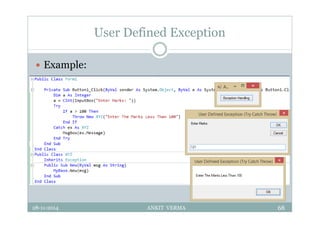
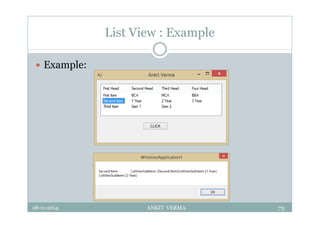
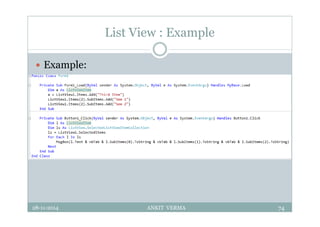
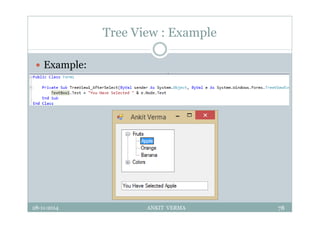
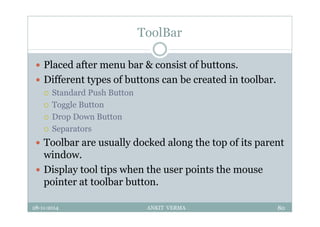
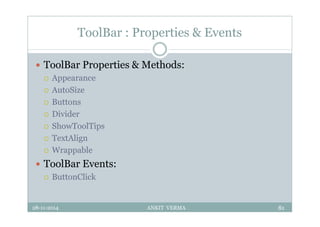
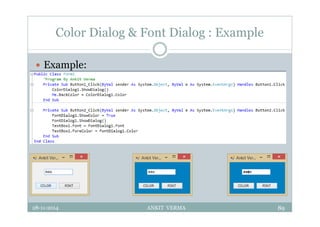
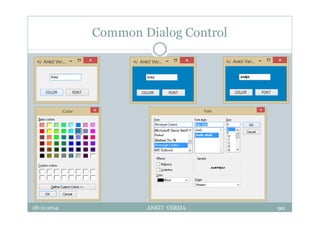
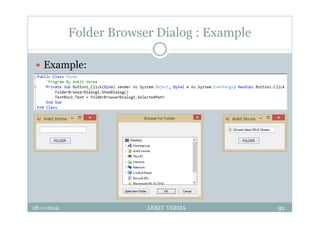
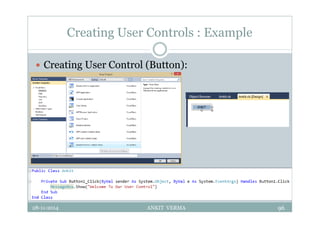
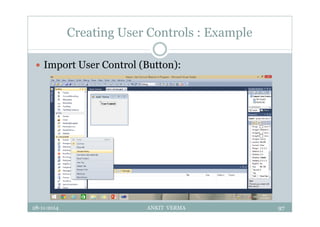
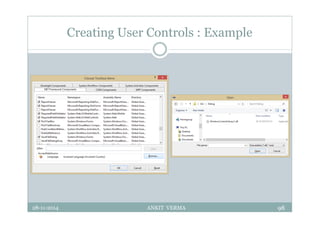
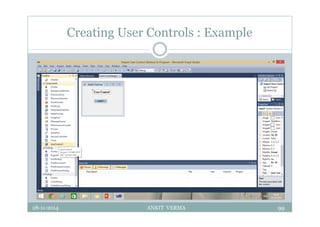
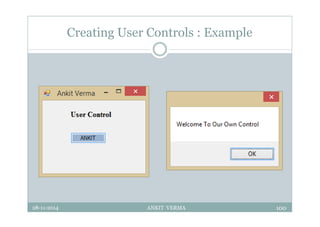
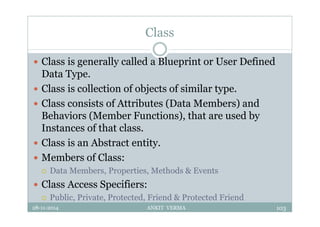
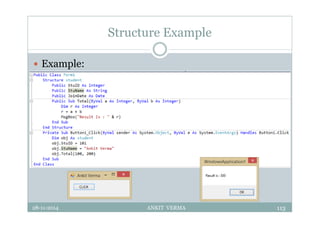
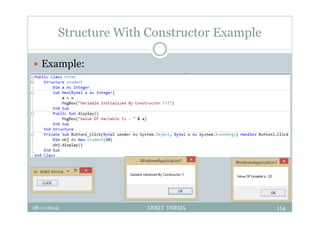
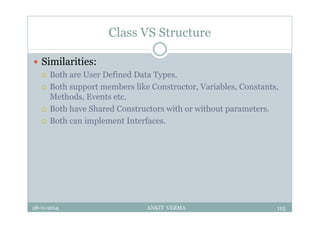
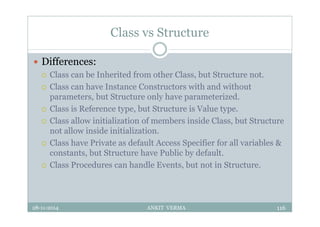
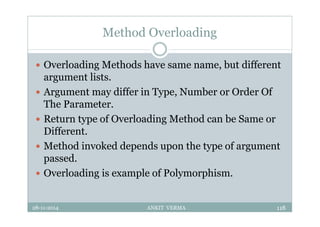
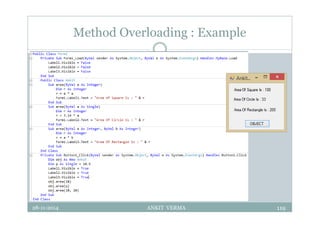
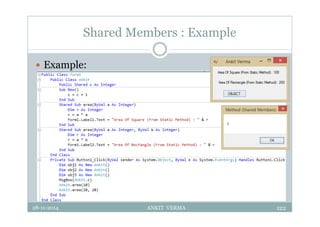
