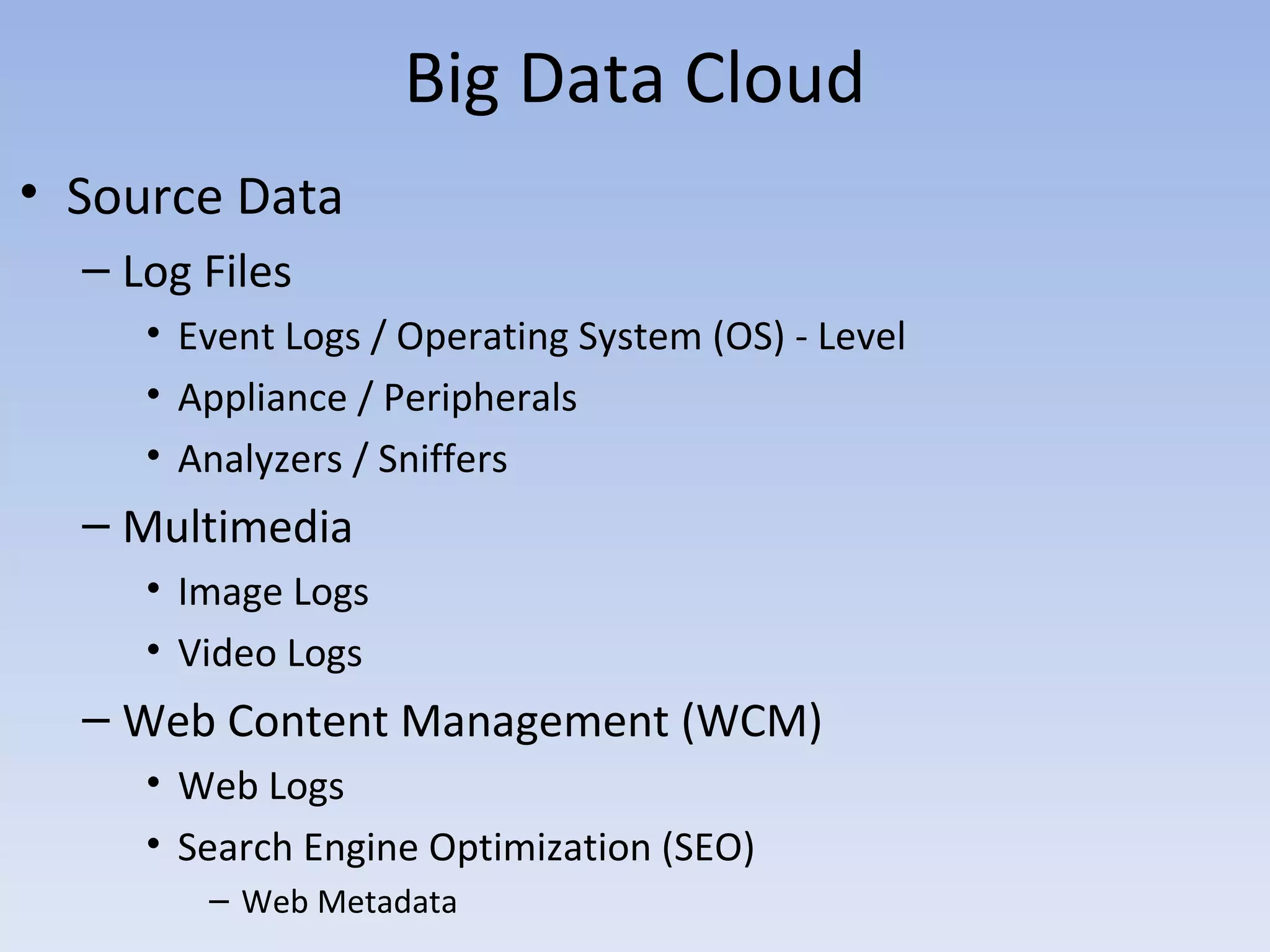
The document discusses big data and cloud computing. It provides an overview of big data sources and how data is aggregated and processed. It also discusses how cloud platforms can be leveraged for big data solutions, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS) offerings. Security considerations are also covered, such as identity and access management, electronic discovery, and privacy regulations. The presentation emphasizes that big data in the cloud requires secure implementation with access controls, logging, and separation of duties.








