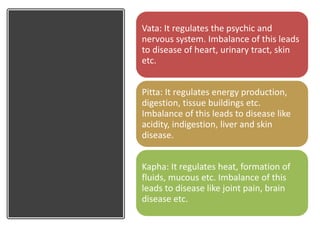
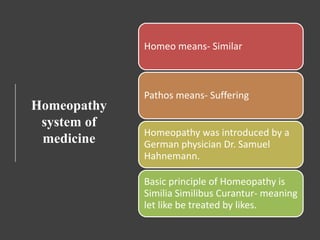
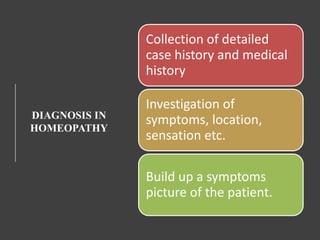
The document provides an overview of the basic principles of Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, and Homeopathy systems of medicine. It discusses the key concepts in each system such as the Panchamahabhutas (five elements) and Tridosha theory in Ayurveda, Triguna and treatment methods in Siddha, humoral theory and diagnosis in Unani, and the principles of similars and minimum dose in Homeopathy. It also describes some common Ayurvedic formulations like Asavas, Aristas, Vati, Ghutika, Churna, Leha, and Bhasma and explains their preparation methods.