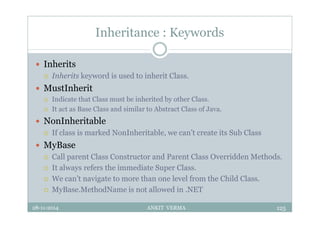
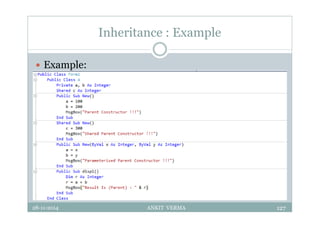
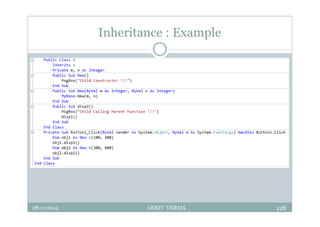
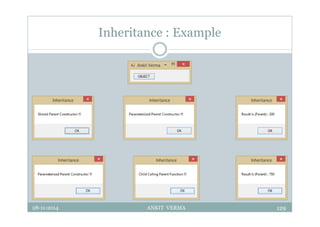
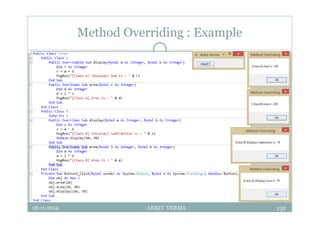
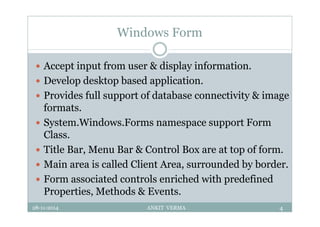
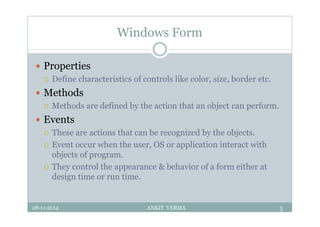
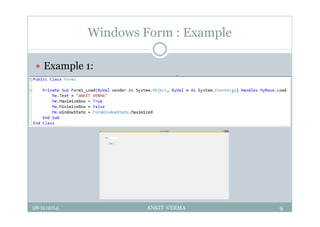
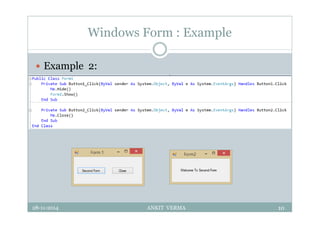
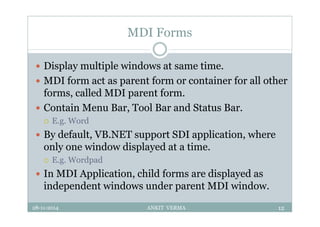
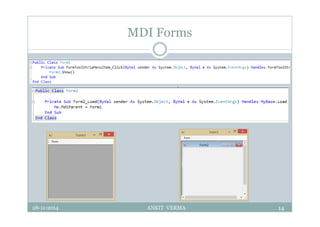
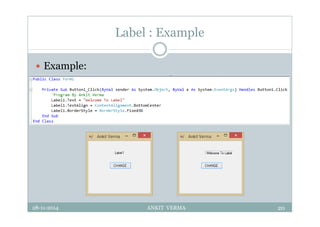
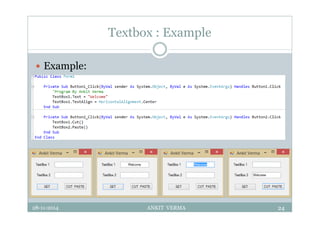
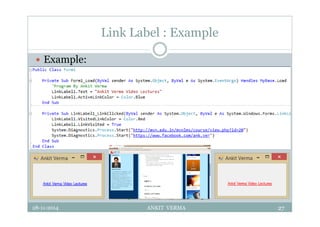
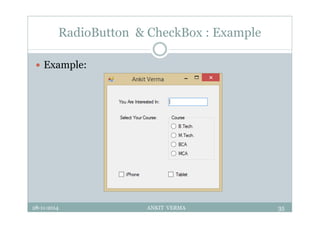
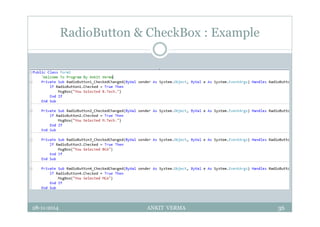
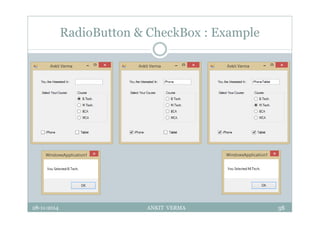
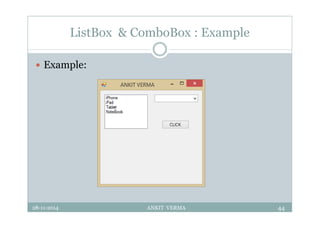
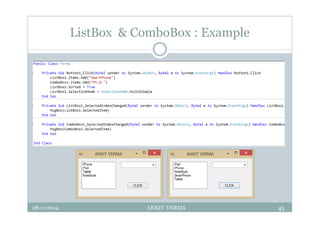
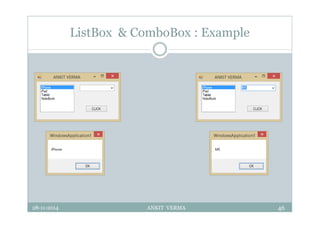
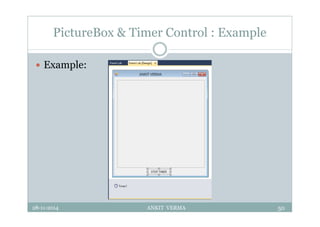
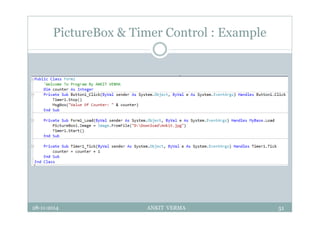
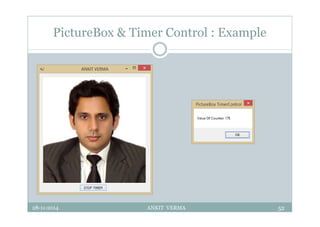