![Big Data Cloud
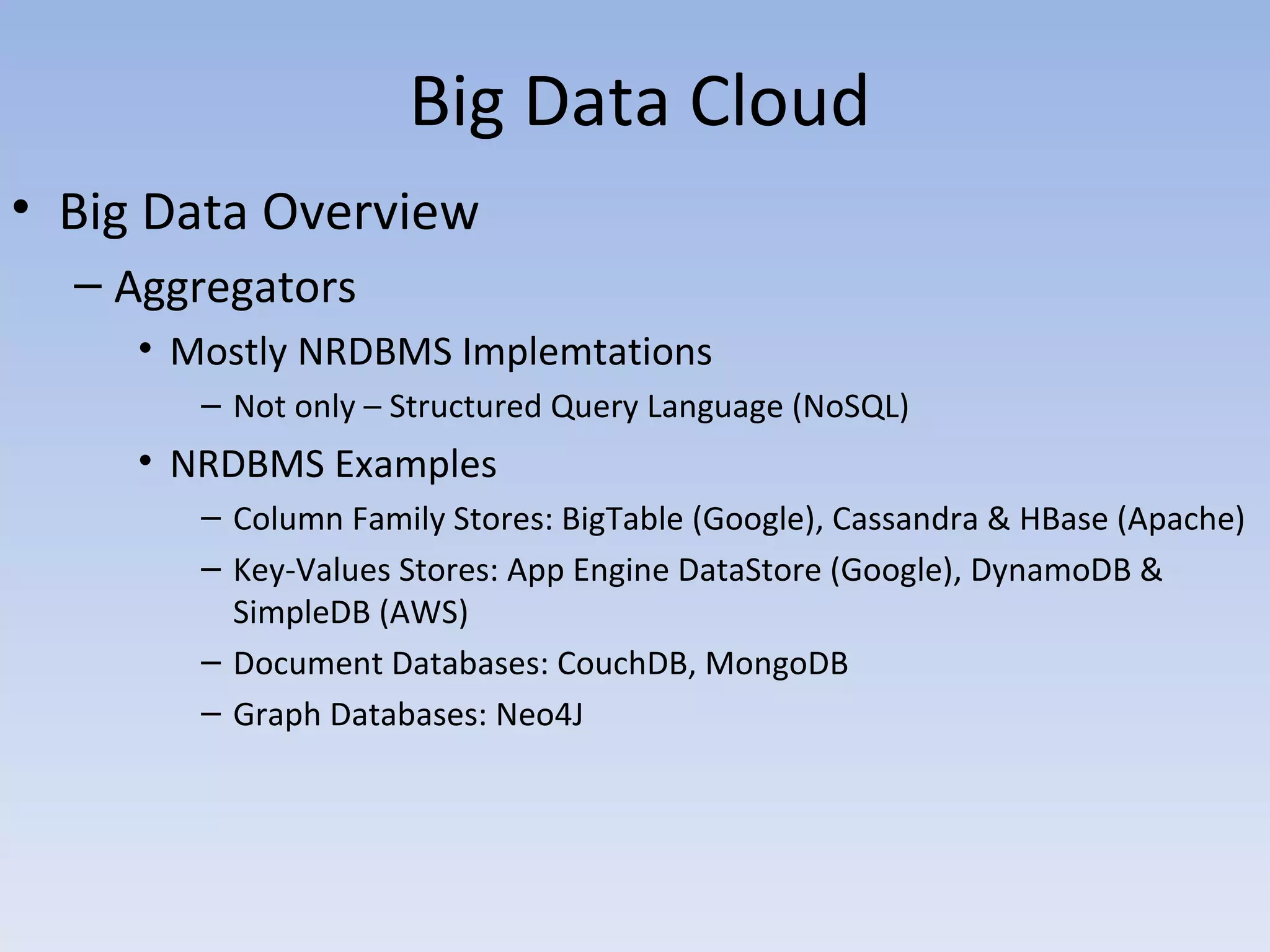
• Big Data Overview
– Serial Processing
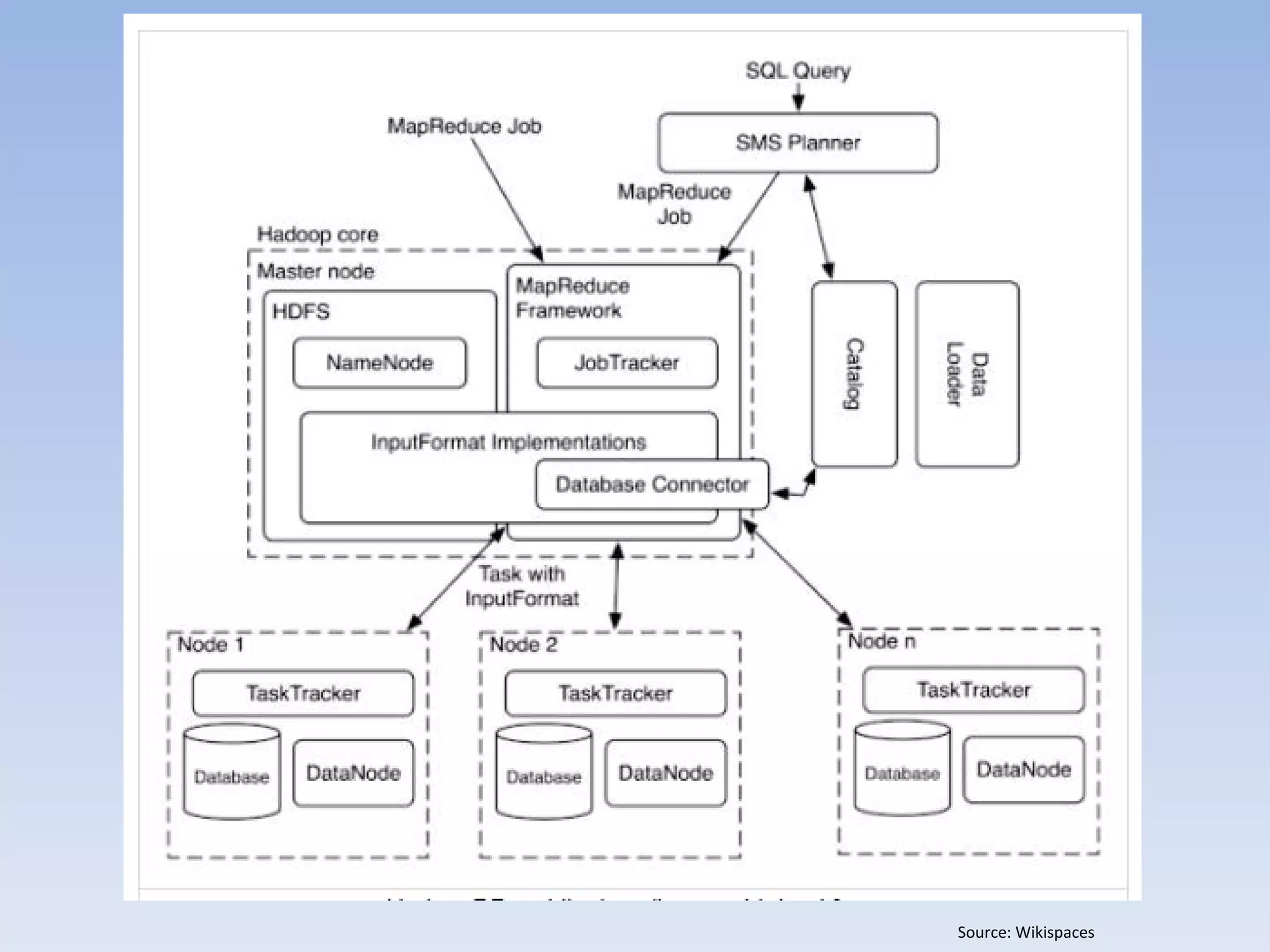
