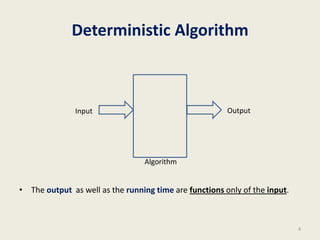
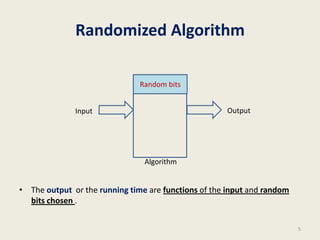
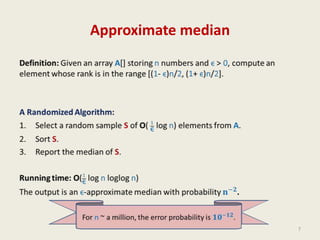
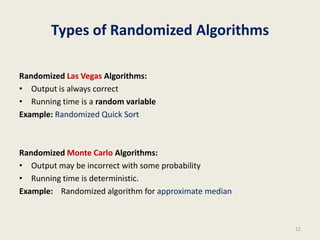
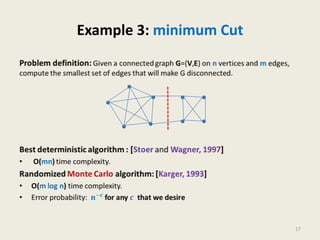
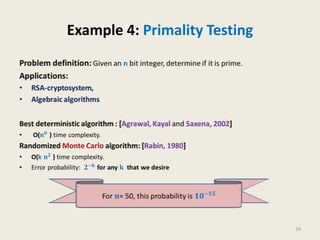
This document provides an overview of the randomized algorithms course. It defines randomized algorithms as algorithms whose output or running time depends on both the input and random bits chosen. Two types are described: Las Vegas algorithms always produce the correct output but have random running time, and Monte Carlo algorithms may produce incorrect output with some probability but have deterministic running time. Randomized algorithms are often simpler and more efficient than deterministic ones. Examples of problems solved more easily with randomized algorithms include sorting, finding the smallest enclosing circle, computing minimum cuts, and primality testing. The course will cover programming assignments, midterm and final exams, with passing criteria outlined. Office hours and contact details are provided.











![Example 2: Smallest Enclosing circle
Problem definition: Given n points in a plane, compute the smallest radius circle
that encloses all n point.
Applications: Facility location problem
Best deterministic algorithm : [Megiddo, 1983]
• O(n) time complexity, too complex, uses advanced geometry
Randomized Las Vegas algorithm: [Welzl, 1991]
• Expected O(n) time complexity, too simple, uses elementary geometry
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-1-cs648-130911122704-phpapp01/85/Lecture-1-cs648-16-320.jpg)

![A real Fact
[A study by Microsoft in 2008]
20
Compare this probability with the failure (or exceeding
the running time) probability of various randomized
algorithms mentioned earlier.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-1-cs648-130911122704-phpapp01/85/Lecture-1-cs648-20-320.jpg)