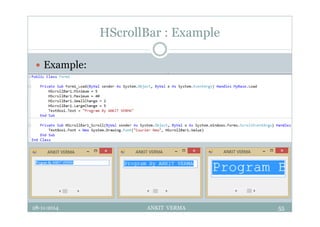
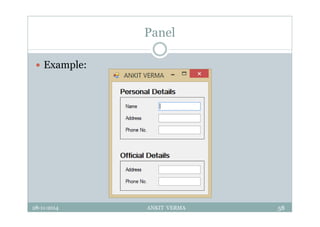
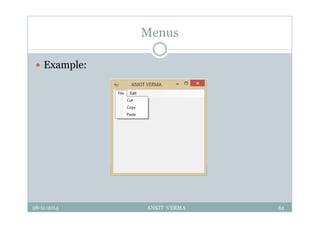
This document provides an overview of front-end design using VB.NET. It discusses user interfaces, Windows forms, controls like labels, textboxes, buttons, and menus. It also covers concepts like MDI forms, properties, methods, and events. The document is a presentation by Ankit Verma on interface design in VB.NET, providing examples of common controls and concepts.








































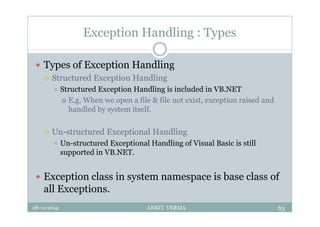


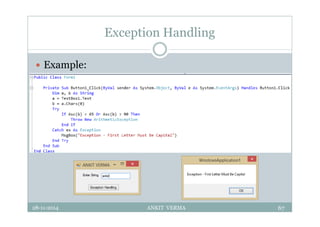
![Exception Handling : Syntax
Syntax:
Try
Catch [exception as type]
Catch [exception as type]
Finally
[finally statement]
End Try
28-11-2014 ANKIT VERMA 66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftpowerpoint-fedtvb-170903020547/85/BCA-IPU-VB-NET-UNIT-III-66-320.jpg)