The document discusses Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in India and their role in economic growth. Some key points:
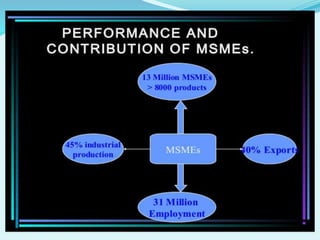
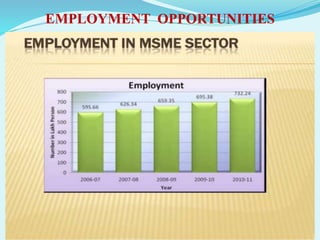
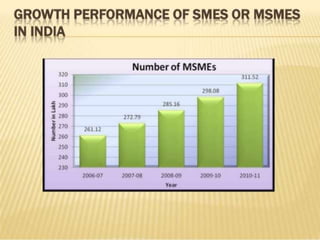
1. MSMEs account for 45% of India's manufacturing output, 40% of exports, and employ over 69 million people across more than 26 million units.
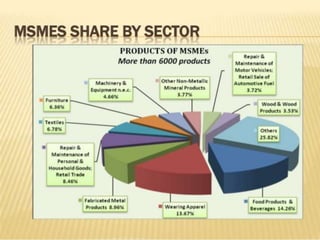
2. MSMEs produce over 6000 products ranging from traditional to high-tech and have a higher labor to capital ratio than large industries.
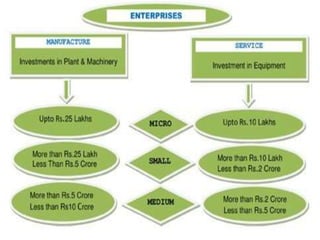
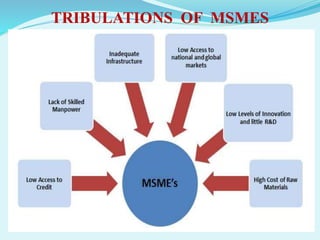
3. The document outlines objectives, methodology, classification criteria for MSMEs, their contributions and trends/policies to support their growth as well as tribulations they face.