• Hadoop
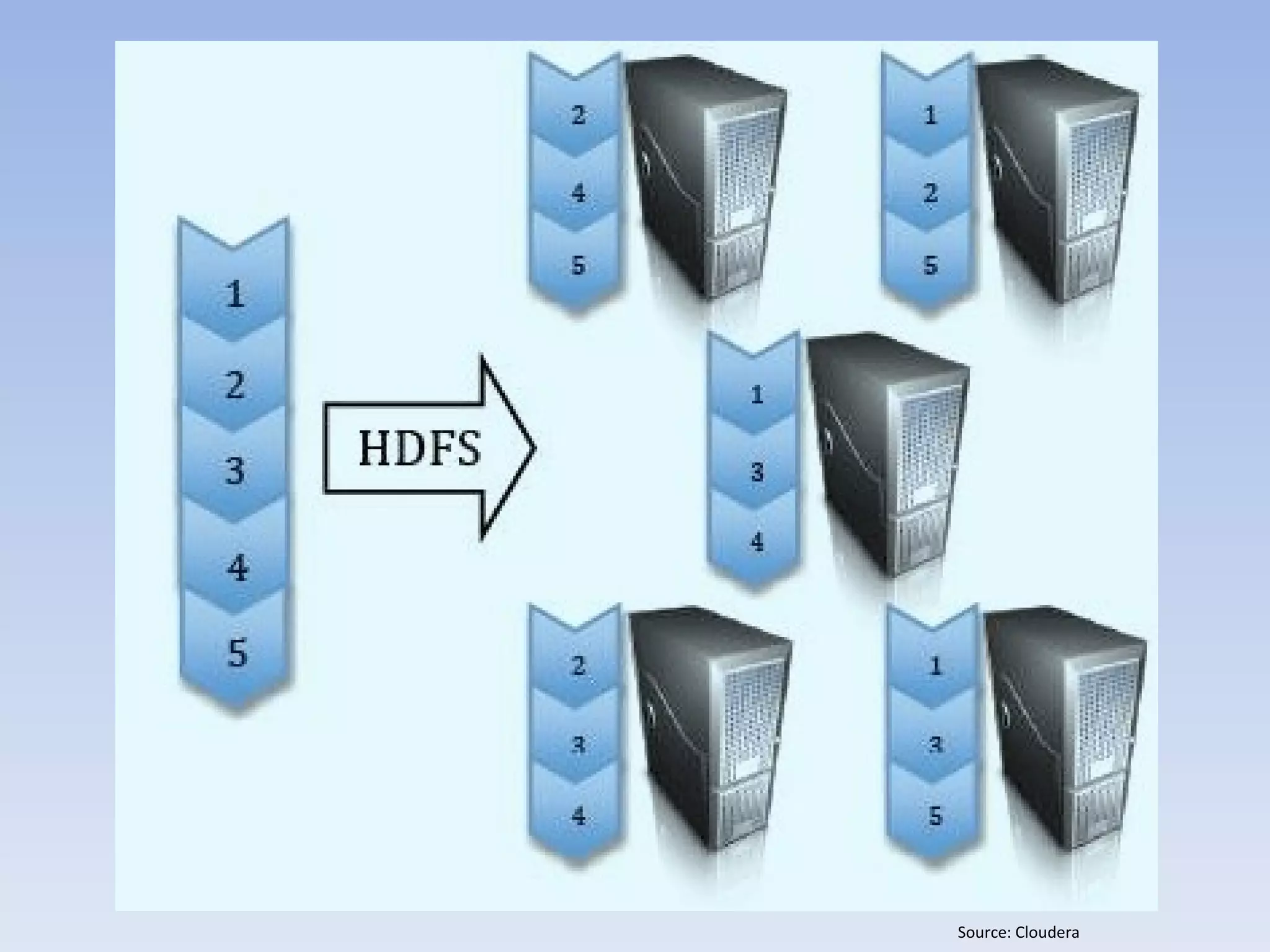
– Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
– Hive – DW
– Pig – Querying Language
• Riak
