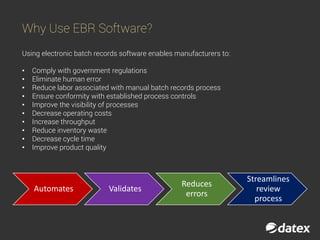
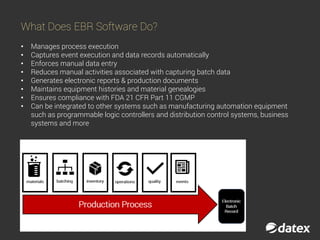
The document discusses electronic batch records (EBR) and batch manufacturing records (BMR), which are essential for complying with good manufacturing practices by documenting the manufacturing process in detail. EBR software automates data management, reduces errors, ensures compliance, and improves efficiency across various industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food products. Key features of EBR include automated tracking of batch production data, documentation of process execution, and integration capabilities with other management systems.