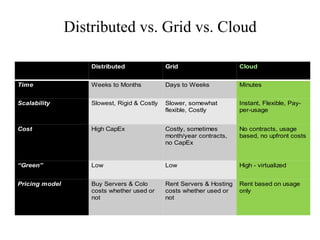
Cloud computing is a model that enables convenient access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services. Resources can be rapidly provisioned with minimal management effort. Cloud providers deliver applications via the internet which are accessed from a web browser, while software and data are stored on remote servers. Common cloud services include SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Clouds can be private, public, community or hybrid. Major advantages include flexibility, disaster recovery, automatic updates and cost savings. Top providers include Amazon, Microsoft, IBM and Salesforce. Government agencies and businesses are increasingly adopting cloud computing.