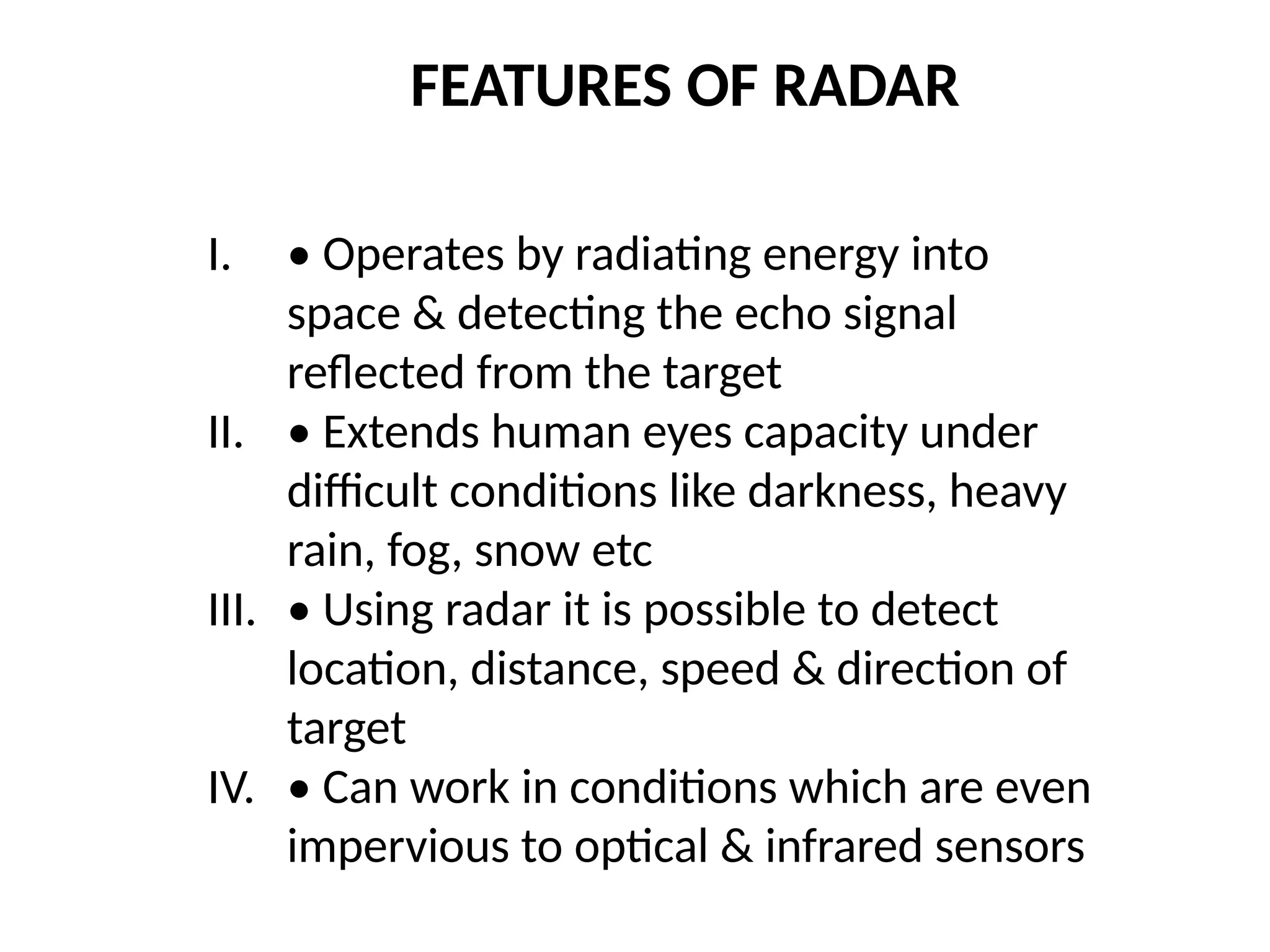
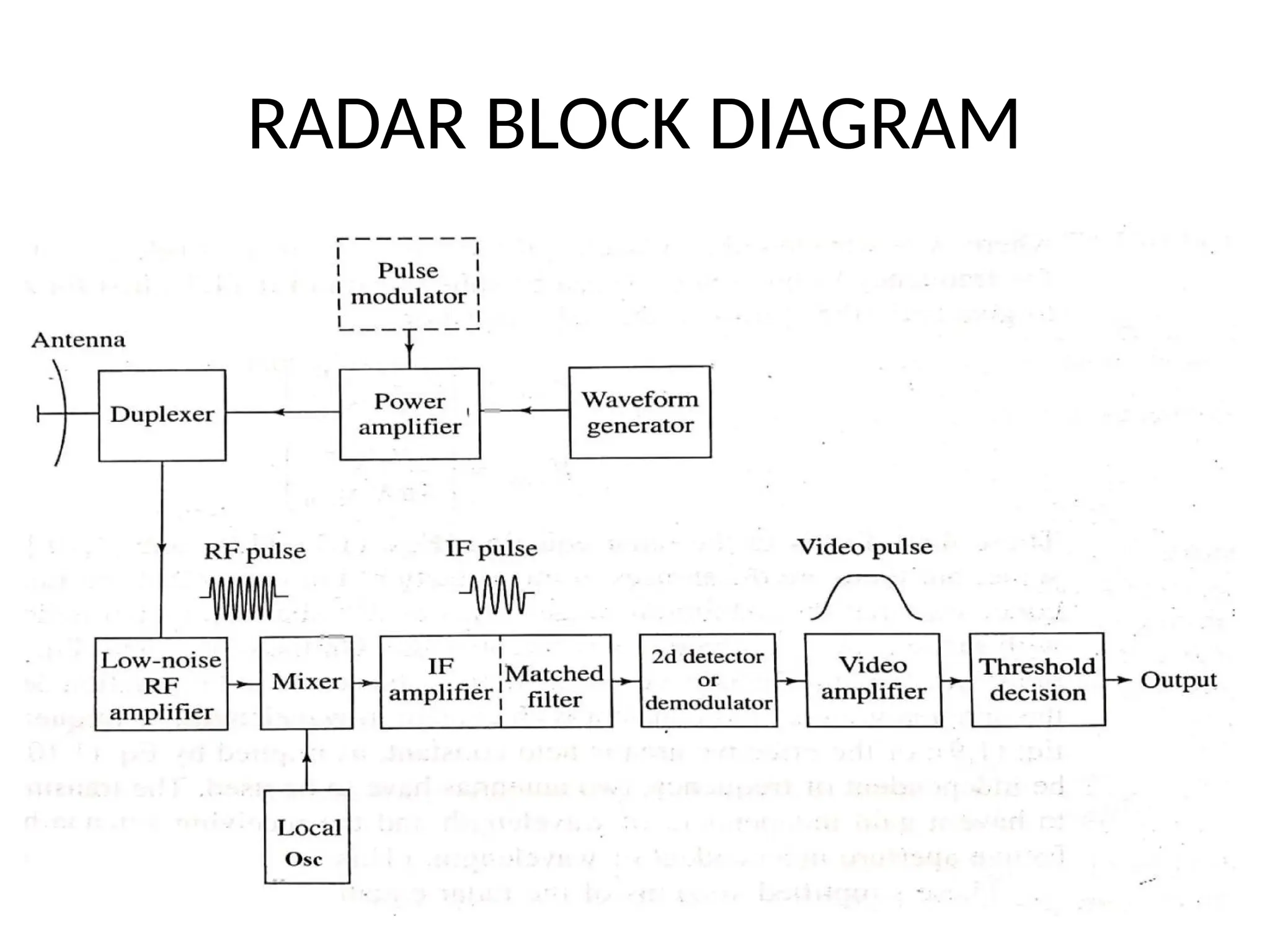
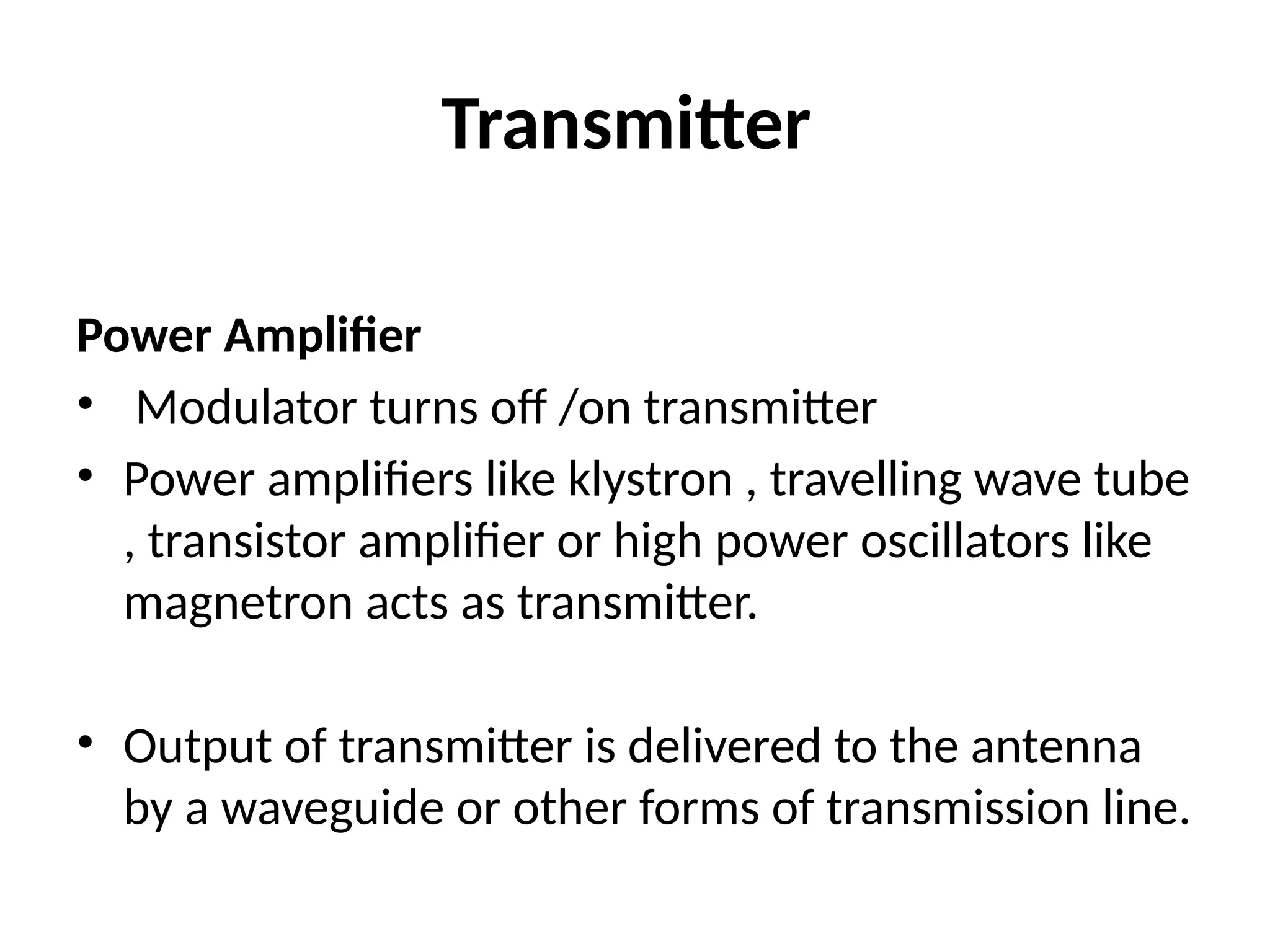
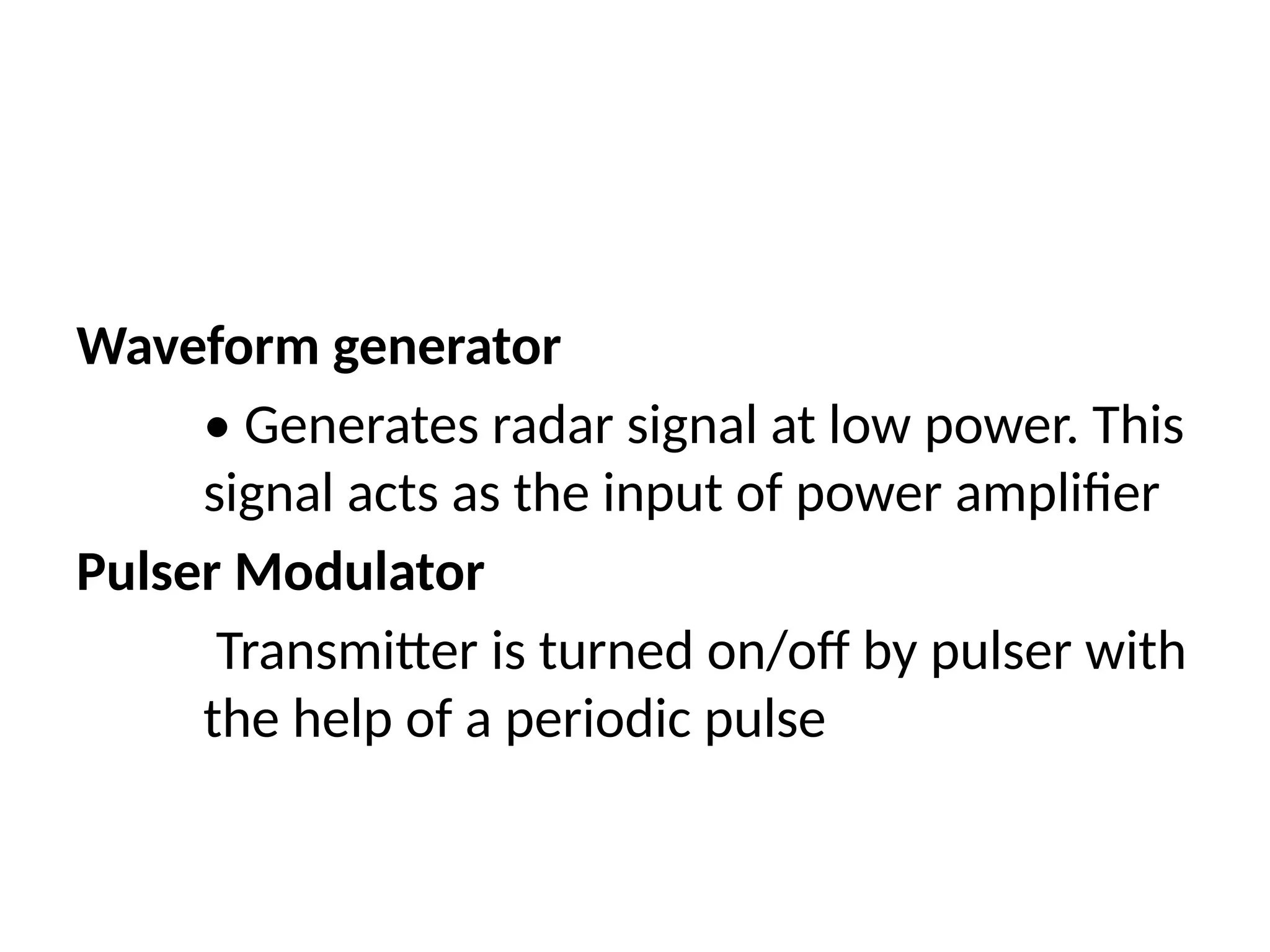
The document provides an overview of radar technology, explaining its operation, key concepts, and performance factors such as signal-to-noise ratio and radar cross-section. It discusses how radar measures distance and direction to detect and locate various targets, including aircraft and ships, and outlines the components involved, such as antennas, transmitters, and duplexers. Additionally, it emphasizes radar's capability to function in challenging conditions where optical sensors may fail.