– Parallel Processing
• HadoopDB
– Analytics
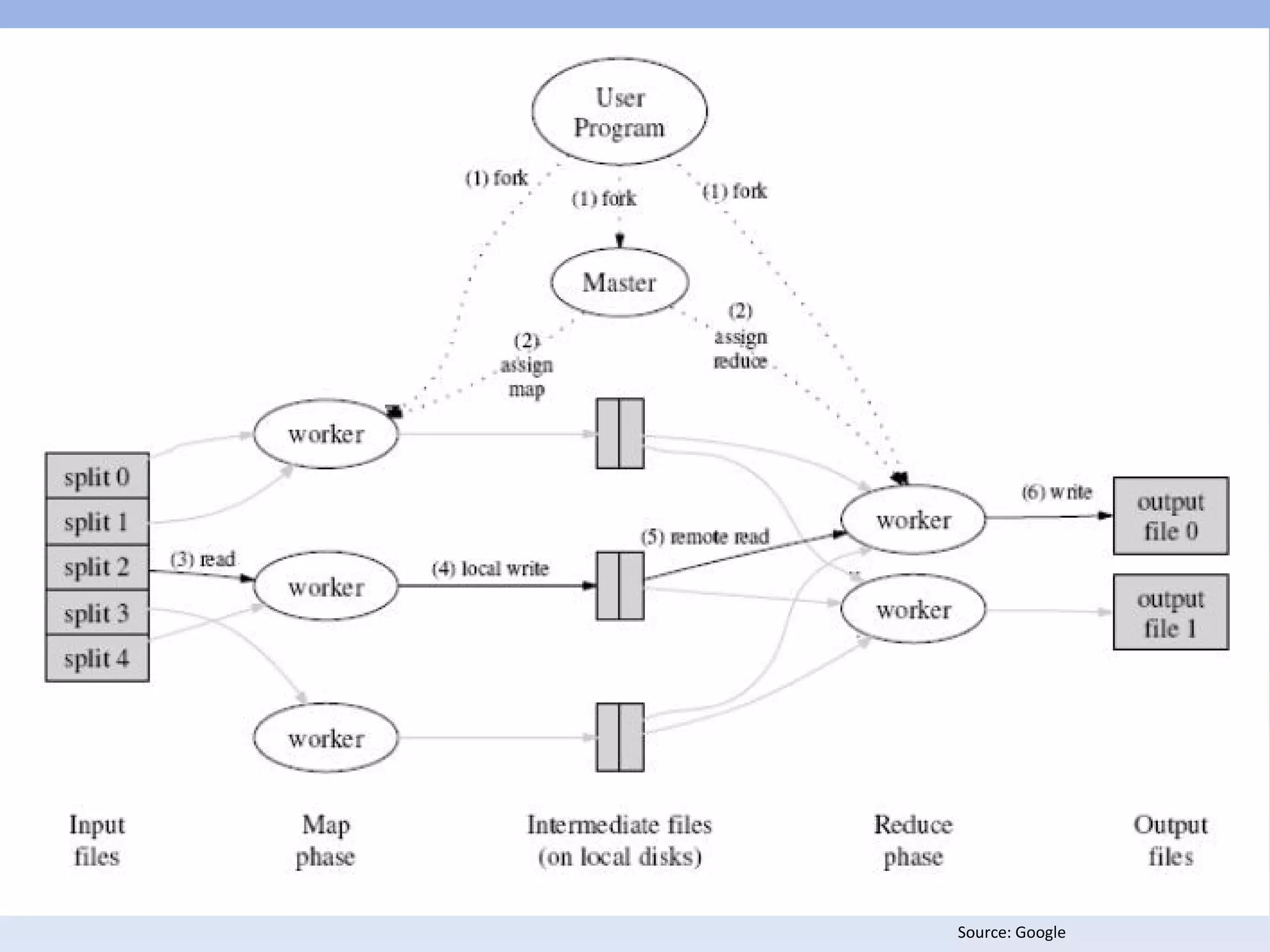
• Google MapReduce
• Apache MapReduce
• Splunk (for Security Information / Event Management [SIEM])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdcloudv3-120621184151-phpapp01/75/Bd-cloud-v3-15-2048.jpg)