The document provides an overview of basic Natural Language Processing (NLP) concepts using Python and the NLTK library, including fundamental programming principles, data manipulation, and NLP techniques such as tokenization and stemming. It includes code snippets for creating functions, reading CSV files, and cleaning text data, along with examples of analyzing word frequency and n-grams. The content also covers data classification and Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI) measurements.


![Basic Python
import random
a_number = 1
a_string = "Python rocks!"
a_list = ["1", "2", "3"]
a_dict = {"film":"Pulp fiction", "francesco": "Python"}
print(a_dict.values())
a_dict_of_list = {"key":["Carlito's way","The godfather"], "francesco":1}
print(len(a_dict_of_list["key"]))
a_tuple = ("Goodfellas", "Kill Bill",)
a_list.append(4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-3-320.jpg)
![Creating functions
def super_function(number):
return number * 2
def factorial(n):
if n == 0: return 1
else: return n*factorial(n-1)
double = lambda item: item * 2
predicate = lambda item: item > 3
assert super_function(3) == 6
assert factorial(3) == 6
assert double(3) == 6
assert list(filter(predicate, [1,2,5,3])) == [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-4-320.jpg)

![Reading files
with open("file", "r") as input:
data = input.read()
import csv
def read_csv():
with open('data.csv', 'r') as francesco:
data = csv.reader(francesco, delimiter=';')
for element in data:
print(element[1])
read_csv()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-6-320.jpg)
![Make data talk
from collections import Counter
import statistics
splitted_chunks = data.split()
print("Data lenght: %s" %len(data))
print("Chunks numbers: %s" %len(splitted_chunks))
print("Unique chunks: %s" %len(set(splitted_chunks)))
print("Avg lenght of chunks: %s" %statistics.mean(map(len, splitted_chunks)))
print("Std dev lenght of chunks: %s" %statistics.pstdev(map(len, splitted_chunks)))
print("Frequency distribution: %s" %
sorted(filter(lambda item: item[1] > 5,
Counter(splitted_chunks).items()), key=lambda item: item[1]))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-7-320.jpg)


![Frequency distribution
from nltk.book import FreqDist
fdist1 = FreqDist(splitted_chunks)
most_common = fdist1.most_common(50)
fdist1.plot(50, cumulative=True)
fdist1.plot(10)
print("Max frequency key: %s" %fdist1.max())
print("Occurrencies of 'Parlamento': %s" %fdist1["Parlamento"])
print("Frequency of 'Parlamento': %s"%fdist1.freq('Parlamento'))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-10-320.jpg)



![Classifying data
def __get_elements_for_classification(self, lfeats, train_number, classifying=True):
train_feats = []
test_feats = []
for label, feats in lfeats.iteritems():
if classifying:
train_feats.extend([(feat, label) for feat in feats])
else:
cutoff = train_number * len(feats)/10
train_feats.extend([(feat, label) for feat in feats[:cutoff]])
test_feats.extend([(feat, label) for feat in feats[cutoff:]])
nb_classifier = NaiveBayesClassifier.train(train_feats)
return train_feats, test_feats, nb_classifier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-14-320.jpg)
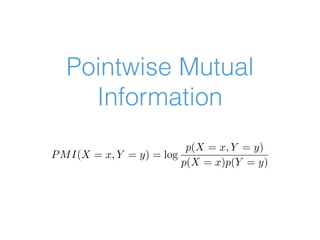




![Compute PMI
def pmi(word1, word2, unigram_freq, bigram_freq):
"""
Find PMI measure
:param word1: the first word
:param word2: the second word
:param unigram_freq: the unigram frequency container
:param bigram_freq: the bigram frequency container
"""
prob_word1 = unigram_freq[word1] / sum(unigram_freq.values())
prob_word2 = unigram_freq[word2] / sum(unigram_freq.values())
prob_word1_word2 = bigram_freq[(word1, word2)] / sum(bigram_freq.values())
a = prob_word1_word2/prob_word1*prob_word2
return round(math.log(a,2),2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicnltk-161030144341/85/Basic-NLP-with-Python-and-NLTK-20-320.jpg)

